Adenoviral conjunctivitis is also called pharyngoconjunctival fever and is a rather contagious infection that manifests itself as an acute lesion of the mucous membrane of the eyes and upper respiratory tract. Adenoviruses provoke the disease.
Often the seasonality of the disease falls on spring-autumn period, and most cases are registered in children's groups. It is not uncommon for an adult to become infected with adenoviral conjunctivitis.
Read more on estet-portal.com causes of infection, typical manifestations, methods of diagnosis and treatment of adenoviral conjunctivitis.
- Risk factors for infection with adenovirus conjunctivitis
- Symptoms of clinical forms of adenovirus conjunctivitis
- Diagnostic aspects and principles of treatment of adenoviral conjunctivitista
Risk factors for infection with adenoviral conjunctivitis
Adenovirus enters the mucous membrane of the eyes by airborne droplets during coughing or sneezing of the patient, as well as when the infection directly enters the conjunctiva.
During epidemic outbreaks, adenovirus serotypes 3, 11 and 7a are detected in patients, and serotypes 10, 7, 6 and 4 types are detected in isolated cases.
The incubation period before the onset of symptoms is on average 5-7 days.
The main factors that increase the risk of infection with adenoviral conjunctivitis:
- impaired hand and eye hygiene;
- improper use and care of contact lenses;
- bathing in polluted pools or bodies of water;
- eye injuries and injuries;
- hypothermia;
- contact with a sick person with adenoviral conjunctivitis;
- SARS;
- surgical treatment of cornea;
- stress.
In the cytological examination of a patient's smear for adenoviral conjunctivitis, destruction of epithelial cells is visible, which is manifested by vacuolization and decay of chromatin, the formation of the nuclear membrane and hypertrophy of the nucleoli.
In the cytogram, mononuclear cellsand.
are more visibleMain aspects and methods of treatment of allergic conjunctivitis
Symptoms of clinical forms of adenoviral conjunctivitis
After the end of the incubation period, the body temperature rises, dyspeptic disorders appear, rhinitis, pharyngitis, submandibular lymphadenitis, and this is accompanied by a headache.
After some decrease in temperature, it raises again, this is the so-called second wave.
At this time, the first local specific signs of adenoviral conjunctivitis appear:
- edema;
- not copious discharge of a mucous or mucopurulent nature;
- burning and itching in the eyelids;
- eyelid hyperemia;
- foreign body sensation;
- excessive lacrimation;
- blepharospasm;
- hypersensitivity to light stimuli.
There are 3 main clinical forms of adenoviral conjunctivitis:
1. Follicular form. It is characterized by the appearance of follicles (blister rashes) on the mucous membrane of the eye. Such follicles can be of different shapes, sizes and localizations.
The follicular form of conjunctivitis outwardly similar to the manifestations of the initial stage of trachoma, but with trachoma there is never fever and nasopharyngitis, and the rashes are only in the conjunctiva of the upper eyelid.
2. Catarrhal form. This form of inflammation proceeds easily and quickly.
Local inflammation is slightly expressed, there is a slight redness, there is relatively little discharge. Complications in the cornea are usually not observed.
3. The membranous form of adenoviral conjunctivitis occurs with a frequency of 25% of all cases and is characterized by formation of thin films that cover the conjunctiva.
The films are gray-white in color, their structure is delicate and they are easily removed with a cotton swab.
However, sometimes hard fibrinous deposits can form, which are difficult to remove from the mucous membrane of the eyes, as they are soldered to it. After removal of such films, areas of bleeding may appear on the mucosa.
There may also be petal hemorrhages under the conjunctiva, which resolve after recovery.
This form occurs with a high temperature (up to 390C), which can last up to 10 days.
The clinical picture described above can be mistaken for diphtheria.
The membranous form of adenoviral conjunctivitis often results in scarring of the mucosa. 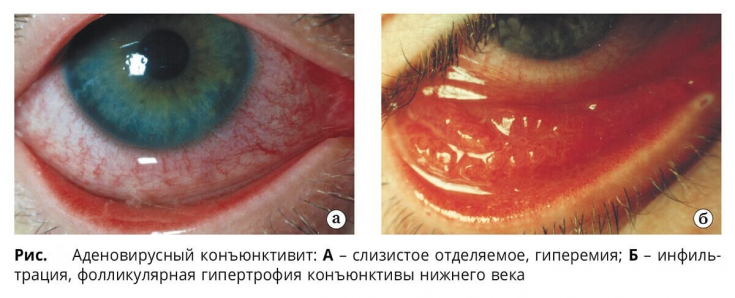
Complications of adenoviral conjunctivitis:
- toxic-allergic or bacterial conjunctivitis;
- keratitis;
- dry eye syndrome;
- tonsillitis;
- otitis media;
- adenoidsm.
Read more of our articles on Facebook!
Aspects of diagnosis and principles of treatment of adenoviral conjunctivitis
If adenoviral conjunctivitis is suspected, the ophthalmologist pays attention to catarrhal changes in the upper respiratory tract, specific symptoms of the disease and regional lymphadenopathy.
For the purpose of early diagnosis, immunofluorescence methods are used, which allow the detection of specific antibodies in a smear taken from the conjunctiva.
Cytological, virological, and serological laboratory methods are used to isolate the virus.
Antibodies to adenovirus in blood serum are detected using IA enzymatic immunoassay and RSK- complement fixation reaction.
Adenoviral conjunctivitis is characterized by a multifold increase in antibody titer.
It is possible to detect adenovirus DNA in a conjunctival scraping using polymerase chain reaction.
Adenoviral conjunctivitis is treated on an outpatient basis using antiviral agents.
Local application of interferon and deoxyribonuclease in the form of instillations up to 8 times a day in the first week of illness and 2-3 times a day in the second week of the process is advisable. They also use antiviral ointments (laid behind the eyelids).
In order to prevent secondary infection, eye drops and ointments with an antibacterial component.
Dry eye syndrome as a complication of blepharoplasty
Until full recovery, artificial tear substitutes must be used to prevent the development of xerophthalmia.
Usually, adenoviral conjunctivitis results in complete clinical recovery.







Add a comment