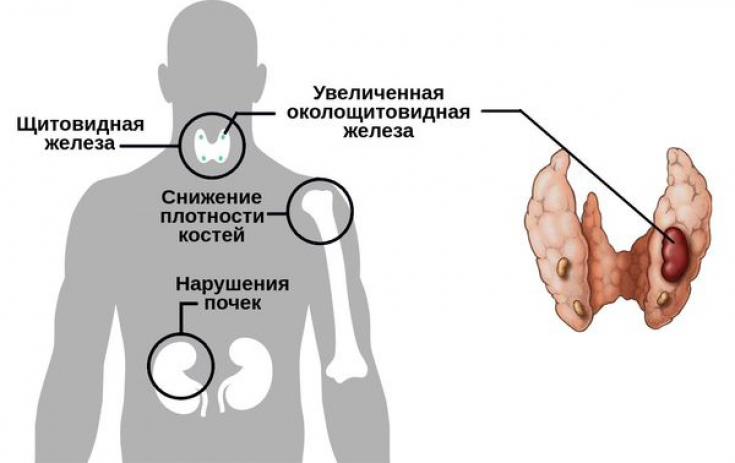
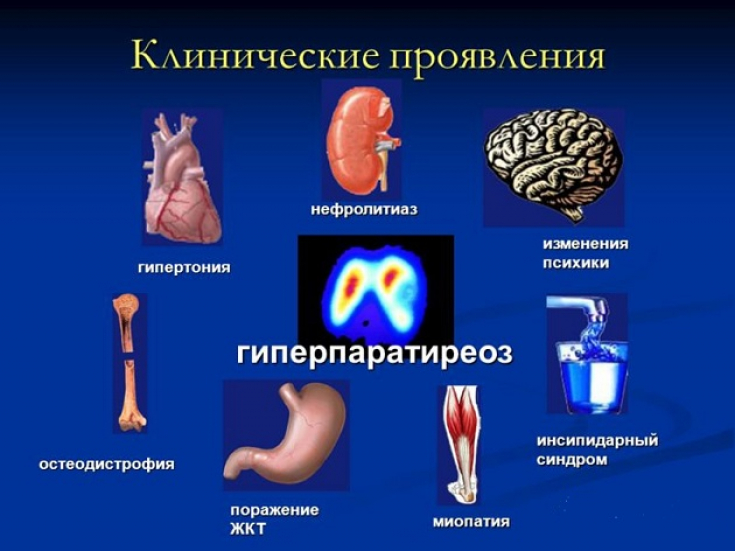
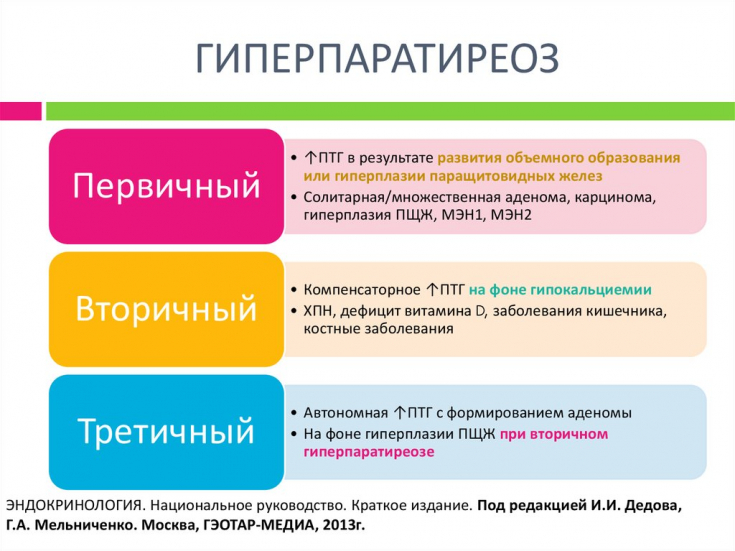
Hyperparathyroidism – This pathology is caused by characteristic symptoms and signs of increased production of parathyroid hormone. This condition is accompanied by a violation of the exchange of calcium and phosphorus, which is manifested by pain in the muscles and bones, osteoporosis, damage to the kidneys and organs of the gastrointestinal tract.
The frequency of the disease increases with age, women during menopause suffer from hyperparathyroidism 5 times more often than men.
Learn in our article on estet-portal.com about modern approaches to the diagnosis, surgical treatment and monitoring of hyperparathyroidism.
Surgical Treatment: Preoperative Diagnosis
Diagnosis of hyperparathyroidism includes: determination of calcium level in blood serum, parathyroid hormone level, calcium level in daily urine, ECG, ultrasound of the parathyroid glands, scintigraphy.
Follow us on Instagram!
Patients who have had prior surgery for primary hyperparathyroidism should undergo preoperative imaging (usually ultrasound) if this would optimize the surgical approach.
Therapeutic Strategies for the Development of Insulin Analogs
It is also important to consider an alternative preoperative imaging modality (usually 99mTc scintigraphy) if this optimizes surgical management. Additional imaging is not recommended if scanning, including the first (diagnosis ultrasound) and second (scintigraphy with 99mTc) methods, did not reveal an adenoma in the patient or their results are questionable.
If a patient is diagnosed with ectopic adenoma on preoperative imaging, the patient should be referred to a specialist with an oncological profile.
Motilin: a hormone-activator of intestinal motility
Surgical treatment type and monitoring
Patients diagnosed with adenoma by preoperative imaging should be offered a choice of surgical intervention (simultaneous removal of four glands - total or subtotal, or focused parathyroidectomy).
Surgical treatment in the amount of subtotal simultaneous removal of four glands is recommended for patients who do not have a single adenoma detected during preoperative imaging.
It is recommended that intraoperative monitoring of parathyroid hormone levels be avoided in patients undergoing primary parathyroid surgery.
In the postoperative period, it is important to determine the level of calcium in the blood serum, taking into account serum albumin, in patients after surgical treatment on the parathyroid glands before discharge, in order to obtain basic information in order to further assess the dynamics.
Attention to the face: signs of possible thyrotoxicosis in the patient
To assess the degree of effectiveness of surgical treatment, it is necessary to determine the level of calcium in the blood serum, taking into account serum albumin, 3-6 months after surgery on the parathyroid glands.
If the level of calcium in the blood serum, taking into account serum albumin, fluctuates within the control range of values 3-6 months after surgery, the surgical treatment was successful. Further monitoring of calcium levels in the blood serum, taking into account serum albumin, is recommended once a year.
Surgical treatment failure
For patients whose surgical treatment for primary hyperparathyroidism was ineffective, it is necessary to conduct a comprehensive assessment of the outcome of the surgical intervention, preliminary imaging data and the results of histological examination, clinical and biochemical indications for reoperation.
Reoperation for primary hyperparathyroidism should be performed by specialists with experience in reoperative surgery for patients of this profile.
Leptin: how to activate the satiety hormone
Calcium mimetics are recommended for patients with primary hyperparathyroidism if surgical treatment has failed or cannot be performed on vital signs and serum calcium adjusted for serum albumin is:
− ≥2.85 mmol/L with symptoms of hypercalcemia or
− ≥3.0 mmol/l with/without symptoms of hypercalcemia.
For patients whose baseline serum calcium level, taking into account serum albumin, is ≥ 2.85 mmol / l with symptoms of hypercalcemia, when deciding whether to continue calcium mimetic therapy, it is necessary to evaluate the individual clinical effectiveness of the drug.
When surgical treatment fails, it is important to consider bisphosphonates to reduce the risk of fracture in patients with primary hyperparathyroidism and an increased risk of bone fracture.
A special approach requires the possibility of surgical treatment in patients with primary hyperparathyroidism who are planning a pregnancy. Since pregnant women with primary hyperparathyroidism have an increased risk of developing hypertension, which has a negative impact on placental circulation.
If necessary − discuss the management of a pregnant patient with parathyroid hyperfunction in accordance with the decisions of the council in a specialized center, if necessary − consultations of narrow specialists. The council takes into account the decisions of such specialists: obstetrician-gynecologist, endocrinologist, surgeon, anesthesiologist.
In patients with asymptomatic hyperparathyroidism, in the absence of indications for surgical treatment, it is necessary to determine the concentration of calcium and creatinine every 12 months. Under the condition of effective correction of calcium-phosphorus metabolism in this pathology, the prognosis is quite favorable.
Obesity Management: Tried and Proven Medications







Add a comment