In the oral cavity, formations can appear that often disturb people. One of these formations is the fibroma of the oral cavity. What are the causes of oral fibroids? Should we be afraid of them? How to identify and get rid of oral fibroids, read on estet-portal.com.
What is a fibroma on the oral mucosa?
Fibroma of the oral cavity is a benign formation of the oral mucosa, which consists of mature connective tissue fibers. The most common fibroma occurs in adolescents.
Fibroma can be localized both on the mucous membrane of the lips, and on the inner surface of the cheeks, soft palate, tongue and gums.
Oral fibroma is a limited rounded nodule on the oral mucosa, which may have a wide base or pedicle. Fibroma is painless to the touch, has a spherical shape and is covered with a pink mucosa, which does not differ in appearance from other parts of the oral mucosa.
Fibroma has a smooth surface, which distinguishes it from papilloma, which has outgrowths and a rough surface. There are cases when ulcerations appear on the fibroma, into which the infection enters, and an inflammatory reaction develops. Then, in the area of the fibroma, redness, soreness and swelling are noted.
Fibroma of the oral cavity grows at a slow pace. At the same time, if it is not subjected to constant injury, it may not increase in size for a very long time. And with constant injury to the oral mucosa, fibroma may degenerate into a malignant tumor.
Causes of oral fibroma formation
The main causes of fibroids include:
- Traumatic damage to the oral mucosa.
- Inflammatory diseases of the oral cavity.
- Hereditary predisposition.
Often, when determining the cause of fibroma formation, it is found that for some time there was a constant biting of the same area of the mucosa in the oral cavity. Fibroma provoking factors – injury to the tooth edge, crown or poorly fixed prosthesis of the buccal mucosa. Chronic inflammatory processes of the oral cavity are also predisposing factors for the development of fibroma.
What are the main types of fibromas that can appear in the oral cavity?
There are 6 varieties of oral fibromas, depending on the consistency, size and shape.
- Soft fibroma – consists of a large number of loosely arranged thin fibers of connective tissue, the fibers have a large number of nuclei. Thanks to this composition, it has a soft texture. Often, such fibromas are located on the mucous membrane of the cheeks and on the tongue. On the mucosa of the bottom of the mouth, formations of a mixed type are possible – fibrolipoma and fibrohemangioma.
- Dense fibroma – consists of coarse fibers of connective tissue with a small number of nuclei that fit tightly to each other. Often a dense fibroma is localized on the hard palate and in the gum area.
- Fibroma from irritation – is the result of reactive mucosal hyperplasia and is not a tumor. This type of fibroma appears with chronic long-term exposure to chemical or mechanical factors.
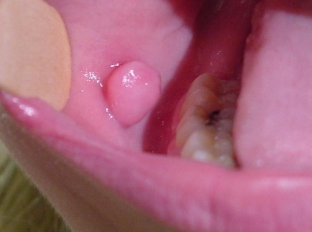 This is the most common type of oral fibroma. A pink papule appears at the site of frequent irritation. With progression, it becomes larger in size and acquires the correct rounded shape. Repeated trauma can lead to ulceration and inflammation of the fibroma.
This is the most common type of oral fibroma. A pink papule appears at the site of frequent irritation. With progression, it becomes larger in size and acquires the correct rounded shape. Repeated trauma can lead to ulceration and inflammation of the fibroma.
- Lobular fibroma – has a bumpy surface and appears with frequent trauma to the gums with a removable prosthesis. This is reactive hyperplasia of the gum tissue.
- Symmetrical fibromas – appear in the area of the third painters on the palatal surface of the gums. They are bean-shaped and firm in texture. Such fibromas do not belong to the neoplasms of the oral cavity, but are the growth of the gums with cicatricial changes.
- Fibrous epulis – the so-called fibroma, which is located on the gum. It is characterized by slow growth and a dense texture.
Methods for diagnosis and treatment of oral fibroma
Usually, when examining the oral cavity by a dentist, an oral fibroma, if present, is diagnosed immediately. Ultrasound is used to determine the depth of a fibroma. If ulceration is detected on the surface of fibromas and an inflammatory reaction, a biopsy of the fibroma is performed. After removal of the fibroma, its histological examination is carried out.
When diagnosing fibroids, it is important to determine the cause of fibroids and take measures to remove them. For this, a thorough examination of the oral cavity is carried out for the presence of sharp dental edges or implants, crowns. For this purpose, radiovisiography, orthopantomogram, periodontogram and radiography are used.
It is necessary to differentiate fibroma from papilloma, neurinoma, epiluses of different structure, wart. If the fibroma is located on the tongue, it is necessary to exclude the tumor of the tongue.
The most effective way to get rid of a fibroma is to surgically excise the fibroma tissue. This is carried out using the radio wave method or laser.
Definitely, even if the fibroma does not increase, does not hurt and does not interfere with a person, then it is worth consulting a dentist about its removal. After all, with constant trauma, which a person may not feel, it is possible for oral fibroids to degenerate into a malignant formation.







Add a comment