Leukoplakia of the oral cavity in every tenth patient ends with cancer, while the disease in the early stages of development is very difficult to notice with an inattentive examination. However, if the oral mucosa is regularly examined by a specialist, dental care and treatment – carefully observed, and factors irritating the oral cavity will be excluded from the patient's life, then the prognosis will not worsen, and even oral leukoplakia that has already occurred may spontaneously disappear.
Causes of oral leukoplakia
Leukoplakia is an increased keratinization of the oral mucosa in the damaged area. Oral leukoplakia initially looks like a lump in the cheeks, tongue, and corners of the mouth, causing slight itching and burning, a feeling of tightness.
The main reason for the development of oral leukoplakia is constant irritation by external factors of the oral mucosa. These external factors are:
- smoking products,
- strong alcoholic drinks,
- abuse of spicy dishes, seasonings and spices,
- too hot or too cold food,
- taking medications (in large quantities and different pharmacological groups);
- sharp edges of teeth, fillings, crowns, dentures.
Researchers suggest a significant role in the development of oral papillomavirus leukoplakia. Provoking factors are such diseases as diabetes mellitus, iron deficiency anemia, diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, lack of vitamins in the body, especially group B.
Main symptoms of oral leukoplakia
The first symptom to pay attention to is the appearance of whitish spots 2-4 cm in size on the mucous membrane of the mouth. Their number and location can be different, usually the spots do not rise and are almost invisible if the examination is carried out inattentively.
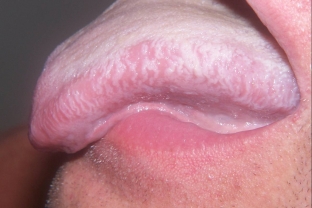
Sometimes the lesions are slightly raised above the mucous membrane, have an irregular shape with scalloped edges and uneven corners. Often patients complain that the surface of such spots is rough and covered with small sores. Plaques of leukoplakia of the oral cavity gradually thicken and coarsen, although they do not cause pain. Only when hot and cold food gets into the mouth, patients complain of sharp pain.
The symptoms of leukoplakia develop from 2 weeks to a month and never disappear again, but may become more acute or subside for a while. Over time, the area covered by the mucous membranes of leukoplakia increases. If the plaques turn brown, thicken, become covered with cracks and sores – it is regarded as a pre-cancerous condition with serious prospects of becoming oral cancer.
Diagnosis and treatment of oral leukoplakia
The physician must remember that early diagnosis of oral leukoplakia will prevent malignancy. Diagnosis is based on visual examination, but can only be confirmed with a biopsy.
Treatment of oral leukoplakia should begin, first of all, with the elimination of the element irritating the mucous membrane – dental treatment, restoration of prostheses, changing the diet, giving up bad habits. If leukoplakia has arisen due to an internal disease, it is recommended to use cryodestruction of the affected area of the oral mucosa. The patient is subject to constant dispensary registration and monitoring of the state of the oral cavity.







Add a comment