Skin and soft tissue infections (SSTI), which are now interpreted in foreign literature as acute bacterial infections of the skin and skin structures, are a frequent pathology in clinical practice and in most cases require the use of antibiotics. The microbial spectrum of causative agents of skin infections is characterized by an increase in resistance to existing antibacterial drugs.
Find out in the article on estet-portal.com which pathogens are most oftenthe cause of severe infectious lesions of the skin and soft tissues.
- skin infections: complexities of treatment
- causes of skin and soft tissue infections
- microbial flora in infections of the skin and soft tissues
Treatment of patients with
skin and soft tissue infections is additionally complicated by the presence of a number of factors that lead to severe complications and intoxication of the body (old age, obesity, diabetes and other severe concomitant diseases).
Subscribe to our page on Facebook!
Infections of the skin and soft tissues due to microbial invasionlead to inflammation of the epidermis, dermis and subcutaneous tissue with signs in various combinations of local hyperthermia, redness, swelling and pain.
Read also: Skin lesions in systemic lupus erythematosus
The skin isthe largest organ of the body and, together with the subcutaneous soft tissues, which include layers of adipose tissue, fascia and muscle, constitutes the bulk of the tissues in the human body. Typically, the skin is colonized by endogenous flora and is represented by various species of staphylococci, corynebacteria, propionibacteria and yeasts in numbers that can vary from a few hundred to several thousand per square centimeter in certain areas, such as the axilla, inguinal and perineum.
This skin flora can act as a competitive inhibitor of pathogenic microbes.From a clinical point of view, it is important to distinguish between those colonizations that do not require Causes of skin and soft tissue infections
Read also: Beware of the fungus! How and why does dermatophytosis infection occur? Skin defects, such as ulcers, burns, surgical wounds or wounds resulting from trauma, cause colonization with a wide range of bacteria. In a number of cases of the above skin defects, these bacterial colonizations do not lead to inflammation, but sometimes, under certain circumstances, the infection can progress and become a source of proper colonization from the surrounding tissues.
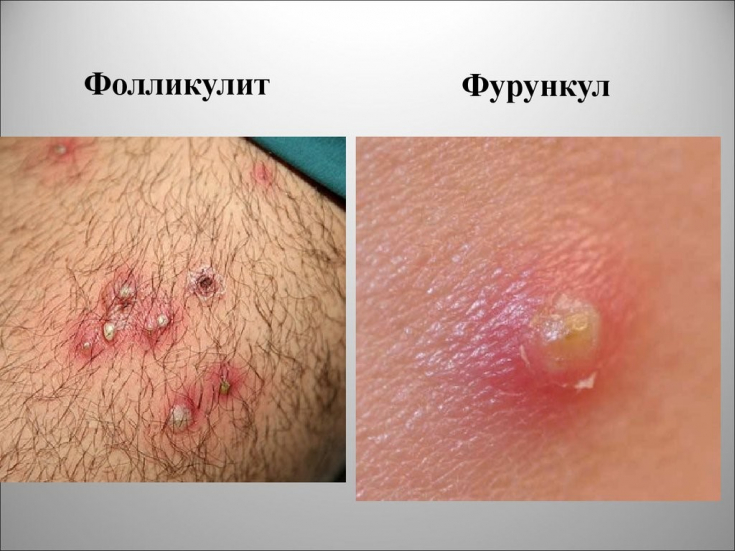
in the presence of allergies, medicinal and microbial dermatitis, re-infection of wounds with hospital highly resistant strains (S. aureus, S. pyogenes, Enterococcus spp., P. aeruginosa,
Microbial flora in skin and soft tissue infections Usually skin and soft tissue infections are caused by several microbes at the same time, but in most cases the causative agent is Staphylococcus aureus (S. aureus). Of particular danger is the widespread strains that are resistant to most antimicrobial drugs: beta-lactam antibiotics, aminoglycosides, lincosamides, fluoroquinolones. So,
S. aureus occupies a leading position in the inflammatory process as uncomplicated and complicated infections of the skin and soft tissues.
An increase in infections caused by resistant strains, predominantly methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA), 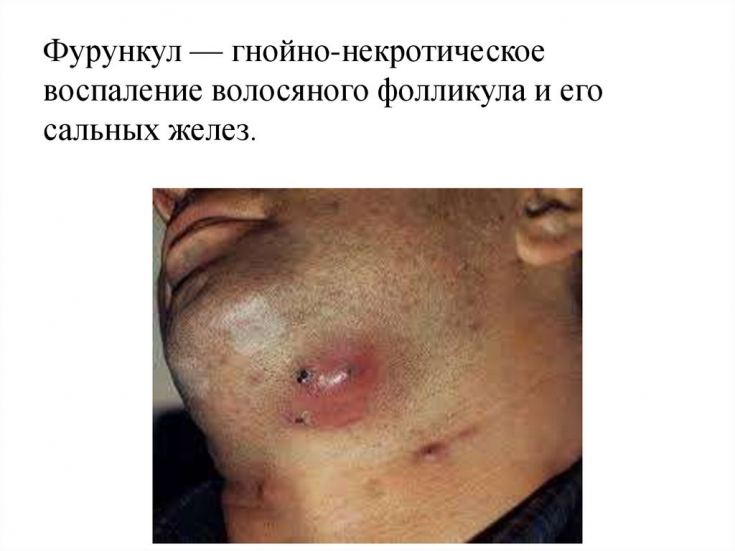 is associated with a significant increase in morbidity, mortality
is associated with a significant increase in morbidity, mortality
Erythrasma: is the disease contagious and is it possible to get rid of it
In addition, Gram-negative bacteria of the Enterobacteriaceae (
Klebsiella spp., Enterobacter spp., E . coli), which are usually resistant to beta-lactams. Knowledge of the current epidemiology and microbiological spectrum in skin and soft tissue infections are key to selecting appropriate antibiotic therapy (ABT) and optimizing treatment. When choosing antibacterial therapy, an approach is extremely important, which is determined by the level of skin and soft tissue lesions, the characteristics of the course of the disease and the presence of the phenomenon of resistance. More useful information on our
YouTube channel:







Add a comment