In the human body, there are several metabolic pathways aimed at counteracting inflammatory processes and oxidative stress. The development of infection is a consequence of both local and systemic pro-inflammatory factors. In the latter case, the initiating role can be played by cross mimicry and systemic translocation of bacteria with the bloodstream, which trigger inflammatory processes far from the original site of colonization of causative microorganisms.
Learn in the article on estet-portal.com about the role of the microbiome in the development of common endocrinological pathologies.
- microbiota and microbiome in type 2 diabetes
- The role of probiotics in microbiome regulation
- microbiome and diseases of peripheral vessels
Microbiota and microbiome in type 2 diabetes
Experimental and clinical studies support the hypothesis that obesity and type 2 diabetes mellitus are associated with significant intestinal dysbiosis.
Follow us on Instagram!
Excess nutrition is one of the main mechanisms for triggering local changes in the microbiota and a systemic inflammatory process. Qin et al. conducted the first metagenomic study of fecal samples from type 2 diabetic patients and found moderate dysbiosis with a decrease in the butyric acid-producing bacteria Roseburia intestinalis and Faecalibacterium prausnitzii and are associated with an increase in the content of some
Another metagenomic study in postmenopausal women, in contrast, found that the presence of R. intestinalis and F. prausnitzii characterized patients with type 2 diabetes.
According to the authors, discrepancies between the results obtained were due to different DNA sequencing technologies, as well as ethnic and dietary differences between the participant populations.
Estrogens, go! Hormone replacement therapy will slow down skin aging Probiotics may play an important role in the medical treatment of diabetic peripheral arterial disease, the basis of which is the modification of the composition of the microbiome.
In another study, patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus had high levels of Lactobacillus compared to individuals without diabetes. These results differ from those of Qin et al., who described a decrease in A. muciniphila in diabetic patients.However, despite some differences, most researchers agree that type 2 diabetes mellitus
is accompanied by intestinal dysbiosis. The microbiome and peripheral vascular disease
Several studies have found a clear link between Helicobacter pylori and atherosclerosis. In
carotid artery samples from patients with peripheral arterial disease, genetic fragmentsof H. pylori and periodontal bacteria were found, suggesting colonization of atherosclerotic plaques. The number of known microorganisms involved in the indirect and direct activation of the immune system and the increase in the burden of atherosclerosis, began to increase, which highlights the need to study the role of the microbiome in the development of atherosclerotic diseases.
How can hypothyroidism be masked? Recent research supports the impact of microbiome and inflammation on outcomes in lower extremity peripheral artery disease (PAD).
Bacterial activity leads to the same adverse consequences as restenosis after arterial angioplastyand major cardiovascular events, which are the main cause of death in patients with PAD of the lower extremities.
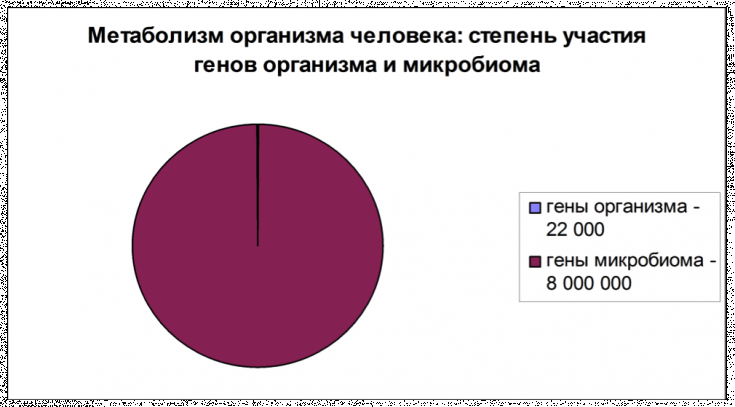
One of the interesting explanations for this fact may be that
bacterial colonization of atherosclerotic plaque acts as an additional factor in the burden of inflammation, enhancing the local inflammatory processinduced by surgical trauma during angioplasty. The combined effect of these two stimuli determines excessive production of cytokines, endothelial dysfunction, induction of foam cells, proliferation and migration of vascular smooth muscle cells (VSMC), the tendency of platelets to stick together and form thrombi.
Appetite under control: how to reduce ghrelin synthesis A recent hypothesis characterizes the microbiota as an indispensable constituent of the human body, and not as inhabitants of the environment that have colonized the human body. Modern research shows that the totality of microbial genomes complements the human genome.
The microbiome is the genetic characteristic of the entire microbiota in a particular tissue.

Its interaction with the immune system
modulates and regulates the immune response. Although the child's microbiota "ripens" already at the age of 3 years, the microbiome continues to change under the influence of epigenetic mechanisms, which are influenced by various endo- and exogenous factors. More useful information on our
YouTube-channel:






