Every doctor, regardless of specialty, can encounter acute toothache in a patient. Sometimes this condition is so distressing that it requires immediate first aid.
Principles for the treatment of acute toothache, set out further in the article, are based on international recommendations and meet the postulates of evidence-based medicine.
For more information about what can lead to acute toothache in a patient, as well as the principles of treating this pathological condition, read on estet-portal.com in this article.
What provokes the occurrence of acute toothache in patients
Acute toothache can be caused by mechanical (chewing processes), thermal (such as cold or hot food) or physical (sweet food) irritants.
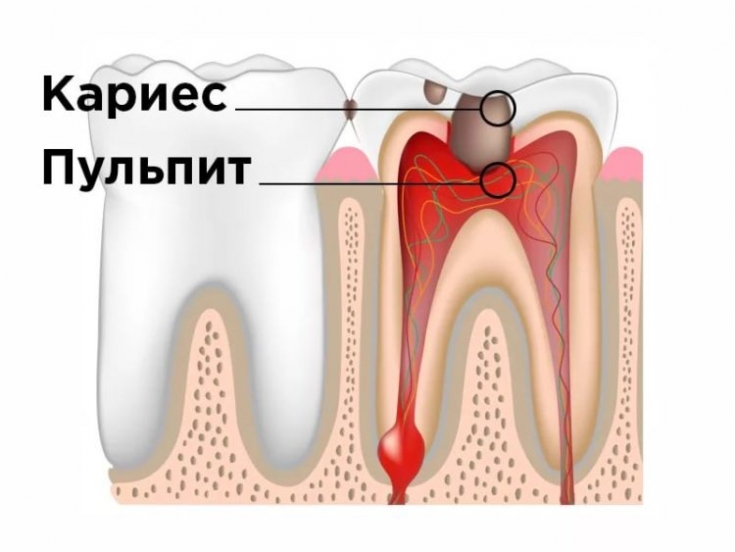
The most common cause of acute toothache is caries.
In addition, the development of acute toothache can provoke pulpitis – common complication of caries. Pulpitis also often occurs against the background of a jaw injury. In such cases, patients note the irradiation of discomfort in the temporal region, while the intensity of pain can be incredible.
With pulpitis, the pain, most often, has a pulsating character. Its intensity is greatly enhanced when touching the tooth.
Follow us on Telegram
Acute toothache with pulpitis: fast and effective treatment
In the treatment of acute toothache caused by pulpitis, the use of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs is often ineffective. The drugs of choice are centrally acting analgesics.
In some cases, it is advisable to combine drugs of peripheral and central action. In addition, the doctor can apply local anesthesia, which immediately eliminates pain: 1 ml of an anesthetic solution must be injected under the gum mucosa.
Peculiarities of treatment of gangrenous pulpitis and implantation of teeth
This type of anesthesia is indicated to eliminate pain that is localized in the teeth of the upper jaw. To anesthetize the lower molars, it is necessary to use transcortical anesthesia. In dentistry, the most commonly used anesthetics are: lidocaine, prilocaine, articaine. They are combined with the introduction of vasoconstrictor drugs, in particular, adrenaline and felypressin.
Principles for the treatment of acute toothache caused by pericoronitis
Severe toothache can be caused by a condition such as pericoronitis – inflammation of the gums against the background of eruption of wisdom teeth. In the development of this pathology, the addition of a bacterial infection plays a key role.
Therefore, with pericoronitis, it is mandatory to prescribe antibiotics: penicillins and macrolides (the latter are prescribed in case of a patient's allergy to penicillin).
Infiltration anesthesia techniques and choice of anesthetic agent
It is advisable to remove the inflamed mucous membrane around the crown of the tooth. After eliminating the inflammatory reaction, it is necessary to remove the tooth if it erupts in the wrong position.
Acute toothache due to extraction of lower molars
Acute toothache can also occur after extraction of molar teeth. It often occurs after the removal of lower molars, especially wisdom teeth.
Systemic antibiotics should be given if the patient has signs of infection.
In such cases, the use of decongestants is effective. If necessary, you can also prescribe a combination of analgesics of peripheral and central action. Thank you for staying with estet-portal.com. Read other interesting articles in the "Dentistry" section.







Add a comment