Genital herpes − a common sexually transmitted disease characterized by lifelong persistence of the herpes simplex virus (HSV) with periodic reactivation.
Herpes simplex virus − A DNA-containing virus, which, depending on the composition of the protein shell, is divided into HSV-1 and HSV-2.
Herpes simplex virus 1 causes lesions predominantly in the oral cavity, and lesions in the genitals, until recently, mainly caused HSV-2.
However, in the US, HSV-1 now causes primary genital infection at the same frequency as HSV-2, or even more often.
Learn in the article on estet-portal.com about modern approaches to the treatment and diagnosis of diseases caused by the herpes simplex virus.
- Mechanism of infection with herpes simplex virus
- Clinical manifestations of herpes simplex virus infection
- Approaches to the diagnosis and treatment of herpes simplex virusa
Mechanism of infection with herpes simplex virus
Primary infection with herpes simplex virus results from contact between an uninfected person and a patient who actively sheds the virus through skin or secretions.
Follow us on Instagram!
Possible prodromal period lasting from several hours to several days, which is manifested by pain, tingling, itching or burning in the area of contact with the infected surface.
During an outbreak that lasts approximately 2 weeks, damage to the epithelium at the site of the infection portal results in vesicles that burst and form ulcers, then re-epithelialization.
What threatens a latent herpetic infection
During the primary infection, viral DNA travels along the axons to sensitive ganglia of the spinal cord, where it remains for life.
During reactivation, the herpes simplex virus travels in the opposite direction through the axons and their processes or through the axons of the opposite side of the body to the skin and mucous membranesam.
Clinical manifestations of herpes simplex infection
An outbreak is characterized by single or clustered blisters on the genitals, perineum, buttocks, upper thighs, or perianal areas that turn into ulcers before healing.
may be accompanied by malaise, fever, or localized lymphadenopathy.
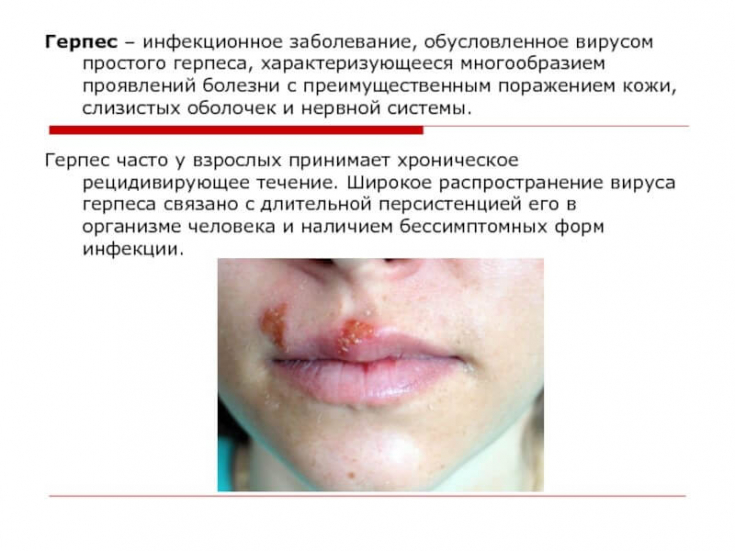
The classic clinical presentation of herpes simplex virus, whether it is a primary infection or a secondary outbreak, is absent in most cases, with many patients complaining of
minimal symptomsor e not at all. Research data show that 65-90% of patients with genital herpes are unaware of the infection at all.
Approaches to the diagnosis and treatment of herpes simplex virus
Although herpes − this is the most common disease that leads to the appearance of ulcers on the genitals, one should not forget
about the possible polyetiology of this pathology. Because HSV-1 and HSV-2 infections cannot be visually differentiated, the type of virus can only be determined by
laboratory testing. If there are active elements of the rash, preference is given to
PCR, the sensitivity and specificity of which exceed 95%.
Effective prevention of herpes zoster It takes 2 weeks to 6 months from exposure to the herpes simplex virus to the formation of antibodies, so a repeat examination may be required to confirm a recent infection.
When the likelihood of infection is low,
false positive test results. It is not clear how to interpret patients
with positive serological testsand negative history of herpes simplex symptoms, so the American Organization for Disease Prevention and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention do not recommend serological screening for herpes simplex.
Virus-specific serological testsshould be offered to partners of patients with herpes simplex virus to determine the risk of infection.

Using serological tests, you can confirm the presence of infection and determine the type of virus.
Because the herpes simplex virus 2 is almost always sexually transmitted, the presence of antibodies against it indicates the presence of
anogenital disease, even if there is no history of symptoms. However, localization of HSV-1 cannot be determined solely on the basis of a positive HSV-1 serological test result.
Ganciclovir in the treatment of cytomegalovirus infection
reducing the severity of the disease;
duration of relapses;- prevention of transmission of infection to uninfected partners.
- Suppressive therapy may be intermittent or continuous. Three nucleoside analogues that inhibit viral DNA, −
- aciclovir ,
and valaciclovir have long been used in medical practice and are well tolerated. The treatment regimen is the same for HSV-1 and HSV-2. Nucleoside analogs
are equally effectivein treating first and subsequent episodes of herpes simplex infection in reducing the frequency and severity of recurrence and slowing down the spread of the virus.






