Today, statistics do not mention epidemics of syphilis, as well as other venereal diseases, but this does not mean that the diseases have disappeared. Previously, cases of such diseases were recorded more carefully, but now a significant number of patients receive outpatient treatment with simplified methods, visit doctors they know, and self-medicate, which does not allow for adequate statistics. Nevertheless, dermatovenerologists note that cases of syphilis, especially secondary, asymptomatic ones, have not decreased, and its signs often resemble other diseases, creating difficulties in diagnosis.
The structure of the incidence of syphilis has changed in recent years: there are more cases of latent syphilis, patients with neurosyphilis are constantly being detected (by the way, early neurosyphilis is not recorded in statistics). The symptoms of syphilis are varied, and there are numerous cases of latent, asymptomatic course of the disease.
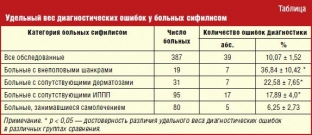
Identification of patients occurs both when they actively seek medical attention for symptoms of the disease, and during preventive serological examination in situations such as stay in a somatic hospital, pregnancy, abortion, childbirth, preparation for surgical interventions, or examination at the place of work . It has long been figuratively noticed that syphilis copies the symptoms of many other diseases. Therefore, it is quite understandable that patients with syphilis conduct a “pre-diagnostic” examination much more often with doctors of any other specialties than with dermatovenereologists.
The detection of syphilis is our common problem, it affects every doctor, nurse and midwife. At the same time, it is not only about the health of the patient, but often about protecting the health of medical workers.
What specialists and in what typical cases should suspect syphilis in their patient?
Let us recall that syphilis is transmitted in the vast majority of cases through sexual contact, but the infection can also be transmitted through blood transfusion from a sick donor, through the placenta from a sick mother to a child, as well as through close household contacts (sharing bedding, hygiene items, etc.) .d.) with patients who have contagious manifestations of the disease on the skin and mucous membranes.
The incubation period of the disease lasts 3-4 weeks, taking treponemicidal antibiotics (penicillins, tetracyclines, macrolides, cephalosporins) for intercurrent diseases can prolong the incubation period up to 2-3 months. The Wasserman reaction in a patient in the incubation period is negative. From the 3-4th week, the immunofluorescence reaction (RIF) and ELISA (enzymatic immunoassay) may become positive. Infection with syphilis from a person who is in the incubation period is possible only through blood.
Primary syphilis
At the end of the incubation period, a hard chancre appears at the site of infection - this is the beginning of the primary period of the disease. A chancre can be a superficial defect on the skin or mucous membrane (erosion) or deeper (ulcer), and it is not necessarily single - multiple is possible. The most characteristic feature of the chancre is a dense, cartilage-like consistency infiltrate at its base, which gave reason to call the chancre hard. A week after the appearance of the chancre, nearby (regional) lymph nodes increase and thicken. Sometimes the diseased people notice enlarged lymph nodes earlier than the chancre, and with this they go to the doctor. Chancre and regional lymphadenitis are signs of the first stage of syphilis, which lasts as long as they exist (6-7 weeks).
In most cases, chancres are located in the genital area, while the inguinal lymph nodes increase. Patients who have an idea about venereal diseases treat such manifestations most often at the address - in the dermatovenerological dispensary, and the diagnosis is usually successful. However, uninformed people go to the surgeon and show only enlarged lymph nodes. I do not recall a case in which a surgeon in this situation took the risk of examining the patient's genitals, asked the patient to expose the head of the penis, examined the inner leaf of the foreskin, or (quite “blasphemously”) examined the external genitalia of women. The surgeon examines only the place corresponding to his competence - the lymph node - and makes a diagnosis: “banal lymphadenitis” or “lymphadenitis of unclear etiology”. He prescribes an antibiotic often (unintentionally) treponemocidal, which leads to a partial or complete regression of the clinical manifestations of syphilis and translates it into a latent stage, which, as you know, is already more difficult to cure. And sometimes he operates - removes the lymph node. Until now, one has to meet with linear scars in the inguinal region in patients with syphilis after the removal of lymph nodes.
The situation is even worse when not the inguinal, but the cervical and submandibular lymph nodes are enlarged. Often this happens in young girls who become infected with syphilis during oral sex. Teenage girls often begin their sexual contacts with him with an underlying thought of maintaining physiological virginity and avoiding pregnancy. With this route of infection, the chancre is located on the oral mucosa, more often in the tonsils, and may resemble lacunar tonsillitis (ulcerative chancre) or exacerbation of chronic tonsillitis (atypical non-ulcerative chancre - amygdalitis, with a sharp increase in the tonsils). A girl can get an appointment not only with a surgeon, but even more often with a therapist, and sometimes with a hematologist, otolaryngologist. If you do not keep in mind the possibility of syphilis and do not take blood for serological tests, syphilis in the first stage remains undetected and, possibly, its course will be perverted by inappropriate use of antibiotics. So, if you have a young girl at your appointment, whom you will not dare to ask a question about oral sex, do not ask anything and refer the patient to donate blood for RV.
Another stumbling block in primary syphilis is an atypical chancre in women in the form of indurated edema resembling bartholinitis, without ulceration, but with a significant increase in one of the labia and a sharp change in its color to purple-bluish. I know cases when gynecologists, without examining for syphilis, prescribed antibiotics, opened an “abscess” and, having not received pus, opened it again. Rule out syphilis! Quickly, promptly, because in this situation time does not endure. Run a precipitation microreaction with blood from a finger and you will get an answer in 20 minutes.
Another type of hard chancre that makes you think about surgical treatment is the anal chancre in homosexual men. Recently, the proportion of men infected through homosexuality has increased (up to 10-15%). Anal chancre is extremely similar to a crack: it is located deep in the anal fold, has a “rocket-shaped”, elongated outline, its base is not infiltrated, and regional lymph nodes located in the pelvic cavity are not visible. Unlike chancres of other localizations, anal is painful. It's easy to make a mistake. I have seen patients undergoing surgery, in whom the results of seroreactions were considered only after the operation. In addition, infection of the operating surgeon is possible, especially if he does not think about the danger.
subjected to surgery, in which the results of seroreactions were considered only after the operation. In addition, infection of the operating surgeon is possible, especially if he does not think about the danger.
Secondary syphilis
There is even more confusion with the diagnosis of secondary syphilis, or the second stage of syphilis, because it is much more diverse and multifaceted in terms of symptoms. As a rule, the chancre has not yet had time to heal, and the lymph nodes are still enlarged when the infection generalizes. Hematogenous seeding with treponemes leads to a profuse rash on the skin.
The duration of the existence of the first generalized rash in an untreated patient is about 1.5–2 months. The rash is located more often on the chest, abdomen and lateral surfaces of the body. Sometimes it is so abundant that it covers the back, and the limbs, and even the face, where its appearance is a rarity. The rash is bright, medium-sized, the elements do not merge with each other. Itching and peeling are absent. The state of health suffers a little, although sometimes the temperature may rise. The rash is most often spotty, elements of pink color, do not rise above the surrounding skin and disappear with pressure. It is good if the occurrence of such a rash leads the patient to a dermatovenereologist.
More often this is dealt with by a local doctor, whose thought can have two directions: a childhood infection (measles, rubella) or an allergy. In the first case, an infectious disease specialist is called, who, as a rule, confirms the diagnosis: after all, most of today's young people did not get measles (rubella) in childhood; the more severe the current infection is expected.
The infectiologist is alert only after 2-3 weeks, when the rash, instead of disappearing, continues to bloom. The life experience of some infectious disease specialists is enough to prescribe a blood test for seroreaction. Others do not, and "measles" remains "measles" and syphilis is detected at some later stage, when the prognosis for a cure is no longer so optimistic. In the case of establishing an "allergy", much depends on the perseverance and awareness of the patient himself.
However, the rash of the secondary fresh period is not always patchy: it can be nodular, and this usually leads the patient to a dermatologist and then a venereologist. A small pustular rash with its papulo-crusts with a large abundance of eruptive elements successfully imitates chickenpox. The patient is without treatment until the absence of regression of the rash in all conceivable terms for chickenpox does not arouse the alarm of the treating infectious disease specialist. And sometimes the patient simply stops coming, the rash eventually resolves, and syphilis goes into a latent stage.
In patients with alcoholism and drug addiction, manifestations of secondary syphilis are often malignant: multiple ulcers covered with purulent crusts form on the skin of the face and trunk. The disease resembles a severe form of pyoderma.
Manifestations of secondary syphilis during relapses of rashes are very diverse, they are usually local, i.e. located on separate areas of the skin and mucous membranes. Rashes on the oral mucosa are usually forced to consult a dentist. It can be whitish oval papules on the tonsils or on the buccal mucosa, dark pink, slightly raised rounded papules on the mucosa of the hard and soft palate, on the mucosa of the lips. In the corners of the mouth, papular elements are often formed, covered with crusts, and then cracks - seizures. The original picture may be the back of the tongue, on which oval areas of bright red color, devoid of papillae, are visible - these are papules of the tongue, and the picture is called “a symptom of a mowed meadow”. All oral manifestations are highly contagious,
One of the most typical, almost pathognomonic manifestations of secondary syphilis is papules on the palms and soles. They are located on the arches of the feet and in the center of the palms. Usually these are towering formations of a dark red or bluish-red color, sometimes with scales along the periphery. A doctor of any specialty, noticing such manifestations, should examine the patient for syphilis.No less typical are the characteristic changes in skin pigmentation and hair lesions in secondary syphilis, which are more common in women. On the posterolateral surfaces of the neck, small oval specks of hypopigmentation appear against the background of slightly hyperpigmented surrounding skin. There are several spots, and there may be many. This painting was called the “necklace of Venus”, and its medical name is syphilitic leukoderma. The pattern of leukoderma is compared to lace or to the play of sunlight breaking through the foliage.
Syphilitic alopecia can be diffuse - hair falls out over the entire head, and sometimes they are lost quickly ("in the morning they remained lying on the pillow"), and sometimes slowly - within 1-1.5 months. By the end of this period, the remains of thinned hair are no longer able to cover the skin. With small-focal baldness, the scalp looks like “fur beaten by moths”. Eyebrows and eyelashes also fall out. Regarding hair loss, women tend to turn to cosmetologists. Until now, there are cases when in cosmetology institutions they are treated for this reason without examining the blood for seroreaction.
Here it is appropriate to dwell on the possibility of professional infection of medical personnel from an untreated patient with syphilis. This can happen during surgery if the surgeon's hands are injured and the patient's blood gets into the wound. Cases of infection of pathologists with hand injuries during autopsy are described. It is possible to infect a dentist who has microtraumas on his hands by contact with infectious manifestations of syphilis on the oral mucosa and with the patient's blood. A dentist can become infected not only through direct contact with infectious manifestations (ulcers, erosions, erosive papules), but also through tools and a drill handle that come into contact with similar manifestations located on the lips, on the mucous membrane or in the corner of the mouth. gynecologists and midwives during childbirth from an unexamined woman, a patient with a contagious form of syphilis. The blood and secretions of such a woman are contagious, as well as the blood and discharge of erosive elements, if the child has them. If the possibility of such occupational infection has taken place, you should consult a venereologist about the degree of danger and, on his recommendation, carry out preventive treatment with durant penicillin preparations.
In conclusion, I would like to remind doctors of all specialties once again: a patient with syphilis may knock on any of you tomorrow. Consider this as good luck, because the patient is curable. And the first thing to do is a blood test for the Wasserman reaction.
According to www.rmj.ru






Add a comment