Mechanical dermabrasion, chemical peeling and laser resurfacing are used to rejuvenate the skin of the face and even out its relief.
Mechanical dermabrasion eliminates almost all types of wrinkles, as well as small scars, is performed with a rapidly rotating cutter with an abrasive nozzle (spraying with a diamond or corundum chips with a grain size of up to 100 grit).
The disadvantages of mechanical dermabrasion include: frequent occurrence of extensive scars (40-50%), prolonged erythema (up to 6 months), high pain of the procedure, high probability of secondary infection, depigmentation or hyperpigmentation.
MD, Professor, Honored Doctor of Ukraine, President of the Ukrainian Society of Aesthetic Medicine, General Director of the Ukrainian Institute of Plastic Surgery and Aesthetic Medicine "Virtus" Vladimir Tsepkolenko.
Chemical peeling is no less widely used, which, depending on the depth of exposure, is divided into:
- surface,
- middle and
- deep.
Superficial and median peels are not effective enough in the treatment of pronounced scars and are accompanied by a relatively high risk of complications.
Among the disadvantages of deep peeling are:
-
- scarring,
- prolonged erythema (up to 6 months),
- soreness,
- high probability of joining a secondary infection,
- depigmentation and
- hyperpigmentation.
The intensive development of ablative laser technologies has allowed them to gain recognition in skin rejuvenation, wrinkle removal and correction of the effects of acne. The vast majority of lasers used for this purpose are focused on the absorption of radiation by ubiquitous intracellular water, maximum in the IR range (2600 nm and more).
CO2 and short-pulse Er are the most widely used:
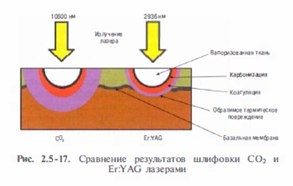
Table 3. Comparative characteristics of three types of ablative lasers
| CO2 | ErCr:YSGG | Er:YAG | |
| Gas | Solid State | Solid State | |
| 10600 nm | 2790 nm | 2936 nm | |
| 800 cm | -1 | 5860 cm-1 | 12000 cm-1 |
| ≈600 cm | -1 | ≈4900 cm-1 | ≈1000 cm-1 |
| 2-3=µm/(J x cm | 2 ) | 2-3=µm/(J x cm2 ) | 2-3=µm/(J x cm2 ) |
| 100-250 µm | 40-100 µm | 20-50 µm |
Combination of laser resurfacing and other aesthetic procedures:
Of all the areas prone to wrinkles, the perioral and periorbital areas lend themselves best to laser resurfacing. Wrinkles in this localization are not amenable to improvement during traditional facelifts.
Resurfacing of the entire face brings more successful clinical results. For example, the treatment of the entire volume of the cheeks contributes to a better tightening of the nasolabial folds, the lateral part of the “crow's feet” and wrinkles of the middle part of the cheek.
With a complete treatment of the forehead, the condition of the interbrow, lateral temporal wrinkles and the upper part of the “crow's feet” improves. Smoothing the relief and uniform skin color contribute to a better cosmetic effect than mixing skin with renewed and skin with age-related changes, creating a pattern of multi-colored patches (checkerboard effect).
With a full face treatment, there is no need to hide the boundaries between postoperative erythema and untreated skin. It is not recommended to grind individual wrinkles or scars, only one anatomical zone or two isolated closely spaced areas. Thus, lifting of the lower two thirds of the face and eyelid surgery are well combined with laser resurfacing of the forehead and perioral area, endoscopic lifting of the forehead and middle third of the face – with polishing of the entire face.
Expression lines – frontal, between the eyebrows, “crow's feet” – are the result of muscle contractions therefore inevitably recur even in the case of complete smoothing. Blocking nerve signals with botulinum toxin type A 1-2 weeks after resurfacing stops the functionality of these muscles for 3-4 months – the period required for the formation and restructuring of new collagen. This results in better and more sustainable clinical results.
Indications for ablative laser resurfacing
Age-related changes in the skin.
When rejuvenating slowly healing areas with relatively few adnexal structures (such as the neck and arms), short-pulsed Er:YAG laser has the advantage, using a CO2 laser for treatment these areas are much less effective due to severe thermal damage and more side effects.
When rejuvenating the skin of the neck, 2-3 passes of the Er:YAG laser (3-5 J/cm2) and one more are usually used – when processing hands.
Wrinkles.
The choice of laser is determined by the depth of wrinkles:
- weakly and moderately expressed wrinkles - Er:YAG laser;
- & nbsp;medium – long-pulse Er:YAG , ErCr:YSGG and CO2;
- deep – CO2 laser.
In the treatment of medium and deep wrinkles, the contraction and reconstruction of skin collagen is important, most strongly manifested in the treatment of CO2 laser, and to a lesser extent - long-pulse Er:YAG , ErCr:YSGG. 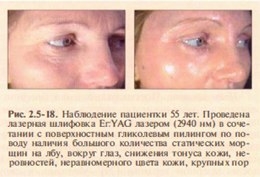
Benign epidermal and dermal neoplasms are safely and effectively removed by all ablative lasers.
If the removal process is accompanied by a high risk of bleeding, CO2, long-pulsed Er:YAG or ErCr:YSGG lasers are preferred.
The most sensitive areas are best treated with a short-pulsed Er:YAG laser.
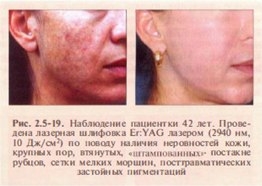 Acne scarring.
Acne scarring.
Laser resurfacing can significantly improve the condition of acne-affected skin. During the procedure, the edges of the scar tissue are very carefully processed, where it is necessary to evaporate a larger amount of tissue, and the remaining areas are subjected to only surface grinding.
Skin reduction due to CO2 laser treatment can give very good results in the treatment of soft atrophic scars with sloping edges.
Short pulsed Er:YAG laser achieves mild to moderate improvement with minimal risk of side effects. Deep scars respond best to CO2 and long-pulse Er:YAG lasers (Fig. 2.5-19).
Multiple treatments are required to achieve maximum results, and the most difficult areas may require additional treatments: exfoliation, excision, dermal fillers, implants. and melasma can be removed simultaneously with the correction of other age-related changes, while the daily use of sunscreen, as well as tretinoin and hydroquinone, for a long period before and after laser therapy, is important.
Melasma, due to its etiopathogenetic features, tends to recur after treatment, so its resurfacing should be preceded by hormonal correction.
Superficial and deep dermal pigmentation and dispigmentation respond well to short-pulse Er:YAG laser treatment, which is also effective in preparing the recipient site for epidermal grafting in cases of vitiligo.
To combat excessive pigmentation without concomitant resurfacing, pulsed lasers, the main chromophore of which is melanin (600-900 nm), are more effective, because they do not require major anesthesia and healing is faster after their use.
Actinic cheilitis.
CO2 laser treatment involves a single pass over the red border followed by treatment of stubborn plots. The treatment of lesions localized on the back of the hands and scalp is especially effective. Healing takes up to 10 days.
Post-traumatic and surgical scars.
Er:YAG laser resurfacing at the stage of collagen reconstruction (first 90 days after injury) can significantly improve the cosmetic appearance of both post-traumatic and surgical scars. Linear scars are most effectively treatable. Large atrophic scars are well treated with CO2 laser due to the strong positive effect of collagen reduction.
Contraindications for ablative laser resurfacing
High risk of complications at the healing stage in the presence of keloid and hypertrophic scars, scleroderma, collagenosis; in case of taking isotretinoin in the last 1-2 years or immunosuppressive therapy.Reduction in the number of skin appendages due to post-burn scarring, previous radiotherapy or deep phenol peeling.
Presence of diseases: infectious, such as HIV (AIDS), active herpes simplex, hepatitis C or a history of recurrent infections; diabetes mellitus, unstable hypertension, severe cardiovascular, pulmonary, etc.
Preoperative period
An important element of preoperative preparation of the skin for laser resurfacing is hydroderma (deep hydration reduces thermal tissue damage).
According to indications, chemical peeling or microdermabrasion is performed, which thins the epidermis and allows to reduce the number of laser passes, which reduces thermal damage to the dermis and, accordingly, the intensity of complications (especially important when resurfacing with a CO2 laser).
Prevention herpes is considered necessary for all patients undergoing a full facial resurfacing or perioral resurfacing. The likelihood of an outbreak of infection at the postoperative stage is up to 7%, it can develop even in patients who did not have a history of episodes of this disease.
Result –
Immediate preoperative preparation
At the end of the procedure, the eyes are washed with a sterile solution. If treatment of the periorbital area is not planned, the eyes can be closed with wet gauze pads. to avoid accidental laser contact with untreated skin or flammable surfaces. A wet gauze pad can also be used to protect tooth enamel.
Lasers for cosmetology and surgery: skin resurfacing CO2 laser
The advantages of skin resurfacing with this laser include precise control of tissue vaporization and stable hemostasis. Each pulse removes a layer with a thickness of about one optical penetration depth (20-30 μm), while the thickness of the layer of residual thermal damage is 2-4 times greater.
With a relatively slow continuous energy supply, heat diffusion becomes significant (because ablation begins only at 100 ° C), a significant part of the heat has time to spread into skin depth.
At the same time, the process of dehydration takes place, reducing the effectiveness of ablation and the share of heat going to it – the tissue can be heated up to 400-600 °C, which ultimately leads to a huge (compared to the pulsed mode) thermal damage to the skin, which prevents wound healing and significantly increases the risk of developing scar tissue. To avoid this, the duration of energy delivery to the skin should be less than its thermal relaxation time (about 1 ms).
The primary passage of the CO2 laser removes the epidermis and causes the formation of a subepidermal vesicle. A white dehydrated protein residue remains on the surface, which must be removed with a napkin with saline solution. The depth of thermal damage in this case is 40-70 microns, depending on the density of the epidermis: areas with a thin epidermis (for example, the skin of the eyelids and neck) are more damaged.
which must be removed with a napkin with saline solution. The depth of thermal damage in this case is 40-70 microns, depending on the density of the epidermis: areas with a thin epidermis (for example, the skin of the eyelids and neck) are more damaged.
which must be removed with a napkin with saline solution. The depth of thermal damage in this case is 40-70 microns, depending on the density of the epidermis: areas with a thin epidermis (for example, the skin of the eyelids and neck) are more damaged.
After the second pass, the total thermal damage increases.
The third pass is applied selectively in areas with significant age-related changes and the presence of wrinkles in the areas above the bridge of the nose, upper lip, nasolabial folds and the lateral surface of the cheeks.
The fourth pass is only necessary in exceptional cases, as causes excessive damage to the skin.
When performing laser resurfacing, the following guidelines should be considered:
• When treating the face, 2-3 laser passes are used.
• Impact on transitional zones (at a distance of 5-15 mm from the hairline and 3-5 cm under the chin line) is softened by a decrease in the energy density of the radiation.
• A single pass of a 3 mm beam along the border of the red border of the lips smooths out deep purse-string wrinkles and emphasizes the contour. You can enter the red border of the lips only for a single processing of the lines crossing it.
• After completing the main treatment, it is recommended to vaporize the residual effects of seborrheic and actinic keratosis, hyperkeratosis, hypertrophic scars with additional single pulses of the Er:YAG laser.
• It is necessary to carefully observe the response of the tissue (reduction, the acquisition of a yellow-brown color). Persistence of color change after saline treatment is a sign of thermal necrosis.
Treatment should be terminated if one of the following conditions is present:
• Removed wrinkles or scars.
• Visible thermal damage – the skin has acquired a yellow-brown tint.
• There is no further skin contraction.
• Er:YAG laserDue to the proximity to the maximum absorption of light by intracellular water, the penetration depth of Er:YAG laser radiation is 1 µm versus 20 µm for a CO2 laser with the same ablation efficiency (energy density of at least 1 J/cm2 ), but with minimal thermal damage.
Tissue dehydration after several pulses and the accompanying “ablation plateau” do not come. For complete vaporization of the epidermis at a radiation energy density of 7-9 J/cm2, 2-3 passes of the Er:YAG laser are required, and the thickness of the zone of concomitant residual thermal damage, as a rule, does not exceed 50 µm.
Determination of the ablation depth is carried out by multiplying the number of passes by the thickness of the tissue layer removed in one pass (determined by the radiation energy density). Due to the extremely strong absorption of radiation, even a slight increase in the energy density on the skin increases the depth of ablation in this place, which, at small spot sizes, leads to the creation of a deepening and unevenness of the surface.
It is recommended to wipe the plaque formed during the treatment from the remains of destroyed cells with a wet sponge, which ensures unhindered access of radiation to the untreated tissue. Strong knocking out of the smallest pieces of tissue requires the protection of the respiratory tract of the patient and medical staff.
The short-pulse Er:YAG laser is many times inferior to the CO2 laser in terms of the degree of collagen contraction.
It is recommended to completely remove the epidermis over the entire treatment area, and then assess the irregularities of the dermal layer. surface irregularities and wrinkles originate in this layer. 1-2 even passes are performed, removing 15-30 microns of tissue.
After treatment, the papillary dermis has a smooth, shiny surface, while ablation of the reticular dermis results in irregularities due to the sebaceous lobes becoming visible.
At this stage, irregularities in the dermis can also be removed with tissue grafting.
Unlike Er:YAG laser resurfacing, Er: YAG laser can often be performed using only local anesthesia, which is usually supplemented by internal sedation.
ErCr:YSGG and modulated Er:YAG lasers
Despite effective ablation with a short-pulsed Er:YAG laser (350 μs), its weak coagulation capabilities prevent stable hemostasis and significantly limit the depth of ablation, and the result of a small thermal damage to the dermis is a weak contraction of skin collagen, leading to a relatively low stability of the resurfacing results.
Currently, Er:YAG lasers with variable pulse duration (modulated) are most widely used: short pulses provide ablation, and long – blood coagulation and collagen contraction.
Another solution to this problem is the use of short-pulse lasers, whose radiation is absorbed by water (ie skin) weaker than Er:YAG lasers, but stronger than CO2.
For example, in recent years, the ErCr:YSGG laser has been actively gaining ground. The practice of its use indicates excellent hemostasis even at an ablation depth of 84 µm.
The thickness of the thermal damage zone at an energy density of 5 J/cm2 is 30-40 µm. Mean clinical improvement – 25-50%, and the duration of the re-epithelization period (3-5 days), erythema retention (up to 3 weeks) and edema also takes intermediate values between traditional Er:YAG and CO2 lasers.
The quality of wrinkle treatment of grade III and above also approaches that of CO2 laser treatment with significantly fewer side effects.
The modulated laser ablation mode can be used to accurately treat tissue and remove areas of residual thermal necrosis, remaining after the application of the coagulation mode or CO2 laser, which, as a rule, improves the process of postoperative recovery.
- no capillary bleeding (which plays a signal role when resurfacing with a conventional Er:YAG laser) and
- there is no skin discoloration (used in CO2 laser treatment).
- The only more or less reliable way to control is the knowledge of the dependence of the ablation depth on the laser parameters. For example, the epidermis of the eyelid skin (its thickness is approximately 60 µm) can be removed with 2 passes of a modulated Er:YAG laser at an energy density of 9 J/cm2. Since most of the complications are associated with the magnitude of non-specific thermal damage to the skin, then their greatest number is noted after treatment with a CO2 laser.
Short-pulse Er:YAG laser – opposite – causes a minimum number of side effects,
and coagulating erbium lasers occupy an intermediate position.
More or less pronounced edema, erythema and pruritus are considered normal in the postoperative period.
Erythema occurs to some degree in all patients and is a consequence of increased blood flow and angiogenesis that occurs during the healing of the dermis .
The severity of erythema is directly related to the depth of the ablation performed and the degree of residual thermal damage. Occurrence probability: Er:YAG laser – 25% (remains 1-4 weeks); CO2 – up to 50% (1-3 months); prolonged erythema – 20%.
Postoperative edema of varying degrees reaches a maximum on the 2nd-3rd day and persists for 5-7 days, it is recommended to apply ice packs.
Contact dermatitis may develop. In the absence of the mentioned signs, itching is well stopped by antihistamines.
Postoperative edema of varying degrees reaches a maximum on the 2nd-3rd day and persists for 5-7 days, it is recommended to apply ice packs.
Itching often occurs during wound healing, especially in the second postoperative week.
Itching may indicate an infection (particularly candidiasis) and is often accompanied by poor healing, erythema, and exudate.
Contact dermatitis may develop. In the absence of the mentioned signs, itching is well stopped by antihistamines.
Postoperative edema of varying degrees reaches a maximum on the 2nd-3rd day and persists for 5-7 days, it is recommended to apply ice packs.
Itching often occurs during wound healing, especially in the second postoperative week.
Itching may indicate an infection (particularly candidiasis) and is often accompanied by poor healing, erythema, and exudate.
Contact dermatitis may develop. In the absence of the mentioned signs, itching is well stopped by antihistamines.
Itching often occurs during the wound healing process, especially in the second postoperative week.
Itching may indicate an infection (particularly candidiasis) and is often accompanied by poor healing, erythema, and exudate.
Contact dermatitis may develop. In the absence of the mentioned signs, itching is well stopped by antihistamines.
Itching often occurs during the wound healing process, especially in the second postoperative week.
Itching may indicate an infection (particularly candidiasis) and is often accompanied by poor healing, erythema, and exudate.
Contact dermatitis may develop. In the absence of the mentioned signs, itching is well stopped by antihistamines.
Petechiae appear immediately after the completion of re-epithelialization, disappear on their own within a few weeks.
Reason – subepithelial bleeding of immature basement membrane and underdeveloped network of blood vessels, and therefore the skin is easily injured as a result of slight friction.
Er:YAG laser has a significant advantage (10-20% versus 30% after CO2 in patients with skin phototype III and 50-70% versus 100% in patients with phototype IV+). Therapy takes 2-4 months: the use of a sunscreen with a high protection factor and the exclusion of sun exposure, the use of hydroquinone and tretinoin. Pigment-inhibiting glucosamine, azelaic and kojic acids may be used.
The cause of true hypopigmentation – a decrease in the number of melanocytes in the dermis due to severe thermal damage during aggressive processing, as evidenced by the accompanying longer erythema, acne, milium and often – scarring areas.
Treatment includes treatment with ultraviolet light sources. With segmental hypopigmentation or pseudohypopigmentation, rejuvenation of the remaining part of the face is performed, reducing the contrast of spots.
Infection after laser resurfacing occurs in 8-10% of cases. Wet wound care techniques and the necrosis layer help create a favorable environment for Candida and bacteria to thrive.
The lack of an epidermal barrier makes it easier for infection to enter through the surface of the treated area. Bio-occlusive dressings also increase the chance of infection.
Symptoms of probable infection:
The absence of an epidermal barrier makes it easier for infection to enter through the surface of the treated area. Bio-occlusive dressings also increase the chance of infection.
Symptoms of probable infection:
The absence of an epidermal barrier makes it easier for infection to enter through the surface of the treated area. Bio-occlusive dressings also increase the chance of infection.
Symptoms of probable infection:
• sudden onset or long-lasting pain (50% of patients);
• burning (30% of patients) or severe itching on the 2nd-3rd day after surgery;
• expressed erymatous spots, yellow exudate, eschar, papules, pustules;
• Erosion formation on a wound that has already passed the stage of re-epithelialization.
In 80% of cases, the infection develops within one week. If it is suspected, it is necessary to carry out native smears and bacterial cultures, as well as cultures for yeast fungi and the herpes virus. Clinical manifestations of infection may be atypical due to the absence of epithelium and tissue edema, the presence of necrotic masses.
With candidiasis, fluconazole (400 mg) and the release of the wound surface from occlusion are recommended. Therapy for bacterial infections depends on the results of culture and the sensitivity of bacteria to antibiotics. The use of antibiotics for 1-2 weeks is good at eliminating postoperative bacterial infections.
Scarring is usually the result of excessively deep ablation or excessive thermal damage to the underlying tissues (especially true for CO2 laser).
Short pulsed Er:YAG laser rejuvenation usually results in a low percentage of scarring (up to 10%, most likely on the chest, lower eyelid and upper lip).
Other causes of scarring may be postoperative infection or multiple surgeries that have altered the anatomy of the treated area.
The increased risk of scarring of non-facial areas of the skin is associated with a relatively small number of adnexal structures of the skin, a small thickness of the dermis, increased tissue tone and its stretching during movement.
The first signs of scar formation are erythema and itching – it is recommended to take a culture for the presence of infection and topically apply high-potency corticosteroids 2-3 times a day.
If the problem area begins to thicken, it is recommended to inject corticosteroids into the scar (diprospan in various dilutions). It is also necessary to apply local silicone dressings.
If there is no effect of therapy, a monthly treatment with a vascular pulsed laser should be carried out.
Acne and sebaceous cysts (milium) often form after CO2 laser treatment due to heat trauma, which can lead to rupture of the sebaceous glands, anaplasia of the adnexal structures, and deviation of the sebaceous duct. Another reason may be Vaseline-based ointments.
Treatment is the same as traditional and includes antibiotic therapy, limiting the use of ointments under an occlusive dressing, prescribing tretinoin and alpha hydroxy acids.
Ectropion.
tension and exposure of the conjunctiva. It is usually observed in patients who have undergone a laser rejuvenation procedure after lower eyelid blepharoplasty or when the treatment of this area is too aggressive.
It is recommended to test the elasticity of the patient's skin before the rejuvenation procedure: if the edge of the eyelid moves easily, then during the operation it is necessary to prevent excessive tension on the eyelid. The radiation energy density in this place should not exceed 30% of the usual. The cheeks are treated to the periorbital area to observe the effect of tension in this area.
Synechia is formed when two adjacent areas of de-epithelialized skin touch each other inside the fold, forming an epithelial bridge over it. In the area of the lower eyelid, synechia is formed 1-2 weeks after the operation and looks like an unusual crease or pale line.
Treatment – surgical cutting of the epidermal bridge, followed by frequent smoothing to avoid recurrence.







Add a comment