There may be formations in the human body that he does not even know about. Often such findings are detected during medical examinations and with instrumental research methods for concomitant diseases. Thus, cysts are revealed. Cysts do not carry any danger, provided that their size is small. Cysts can also form in the maxillary sinus. There is a specific symptom that indicates the presence of a cyst of the maxillary sinus. Causes, symptoms of manifestation and the need for treatment of maxillary sinus cysts read in our article.
What are the main reasons that provoke the development of a cyst of the maxillary sinus?
Frequent development of rhinitis and/or sinusitis for some time stops aeration and air saturation of the maxillary sinus. At the same time, the inner walls of the maxillary sinus, which are represented by the mucous membrane, lose the ability to perform their physiological functions. The mucous membrane of the maxillary sinus has glands, the secret of which is secreted by the excretory ducts.
In case of inflammatory processes in the sinus or frequent rhinitis, the excretory ducts of the glands of the mucous membrane of the maxillary sinus are clogged. Since the fluid has nowhere to go, it stagnates in the sinus. A cyst of the maxillary sinus is formed, the walls of which are represented by epithelium, which continues to produce mucus. The cyst contains fluid that is getting bigger.
The second reason for the development of a cyst of the maxillary sinus is the anatomical feature of the structure of the nose. There is a curvature of the nasal septum, which prevents the normal passage of air into the sinus. Also, the incorrect structure of the fistula, through which air enters the sinus, can also have its own anatomical features or be narrowed after suffering often recurrent sinusitis. Dental pathologies can also cause the development of a maxillary sinus cyst. Infection from diseased teeth spreads to their roots, from where the process passes into the maxillary sinus.
What specific symptom would indicate a maxillary sinus cyst?
A maxillary sinus cyst may appear several years after its appearance, or it may even form and pass on its own without causing any symptoms. Often, a cyst of the maxillary sinus is found during an x-ray of the skull with acute sinusitis or injuries. Rarely, a cyst of the maxillary sinus greatly disturbs the patient, which makes him seek medical help. In some cases, the cyst may grow rapidly, causing the following symptoms:
- Persistent discharge from the nose of a mucous nature or mucus running down the back of the throat.
- Nasal congestion and difficulty in breathing through the nose usually associated with a cyst.
- Headache of a bursting nature, which is aggravated by lowering the head.
- Frequent relapses of rhinitis and sinusitis accompanied by purulent discharge from the nose, fever, headache and general malaise.
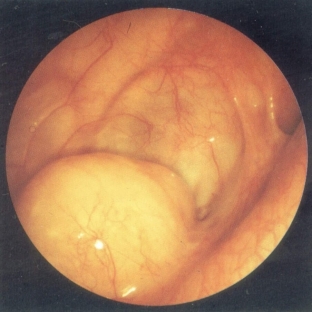
A specific symptom that only indicates the presence of a maxillary sinus cyst is the periodic discharge of a clear, bright yellow liquid from one nasal passage (on the side of the lesion).
The release of fluid in the cyst of the maxillary sinus occurs when the head is suddenly lowered down or during sleep. At night, when the patient's head is in a horizontal position and all the vessels are dilated, the patient may wake up from the sensation of supposedly bleeding from the nose, but the color of the fluid flowing out is not red, but yellow. This indicates an overflow of the maxillary sinus cyst, as a result of which excess fluid comes out.
Diagnosis of cysts of the maxillary sinus. When is cyst treatment needed?
In most cases, a maxillary sinus cyst is an incidental finding. If the patient has complaints, after taking anamnesis and rhinoscopy, the doctor can determine the presence of a maxillary sinus cyst. To confirm the diagnosis, an x-ray of the sinuses is performed, if necessary, a CT scan is performed. In some cases, a diagnostic puncture of the maxillary sinus is required.
If a cyst is discovered by accident and does not disturb the patient, it does not need to be treated. With periodic leakage of fluid from the nasal cavity, treatment is also not required. If the patient is concerned about symptoms such as persistent nasal congestion, headaches and frequent sinusitis – cyst treatment is mandatory.
Treatment and prevention of maxillary sinus cysts
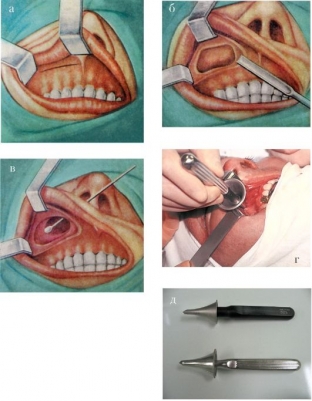
Before treatment, the patient should be examined by a dentist to rule out the cause of the cyst due to diseased teeth. Treatment of cysts of the maxillary sinus is only surgical. However, if the patient has acute sinusitis, the operation is postponed.
During the operation, access through an incision in the upper lip is more often used. If the patient has a deviated nasal septum, during the operation, the deviated septum is eliminated and the cyst of the maxillary sinus is removed through the fistula. After the operation, the nasal passages are plugged.
To prevent a cyst of the maxillary sinus, it is necessary to visit the dentist regularly and, at the first symptoms, contact an otolaryngologist.







Add a comment