Infectious exanthema is also called "Boston" because its causative agent was first isolated and described in the 1950s in Boston. The peculiarity of viruses that cause infectious exanthema is & nbsp; in many serotypes tropic to muscles, nervous tissue, epithelial cells. This explains the difficulty in diagnosing the disease, since the symptoms can look like a skin rash with measles, and like herpetic sore throat, and like intestinal upset, and like acute aseptic meningitis. The disease has a favorable prognosis with timely treatment.
By what signs can infectious exanthema be recognized
Infectious exanthema is most often caused by ECHO viruses, which are enteric viruses and have many serotypes. These viruses can affect the central nervous system, cause inflammation in the striated muscles, provoke gastroenteritis, cause acute respiratory diseases and inflammation of the choroid. Often ECHO viruses can provoke poliomyelitis-like diseases, myocarditis, uveitis.
A common symptom of the development of infectious exanthema is a significant increase in temperature to very high values, and this is especially true for adult patients – their fever may be accompanied by a feeling of prostration, symptoms of meningitis and even encephalitis.
Another sign of infectious exanthema can be considered signs of pharyngitis with small ulcers on the mucosa. In children, this symptom is especially pronounced, resembling the manifestations of herpetic sore throat.
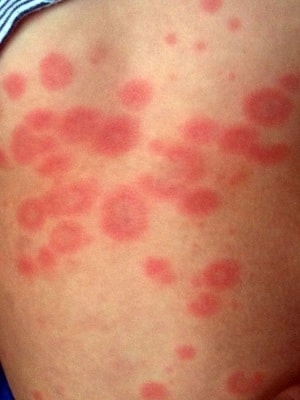 The third characteristic sign of infectious exanthema is a small pink rash in the form of papules, which most often covers the face, chest, palms, but can spread throughout the body. It usually lasts a couple of days and passes on its own without consequences. In adults with a strong manifestation of neurological symptoms, the rash may not be present, in children the rash may remain on the body for up to five days.
The third characteristic sign of infectious exanthema is a small pink rash in the form of papules, which most often covers the face, chest, palms, but can spread throughout the body. It usually lasts a couple of days and passes on its own without consequences. In adults with a strong manifestation of neurological symptoms, the rash may not be present, in children the rash may remain on the body for up to five days.
Other symptoms of infectious exanthema include the following possible manifestations of the disease:
- enlargement of behind-the-ear and cervical lymph nodes,
- sore throat,
- muscle pain,
- general weakness, headaches.
Special variant of infectious exanthema – this is when, against the background of general intoxication, which is not too strong, small pimples with an inflamed corolla appear on the fingers and toes, protruding above the surface of the skin, and at the same time small single sores appear on the tongue and oral mucosa.
Peculiarities of diagnosis and treatment of infectious exanthema
Signs of infectious exanthema can be blurred, moreover, not all doctors are aware of the features of the manifestation of this infection, so laboratory serological tests will be helpful in diagnosing. Infectious exanthema should be differentiated from measles, rubella, tonsillitis, pharyngitis.
Treatment of infectious exanthema is symptomatic, especially in neurological manifestations of the disease. In severe cases, it is possible to prescribe corticosteroid drugs for a course of five to seven days. Immune strengthening agents are recommended, and if necessary, antipyretic and analgesic drugs.
A very important factor regarding infectious exanthema – this is a risk of infection for pregnant women, since ECHO viruses are capable of infecting the fetus in utero.
It should be noted that infectious exanthema has a favorable course, and after the illness, the patient acquires specific immunity – but only to the type of virus that caused the disease.







Add a comment