In most cases extraction of teeth is not accompanied by the development of any complications. However, they develop in about 10% of cases of this dental procedure, which is not uncommon.
For doctors of any specialty, it is important to understand the causes of development and know the main principles of treatment of the most common complications of tooth extraction – alveolitis and perforation of the maxillary sinus.
In this article on estet-portal.com read about the most common complications of tooth extraction – post-extraction alveolitis and maxillary sinus perforation.
Tooth extraction: why it is important to use a dental swab
After the extraction of teeth, the filling of the tooth socket with blood can be observed within a few hours.
It is important that the patient compress the dental swab for about 15-20 minutes after tooth extraction.
A blood clot formed in the alveolus will contribute to the deposition of fibrin and, as a result, the formation of granulation tissue. Granulation tissue covered with epithelium will grow from the bottom of the socket up and along its sides.
If the blood clot shifts or does not form at all, then after the extraction of the tooth, a complication such as post-extraction alveolitis may develop.
Follow us on Telegram
Complications of tooth extraction: clinical symptoms of post-extraction alveolitis
The diagnosis of post-extraction alveolitis is established clinically. The key syndrome of this complication is the appearance of severe, in some cases, throbbing pain in the hole 2-3 days after tooth extraction. Quite often, the presence of bad breath (halitosis) is objectively determined in a patient.
Post-extraction alveolitis often complicates the extraction of the teeth of the lower jaw and occurs in 1-10% of cases.
Today there is no single opinion regarding the etiology of post-extraction alveolitis. Probably, this condition is a consequence of ischemic bone necrosis and local osteitis.
Bad breath: causes and remedies
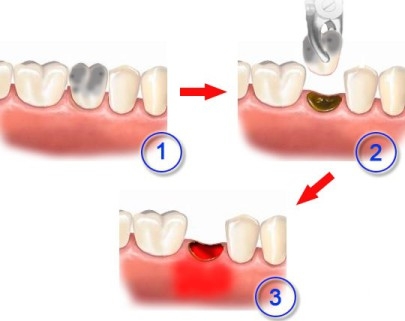
Treatment of post-extraction alveolitis: are antimicrobials needed
Treatment of post-extraction alveolitis consists in irrigating the affected tooth socket and placing a paraffin gauze swab soaked in iodoform there. The tampon should be changed every 1-3 days until the symptoms disappear completely.
In most cases, the patient needs analgesics.
According to current international recommendations, there is no evidence base regarding the effectiveness of the use of systemic antimicrobials in post-extraction alveolitis.
Antimicrobials should only be given if symptoms of a generalized infection appear.
Acute toothache: quick professional help for the patient
Perforation – possible complication of maxillary tooth extraction
As for the complications of the extraction of the teeth of the upper jaw, it should be noted the formation of perforations of the oral cavity into the maxillary sinus.
The fact is that the root ends of the upper molars are located in the maxillary sinus, and their extraction can lead to the formation of corresponding holes.
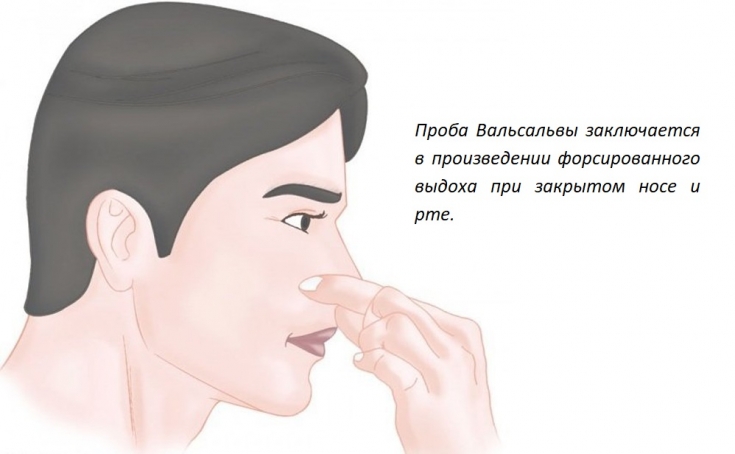
In this case, while the patient performs the Valsalva maneuver, his mouth cavity is filled with air.
The Valsalva maneuver consists of forced exhalation with the nose and mouth closed.
Small perforations in most cases heal on their own if a good blood clot forms after extraction. Such patients should be advised to refrain from blowing their nose vigorously for 3-4 weeks after tooth extraction.
If the perforation does not heal within 3 weeks or is initially large, consultation with an oral surgeon is required.
Thank you for staying with estet-portal.com. Read other interesting articles in the "Dentistry" section. You may also be interested in: Should I get a crown on my tooth: indications and alternatives







Add a comment