Modern technologies have opened the door to a new world for science and medicine, and diagnostic capabilities have significantly expanded the range of diseases previously unknown to science and their treatment methods. But there are pathologies that are considered "elders" over all diseases, because they were known to science even before our era. One of these pathologies is gout – excessive accumulation of uric acid salts in the human body. Signs of gout are quite specific, and with a properly collected anamnesis, the doctor will be able to recognize the disease only by a characteristic clinical picture.
Typical signs of gout will help to recognize the disease
Scientists have found out a surprising fact about gout: despite the fact that hyperuricemia occurs in all patients with gout, the disease itself is clinically manifested in only 5% of patients. Based on this, it becomes especially important to know the characteristic signs of gout, which for a long time can simply go unnoticed by either the doctor or the patient. Read more about these signs on estet-portal.com.
Typical symptom of gout – inflammation of the joint, may indicate some other pathologies that doctors immediately try to exclude.
And the sooner they manage to establish that uric acid is the cause of arthritis – the sooner effective treatment of the disease will begin.
Signs of gout:
- early signs of gout: attacks of acute arthritis;
- peculiarities of the interictal period in gout;
- late signs of gout: formation of tophi.
Early signs of gout: attacks of acute arthritis
The earliest sign of gout is an attack of acute gouty arthritis, which occurs very suddenly and violently, often at night. In most cases, the 1st metatarsophalangeal joint is affected, due to which the patient cannot get out of bed and stand on his foot. In the future, the process may spread to the joints of the arch of the foot, forming the so-called "gouty foot". Acute gouty arthritis occurs with all elements of the inflammatory process, which include:
- swelling of the joint;
- hyperemia or sometimes cyanosis of the skin;
- increased body temperature up to 39°C, the skin at the site of the lesion is hot to the touch;
- the joint is sharply painful, especially when moving.
Peculiarities of the interictal period in gout
In the first years of gout development, a characteristic symptom of the disease is the alternation of attacks of acute arthritis and interictal periods. An attack of acute gouty arthritis lasts up to 10 days, after which the function of the joints is completely restored. In about 7% of patients, the second attack may not occur at all, while 60% note the recurrence of gouty arthritis during the 1st year of the disease. As the disease progresses, the duration of attacks increases, and the duration of the interictal period decreases. The localization of the lesion can also vary, but gouty arthritis is characterized by asymmetric joint damage.
Late signs of gout: formation of tophi
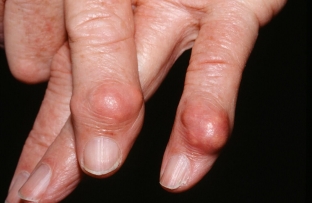 Chronic gouty arthritis occurs in most cases in the complete absence or insufficiently effective treatment of the disease. Over time, in such patients, the rate of urate production begins to exceed the rate of their excretion, as a result of which uric acid salts accumulate in cartilage, tendons, soft tissues and synovial membranes, forming tophi – characteristic clinical sign of gout. Urate crystals are deposited in the auricles, on the fingers and toes, or on the back of the elbow joints. Tophi can open, forming fistulas and secreting a white mass.
Chronic gouty arthritis occurs in most cases in the complete absence or insufficiently effective treatment of the disease. Over time, in such patients, the rate of urate production begins to exceed the rate of their excretion, as a result of which uric acid salts accumulate in cartilage, tendons, soft tissues and synovial membranes, forming tophi – characteristic clinical sign of gout. Urate crystals are deposited in the auricles, on the fingers and toes, or on the back of the elbow joints. Tophi can open, forming fistulas and secreting a white mass.
The clinical picture of gout is quite specific, attracts attention and requires immediate search and elimination of the causes of such a disease.
Knowing the signs of gout will help to diagnose the disease in time and start its effective treatment.







Add a comment