UV radiation causes damage at the cellular level. UV mutates a tumor suppressor gene, playing a major role in the pathogenesis of skin cancer. UV radiation causes direct DNA damage, but it can also lead to the formation of reactive oxygen species and reactive nitrogen intermediates, which then cause indirect oxidative DNA damage. Therefore, photoprotection of the skin is one of the most important methods for preventing the development of skin neoplasms. The most common types of skin cancer are squamous cell and basal cell skin cancer. Read more about diagnosing these diseases at estet-portal.com.
- Causes and types of skin cancer
- Appearance and dermatoscopy of skin cancer
- Clinical presentation of basal cell skin cancer
Types and causes of skin cancer
Although basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell skin neoplasms are the most common types of skin cancer, they are easily treated if detected early, in about 95% of cases.
Follow us on Instagram!
Squamous cell skin cancer (SCCC) is a malignant neoplasm that develops from keratinocytes with the ability to metastasize in 2-3% of cases. Occurs in the elderly, occurs twice as often in men.
Read also: Acne treatment: sulfur, zinc, resorcinol
Among the causes of occurrence are: UV radiation, X-ray exposure, genetic diseases (albinism, xeroderma pigmentosum), diseases of the mucous membranes (lichen planus, lichen sclerosus), human papillomavirus (HPV), PUVA therapy, immunosuppression. Squamous cell skin cancer often develops against the background of actinic keratosis.
Distinguish between intraepidermal and invasive squamous cell skin cancer. Bowen's disease and Queyre's erythroplasia belong to intraepidermal forms. Invasive SCCC can be exophytic or endophytic. Clinically, neoplasms appear in the form of a plaque, increasing in size and taking on a nodular shape. The surface may be covered with horny masses or ulcerative. The ulcer is often covered with a crust, under it there is a purulent base, as tissue destruction occurs. The edges of the neoplasm are dense and raised, compared with basaliomas, the edges of which are often everted and uneven. Neoplasms grow at the rate of keratoacanthoma, much faster than bisal cell skin cancer.
Dermatoscopy and external manifestations of skin cancer
Squamous cell skin cancer appears in open areas: on the face, auricles, lower lip, back of the hands, forearm, lower leg. You can usually see signs of skin photodamage in the surrounding areas. SCCC can metastasize to the lymph nodes and be fatal. Several factors influence the prognosis: the presence of precursor neoplasms (eg, in the background of Bowen's disease, actinic keratosis, SCCC rarely metastasizes, its appearance on clean skin or after X-ray irradiation is more often associated with metastases), localization of the neoplasm ( on the auricle and red lip rim disease is more severe).
Read also: Retinoid side effects: how to control and correct them
Dermatoscopic structure of SCRC:
- keratin pearls - rounded structure with indistinct boundaries, which can be located over the entire area of education;
- clover leaf structures - white structures that look like four leaves and are shaped like clover leaves or rose petals. Can only be seen with polarized light in a dermatoscope;
Follow our updates on Facebook!
- glomerular vessels - vessels tightly twisted into a ball, which can occupy the entire area of the formation;
- vessels in the form of spikes on a white background - small or large vessels in the form of hairpins. The white background forms the surrounding keratin.
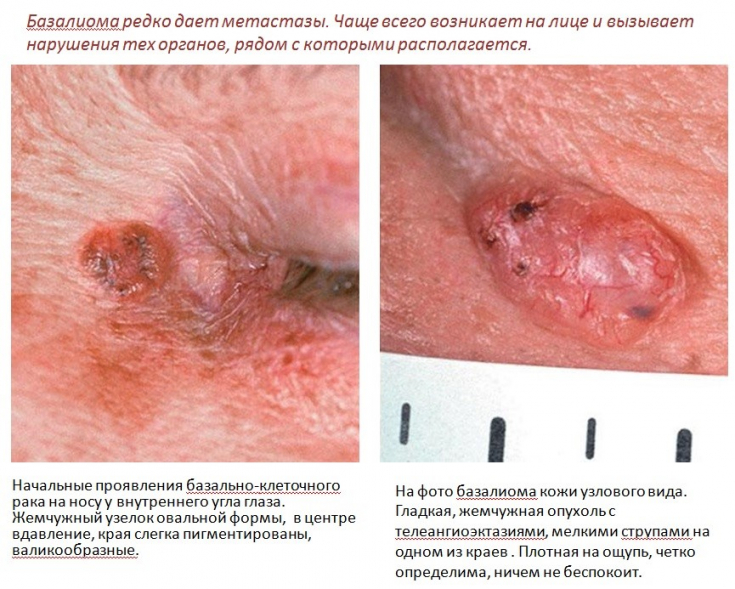
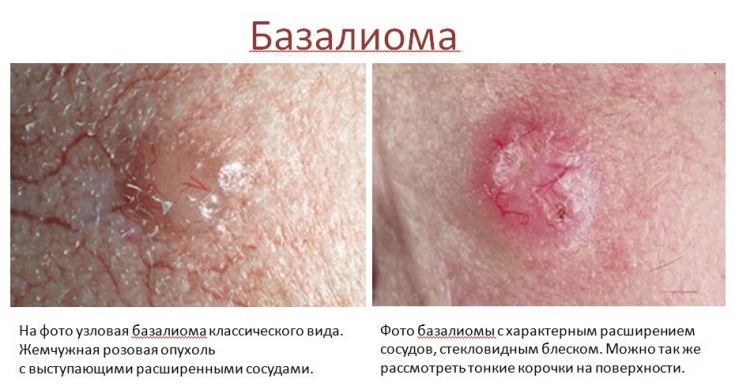
Clinical presentation of basal cell skin cancer
Basal cell skin cancer (BCSC) – a malignant skin lesion that develops from the basal cells of the epidermis and has destructive properties. There are several types of this skin cancer: ulcerative form, pigmented form, cystic form, scleroderma-like form, superficial form, Pinkus fibroepithelioma, Gorlin's syndrome.
People with skin phototype 1.2, a history of sunburn, the elderly, and those with a family history of skin cancer tend to develop basaliomas. The melanocortin 1 receptor gene (MC1R) is associated with fair skin, red hair, and an increased risk of melanoma and non-melanoma skin cancers. The increased risk with patient age may be due in part to a reduced ability to repair DNA damage from ultraviolet radiation, leading to the accumulation of carcinogenic products.
Basaliomas often form on the skin of the face (in 80%) and rarely on the skin of the trunk (20%); histologically, the tumor consists of islets of cells of the basal layer of the epidermis and adnexal structures.
Clinically, patients notice a wound that does not heal and bleeds intermittently. Basaliomas are often missed because the skin wound does not hurt or bother. This is common in the elderly, possibly due to the inability to see well. Basalioma rarely metastasizes, but has a destructive ability and invasive growth.
Read also: Effective Therapeutic Approaches to Treating Acne
You can also observe its development in the areas of natural openings (eyes, nose, ear). If the formation is not diagnosed in time, it deeply infiltrates the tissues, disrupting the functioning of the organs. Since neoplasms develop in open areas of the body, not only on the face, it is recommended that a dermatologist or cosmetologist periodically examine the skin of patients, since this pathology is often overlooked by general practitioners.
More useful information on our YouTube channel:







Add a comment