Melasma – a type of hyperpigmentation, the pathogenetic mechanisms of which include hereditary factors, as well as exposure to solar radiation and heat. To date, hydroquinone-based drugs remain the gold standard for treating melasma. However, this substance has carcinogenic properties, and can also provoke the development of exogenous ochronosis. In addition, due to its high irritant potential, hydroquinone is often combined with fluocinolone acetonide 0.01% and tretinoin 0.05%. Regular use of these agents can lead to an increase in the severity of melasma and post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation. Therefore, the search for new methods of treating melasma – actual task modern dermatology. In the estet-portal.com article, Drs Beverly Johnson, Samantha Marrone and Amit Om present clinical cases of combination treatment of melasma with a cysteamine-based cream and a 650 microsecond laser Nd:YAG 1064 nm.
- Results of combination treatment of melasma: case reports
- Melasma treatment options with cysteamine cream and Nd:YAG laser
Results of combination treatment of melasma: case reports
The article presents cases of treatment of melasma in patients aged 67, 61 and 41 years. Previously, the patients underwent therapy with hydroquinone preparations, the results of which were unsatisfactory.
The patients had not used any topical melasma treatment for the year prior to contacting the authors, nor had they previously undergone laser therapy.
Follow us on Instagram!
Treatment regimen:
- The patients applied a cysteamine-based cream to problem areas of the skin every evening and washed it off after 15 minutes.
- No other topical medications have been used to treat melasma.
- Every day, regardless of weather conditions and activity, the patients applied sunscreen with SPF
- The patients underwent 4 sessions of 650 microsecond Nd:YAG 1064 nm laser therapy with an interval of 1 month.
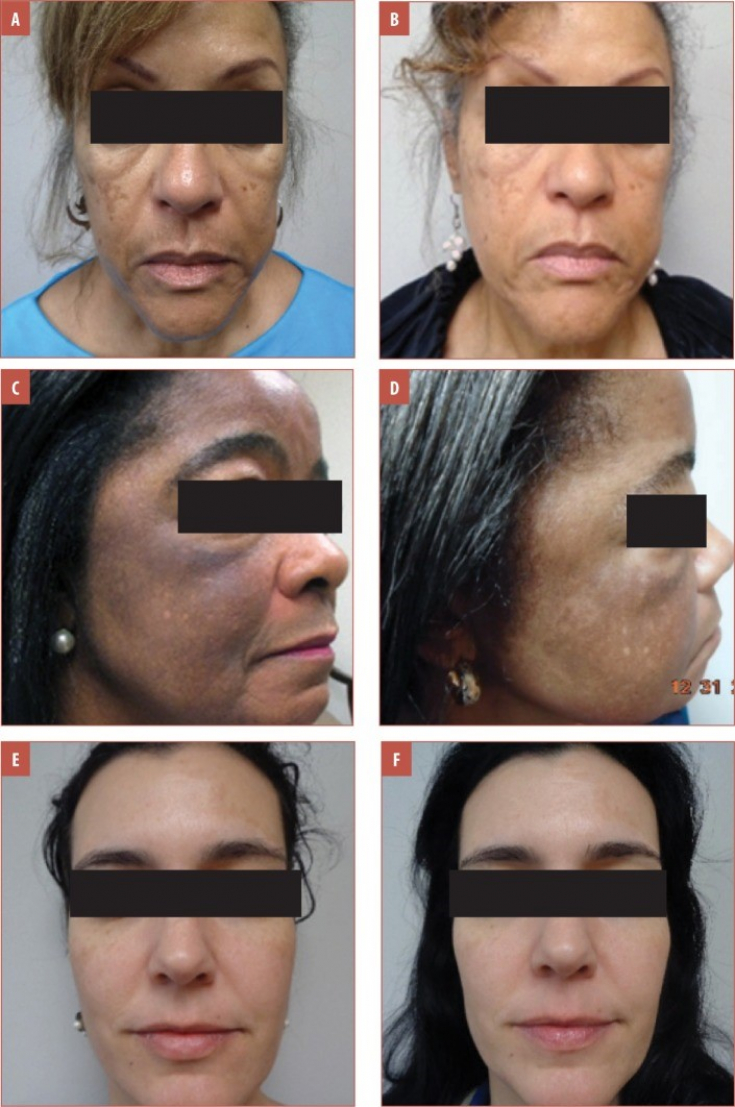
Patient photos before (A, C, E) and after 4 months (B, D, F) after melasma treatment (daily cysteamine cream and 4 laser treatments
All patients were satisfied with the results of combination therapy for melasma.
Treatment was not accompanied by the appearance of:skin irritation;
- sensations of discomfort;
- recovery period;
- "halo" hypopigmentation.
- The effect of therapy was maintained 2 months after its completion.
The patient was informed about the negative effects of UV radiation on the skin, including an increased risk of increasing the severity of melasma, and recommended the constant use of sunscreen. All patients agreed to continue monthly
laser therapy sessions. Melasma treatment options with cysteamine-based cream and Nd:YAG laser
The basis that the authors used for the treatment of melasma is the active substance
cysteamine hydrochloride at a concentration of 5% and niacinamide 5%. The brightening effect of cysteamine is due to the ability of the substance to inhibit melanin synthesis.
The cream also contains:water (75%);
- Vaseline oil (10%);
- shea butter (5%);
- lecithin 5%;
- glyceryl stearate 5%;
- isopropyl myristrate 5%;
- cetyl alcohol 5%;
- ascorbyl palmitate 1%.
Nd;YAG 1064 nm is used to treat melasma on all skin types and does not cause complications. During operation of the laser, a minimum amount of heat is generated. This is an important point, as intense heat exposure can cause melasma to worsen. The interval between laser therapy sessions is 4–6 weeks – the time required for phagocytosis of the pigment. This technology makes it possible to target deep dermal melanin and vascular components, which is not possible with topical melasma therapy.
It can be seen from clinical cases that the combined approach to treating melasma presented by the authors is effective in dealing with different Fitzpatrick skin types and melasma of varying severity.
The authors suggest that cysteamine-based cream and Nd:YAG laser therapy has additional benefits for patients who:
fear the risks associated with the use of hydroquinone;
did not get results after melasma treatment with hydroquinone-based drugs.- You may also be interested in: Effectiveness of tranexamic acid in the treatment of melasma
Clin
Aesthet Dermatol. More interesting videos on our YouTube
-channel!







Add a comment