What is thrombocytopenic purpura, what processes occur during its development and how it manifests itself, you can find out in the first part of our article. But, suspecting that the patient has thrombocytopenic purpura, it is necessary to confirm or refute the diagnosis using a series of tests and specific tests. Only then can treatment begin. What is the diagnosis and treatment of thrombocytopenic purpura?
Methods for diagnosing idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura
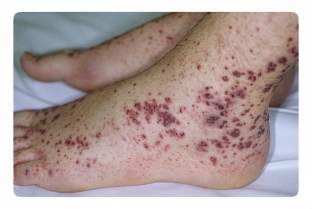
When patients have complaints and symptoms described in the first part of the article, the doctor conducts a diagnosis, which confirms or refutes the presence of thrombocytopenic purpura. For this, specific methods are used, which consist in conducting a tourniquet, a pinch test, as well as a Konchalovsky-Rumpel test – Leede.
These samples are considered positive if hemorrhages occur at the site of the test, which indicates reduced elasticity of the vascular wall. Laboratory research methods are no less informative.
Laboratory results for thrombocytopenic purpura:
- Duke bleeding duration increased to 4 minutes or more;
- blood clot retraction reduced to 60-75%;
- presence of thrombocytopenia below 140х109/l;
- in the bone marrow there are a large number (54-114/µl) of megakaryocytes, which can be morphologically altered;
- presence of antibodies to platelets;
- disturbances in the properties of platelets (change in shape and large sizes);
- the level of bilirubin in the blood is increased;
- increased urea and nitrogen in the blood in cases of kidney damage.
What should be done before treatment for thrombocytopenic purpura?
Before starting treatment, it is advisable to check the level of platelets and leukocyte count in the blood. After all, a single detection of thrombocytopenia and other indicators, although it is the main diagnostic criterion, but to make a residual diagnosis, it is necessary to repeat these tests.
Treatment of thrombocytopenic purpura directly depends on the stage of the disease and the severity. Therapy for ITP can be conservative or radical. The acute period implies immediate hospitalization with strict bed rest. The patient needs to eat chilled food in small portions and drink plenty of fluids.
The main directions in the therapy of thrombocytopenic purpura
As for medical treatment, it is carried out in four directions: antianemic, hemostatic, hormonal and surgical. Let's take a closer look at the methods of treating thrombocytopenic purpura:
- Antianemic – the appointment of vasoconstrictor agents, iron preparations, intravenous injections of immunoglobulins. Also, transfusion of blood, platelet or erythrocyte mass, polyglucin or dry plasma solution is used.
- Hemostatic – intravenous injections of aminocaproic acid (in the absence of blood in the urine), dicynone or etamsylate. Prescribe drugs to increase blood clotting (atropine, adrenaline, peptone). Local treatment of bleeding is carried out using a fibrin or gelatin film, a hemostatic sponge, tampons with hydrogen peroxide.
- Hormonal – it is advisable to use hormones-androgens in acute and chronic forms of the disease in women with hormonal disorders and uterine bleeding. Corticosteroids are used to increase blood clotting and reduce vascular permeability. When "dry" in the form of purpura (bleeding only on the skin), hormones are not prescribed.
- Surgical – involves the removal of the spleen. This method is resorted to when hormonal treatment has not brought an effect. The operation is performed during the period of remission. If splenectomy fails, immunosuppressive drugs are prescribed along with hormonal drugs.
In addition to these methods of treatment, it is important to recommend that the patient follow diet No. 5, drink hemostatic herbal preparations based on water pepper, corn stigmas, rose hips, nettles and yarrow. It is also recommended to use choleretic drugs. It is important to remember that patients with thrombocytopenic purpura are contraindicated in UV and UHF, chlorpromazine, platelet inhibitors.
With timely initiation of treatment for thrombocytopenic purpura, the prognosis can be very favorable. Cases of persistent remission after an acute onset of the disease are described. After all, the most important thing in the treatment of any process is the right treatment started on time.







Add a comment