Cholelithiasis is one of the most common pathologies in modern therapeutic and surgical practice. Cholecystectomy – surgery to remove the gallbladder, the second most common after appendectomy, is the most effective radical treatment for gallstone disease, and leads to a complete recovery of the patient. Modern surgery has found a way to perform a minimally invasive operation to remove the gallbladder – laparoscopic cholecystectomy. This operation was first performed in France in 1987 and has since been successfully performed by abdominal surgeons from different countries.
Contraindications for laparoscopic cholecystectomy
In fact, for any pathology of the gallbladder that leads to a violation of its function, laparoscopic cholecystectomy may be the best solution to the problem. However, there are some contraindications to this surgery, which are divided into absolute and relative.
Absolute contraindications for laparoscopic cholecystectomy:
- serious disorders of the blood coagulation system;
- severe portal hypertension;
- abdominal sepsis or peritonitis;
- acute cholangitis.
Relative contraindications for laparoscopic cholecystectomy:
- acute cholecystitis;
- coagulopathy;
- upper abdominal surgery prior to cholecystectomy;
- liver disease;
- acute pancreatitis;
- pregnancy.
How trocars are placed in laparoscopic cholecystectomy
Laparoscopic cholecystectomy is performed in several stages and begins, like any other laparoscopic operation, with the imposition of pneumoperitoneum – introduction of air into the abdominal cavity using a Veress needle to improve the visualization of the abdominal organs. Next, four trocars are inserted into the patient's abdominal cavity through small incisions:
- 10 mm. trocar through the umbilical port;
- 10 mm. trocar along the midline of the abdomen for a quarter of the distance between the xiphoid process and the umbilicus;
- 5 mm. trocar two fingers below the costal arch along the midclavicular line;
- 5 mm. trocar two fingers below the costal arch along the anterior axillary line.
Through the trocars, an optical system and surgical instruments are inserted into the patient's abdominal cavity, through which the surgical intervention is performed.
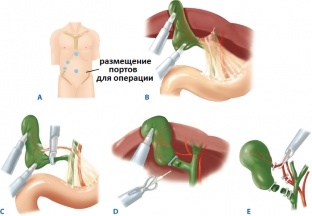
Method of removal of the gallbladder during laparoscopic cholecystectomy
The technique of laparoscopic cholecystectomy is quite simple, but has its own characteristics. Removal of the gallbladder is performed in the following sequence:
- the bottom of the gallbladder is grasped with an atraumatic forceps and the gallbladder is pulled up and towards the diaphragm;
- the second clamp grasps and pulls the neck of the gallbladder, creating tension on the cystic duct:
- the peritoneum is opened above the cystic duct with an electrocoagulator;
- the duct is allocated in a blunt way, brackets are superimposed on it, the duct intersects between them;
- the cystic artery is exposed, which is also clipped and transected;
- The isolated gallbladder is removed from the abdominal cavity. If necessary, crushing of large stones and aspiration of bile are preliminarily carried out;
- the pneumoperitoneum and trocars are removed, all incisions are sutured.
The main advantages of the laparoscopic method over the traditional one
Laparoscopic cholecystectomy is one of the few surgical techniques that has become very widely used in a short period of time. This was facilitated, of course, by the huge advantages of such an operation over the removal of the gallbladder in the traditional way. After laparoscopic cholecystectomy, most patients are discharged home within 24 hours after surgery. More than half of the operated patients do not require the appointment of narcotic analgesics in the postoperative period. Laparoscopic cholecystectomy guarantees a minimal chance of postoperative complications such as pain or infection of the wound. All these advantages confirm the fact that it is laparoscopic cholecystectomy that is currently the gold standard for the treatment of gallstone disease.<







Add a comment