An infectious disease caused by gonococci can develop in both women and men, but in each case it has a special course. Experts note that recently gonorrhea in women has become much more specific than before. In particular, a very sluggish and inconspicuous, subjectively asymptomatic course of the disease is recorded, which is why it remains unrecognized for a long time. This leads not only to the spread of infection, but also to the development of its complicated forms. Read about the features of the course of gonorrhea in women at estet-portal.com.
Paths of infection and distribution of gonorrhea in women
The main route of transmission of gonorrhea in women – sexual, although cases of infection are known after using common towels and washcloths, since in a humid environment the gonococcus is viable during the day. The urethra and cervix are usually infected first, while the urethra and rectum are affected secondarily. During oral sex, the oral cavity may remain the only source of infection.
Recently, the incubation period has become a bit longer – Infection with gonorrhea in women becomes apparent after about two weeks, although due to the asymptomatic course of the disease, women often cannot tell exactly when the infection occurred. The duration of the incubation period for gonorrhea in a woman directly depends on the general and local resistance of her body.
The peculiarity of gonorrhea in women is that at the time of infection, several organs are infected simultaneously and a multifocal lesion develops.
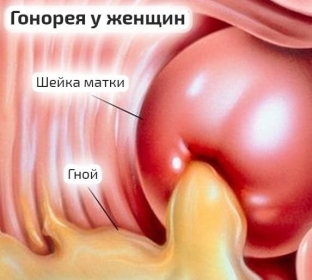
Getting on the mucous membrane of the genital organs, gonococcus causes inflammation, the infection spreads to other organs both directly through the mucous membrane and through the blood, through the lymphatic vessels. The genitourinary organs have a very branched vascular system, which contributes to the rapid spread of gonococci throughout the body.
Gonococci quickly die in the blood, releasing specific toxins that cause general intoxication phenomena – headache, loss of appetite, joint pain. While the inflammatory process is limited to the urethra, cervix, rectum, gonorrhea in women is practically asymptomatic. Later, with the transition of inflammation to the body of the uterus and its appendages, the patient may complain of pain in the lower abdomen, a violation of the general condition, low temperature.
Specific manifestations of gonorrhea in women: associated infections
Specialists note that the asymptomatic, sluggish course of gonorrhea in women is often due to a decrease in ovarian function, leading to & nbsp; followed by a decrease in estrogen production, as well as the intake of sulfonamides. The fact is that small doses of sulfa drugs significantly reduce the virulence of gonococci and the severity of the inflammatory process. If the patient took sulfonamides for some disease, not suspecting infection with gonococci, then the course of gonorrhea will be difficult to distinguish, and the diagnosis of the disease will be very difficult.
A very important feature of gonorrhea in women is that it occurs very often as a mixed infection – in combination with trichomonas, staphylococcus, chlamydia, Haemophilus influenzae and other pathogens.
According to doctors, if a woman has gonorrhea, for example, with copious discharge, the disease is also caused by Trichomonas vaginalis. Moreover, Trichomonas can serve as a reservoir for the storage and reproduction of gonococci. Such a mixed infection often causes damage to internal organs, anatomical disorders of the genitals in a woman, tubal obstruction and infertility.
Recently, women are often diagnosed with such mixed types of infection as gonorrheal-staphylococcal, gonorrheal-colibacillary, gonorrheal-candidiasis, gonorrheal-syphilitic. Infection occurs simultaneously with three infectious pathogens – gonorrhea, trichomoniasis and candidiasis or syphilis, as well as a combination of gonorrhea with chlamydia, corynebacteria, herpes virus type II.
The main problem with co-infections is that it is difficult to find adequate therapy. Thus, yeast-like fungi and Trichomonas are not suppressed by antigonococcal drugs, and therefore contribute to the preservation of the post-gonorrheal inflammatory process, even when the gonococci disappear. In addition, combined infections distort the clinical picture of gonorrhea in women, require multiple laboratory diagnostic studies, cause frequent relapses of the disease, complications, and serious post-gonorrheal inflammatory processes that require the selection of specific therapy.







Add a comment