In recent years, more and more attention is paid to the study of the problem of combining the pathology of the digestive system with other pathological conditions, in particular with obesity, type 2 diabetes mellitus, arterial hypertension. In recent years, new hormones and neurotransmitters have been discovered, which regulate energy metabolism and eating behavior, including ghrelin.
Find out in the article on estet-portal.com where the hormone ghrelin is synthesized and what functions it has, as well as how you can regulate the process of its formation.
- Main sites of ghrelin synthesis
- Biological effects of ghrelin
- Mechanisms for reducing synthesis of heatingon
The main sites of synthesis of the hormone ghrelin
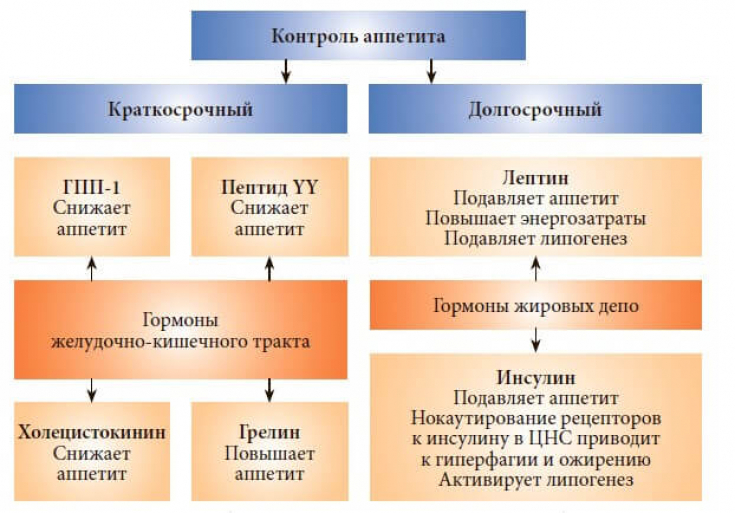
Ghrelin (ghrelin) − a gastrointestinal hormone that elicits various biological properties and effects:
- stimulates the release of growth hormone;
- stimulates appetite;
- has anabolic effect;
- affects carbohydrate metabolism.
Follow us on Instagram!
The cells of the stomach perform excretory and endocrine functions, and also produce ghrelin − orexigenic hormone, consisting of 28 amino acids, has a molecular weight of 3.3 kDa.
Main site of ghrelin synthesis − stomach, in 2nd place − duodenum, less pronounced concentrations are present in the entire gastrointestinal tract and decrease in the distal direction.
Read also: Modern therapy for type 2 diabetes
In the stomach, ghrelin synthesis is carried out by enteroendocrine cells in the acid-producing mucosa, formerly called "X/A-shaped cells"; with an unspecified function. The number of these cells is approximately 20% of the total number of endocrine cells of the gastric mucosa.
A number of scientists separate them into a separate group ghrelin-producing cells ghrelin-producing cells (Gr cells). Most of these cells adhere to the basement membrane, do not directly contact the gastric lumen, and release ghrelin directly into the blood.
This indicates that functionally these cells do not depend on the influence of physicochemical stimuli of the contents of the stomach.
Ghrelin is also produced in small quantities:
- lungs;
- pancreatic islets;
- gonads;
- adrenal cortex;
- placenta;
- hypothalamus.
to the hypothalamus through the blood-brain barrier is being discussed.
Biological effects of ghrelinAt the present stage, the following
biological effects of ghrelin:
1. Appetite regulation − one of the most important functions. Ghrelin initiates food intake. The appetizing effect of ghrelin is quite short.
Human plasma ghrelin levels decrease rapidly after a meal: there is a significant preprandial increase in the daily plasma ghrelin profile to a level that stimulates food intake and appetite, and then − postprandial decrease in ghrelin.Due to the increase in appetite, an increase in food intake is noted, which leads to an increase in the secretion of gastric juice, as well as distension of the stomach.

2. Anabolic Effects ghrelin:
- increases appetite;
- contributes to obesity;
- leads to an increase in muscle mass;
- increases blood glucose levels.
stimulate gluconeogenesison its own. Ghrelin is called the hunger hormonebecause an increase in its plasma level is associated with the onset of hunger.
Read also: How cortisol levels affect a person's quality of life
Ghrelin stimulates food intake, is involved in the regulation of energy homeostasis. An increase in appetite provokes an increase in the amount of food consumed, which leads toan increase in the secretion of the digestive organs.
The load on the pancreas, liver, gallbladder increases, as they need to secrete more and more enzymes and their own secret to digest the increased volume of food. This leads to their rapid depletion, which is manifested by the development of diseases such as pancreatitis, cholecystitis, gallstone diseaseMechanisms for decreasing ghrelin synthesisThe mechanism by which nutrients inhibit ghrelin synthesis is not well understood. But, it is known
that carbohydrates are more effective than proteins, and proteins are more effective than lipids. The relatively weak suppression of the hormone by fat stimulates appetite and may explain the mechanism of weight gain induced by a high-fat diet.
Postprandial inhibition of ghrelin does not require exposure of nutrients directly to the cavity of the stomach and duodenum − outstanding are the processes that occur after absorption in the intestine.
Read also: What effects can testosterone therapy have in women
Ghrelin levels show an inverse correlation between obesity, leptin and insulin levels. During fasting, ghrelin (Ghr) levels rise, and it probably plays therole of an antidepressant. Ghrelin concentration in the blood is inversely correlated with BMI, body fat mass, adipocyte size, leptin concentration, obestatin, with a positive energy balance.
The most useful information on our YouTube channel:







Add a comment