Acute rheumatic fever appears as a complication of pharyngitis or tonsillitis if they were caused by beta-hemolytic streptococcus A. Chronic rheumatic heart disease may develop after acute rheumatic fever. Today, acute rheumatic fever is an urgent problem in medicine, as the incidence and mortality from this pathology has increased over the past decades. About 15 million people are affected worldwide, mostly children aged 5 to 14 years. What are the clinical manifestations of acute rheumatic fever?
Causes and theories of acute rheumatic fever
Acute rheumatic fever is a socially dependent disease. Poverty, malnutrition, cohabitation, and poor medical attention for throat infections increase the likelihood of developing acute rheumatic fever.
The etiological factor in the development of acute rheumatic fever is a throat infection provoked by beta – hemolytic streptococcus.
Today, studies are ongoing in which the role of streptococci of other groups (C and G) is being determined, but so far the main role belongs to group A streptococcus.
There are 3 theories for the development of acute rheumatic fever:
- Infection theory.
- A theory that states that acute rheumatic fever develops as a result of the action of Streptococcus toxins.
- As a result of the interaction of streptococcal antigens, which have molecular similarities with the antigens of body tissues, against the background of changes in the host's immune response, autoimmune reactions are formed. This theory has the most weighty evidence.
Clinical manifestations and symptoms of acute rheumatic fever
Carditis is the only and most important prognostic factor of acute rheumatic fever, since it is damage to the heart tissue that leads to irreversible organic disorders and determines further patient management.
Holosystolic murmur on auscultation of the apex of the heart, pericardial friction rub, or causeless enlargement of the heart with symptoms of heart failure.
At the first attack of rheumatic fever, detection of heart failure is sufficient to establish a diagnosis of active rheumatic carditis.
Rheumatic chorea is characterized by emotional instability, muscle weakness and incoordination with the appearance of violent spastic movements. Manifestations intensify during stressful situations and disappear during sleep. Chorea develops in acute rheumatic fever a month after a throat infection. Chorea is accompanied by changes in handwriting and fine motor skills. Conscious movements are difficult to perform due to violent movements and grimaces.
What are the manifestations of acute rheumatic fever on the skin?
Arthritis is one of the most common manifestations of acute rheumatic fever, occurring in 75% of patients. The manifestations of joint damage in rheumatic fever can range from arthralgia to severe arthritis. Typical arthritis is manifested by migratory polyarthritis of large joints. Affected joints feel hot, pink and swollen, painful to touch.
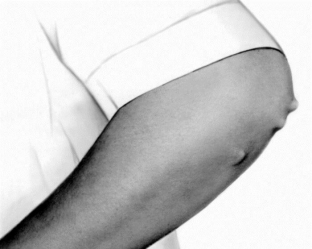
Subcutaneous rheumatic nodules are a rare manifestation of acute rheumatic fever. These are painless mobile subcutaneous nodules over the joints, which are up to 2 cm in diameter. They can also be located above the vertebrae, in the Achilles tendons, under the scalp. The nodules disappear on their own within 1-2 weeks.
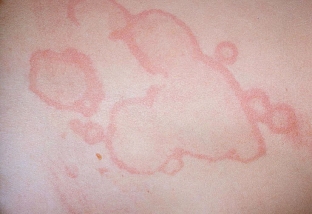
Erythema annulus – it is a rash, specific to acute rheumatic fever, in the form of red erythema or papules on the trunk or extremities, which have enlightenments in the center, disappear with pressure, are not accompanied by pain or itching. Taking anti-inflammatory drugs does not affect the disappearance of erythema.
How to diagnose acute rheumatic fever?
To confirm the diagnosis of acute rheumatic fever, laboratory blood tests are performed, which reveal an increase in acute phase indicators of inflammation. The diagnostic criterion is an increase in temperature to 380C and more, which persists for several weeks. ECG shows RR interval prolongation.
Timely detection of beta group A hemolytic streptococcus can prevent the development of acute rheumatic fever. To do this, in case of inflammatory diseases of the throat in weakened people, it is advisable to take a swab from the oropharynx.







Add a comment