Public awareness of the health issues associated with obesity, coupled with popular fitness trends, has led to a demand for effective, safe, minimally invasive, affordable fat reduction products. deposits and body shaping.
Many studies have shown that liposuction is very effective, however, it comes with a relatively high risk of complications and side effects.
It is therefore not surprising that the demand for non-invasive procedures to reduce body fat has grown by more than 500% since 1997. Read more about non-surgical methods of fat removal at estet-portal.com in this article.
- The main types of non-surgical fat reduction
- Who needs non-invasive fat reduction
- Basic non-surgical methods of fat removal
- Complications and side effectss
The main types of non-surgical fat reduction
Non-invasive methods to reduce body fat are often divided into:
- ablative (cooling, heating, destruction or dissolution of adipocytes);
- non-ablative (lipolytic stimulation or ultrastructural modification).
Ablative techniques aim to cause adipocytes to undergo apoptosis or necrosis.
The most commonly used non-invasive methods for fat reduction include:
- cryolipolysis;
- Low Level Laser Therapy (LLLT);
- radio frequency therapy (RF);
- High Intensity Focused Ultrasound (HIFU);
- injectable lipog.
Injectable lipolysis: what the doctor should remember
Who needs non-invasive fat reduction
In general, there are three types of patients undergoing fat reduction and body contouring procedures:
- Patients who simply want to eliminate fat deposits in problem areas such as the abdomen and thighs.
- Patients who want to achieve a skin lift, such as those with sagging skin in the neck or arms.
- Patients who require both fat removal and skin lifting.
Non-surgical methods of fat reduction are most suitable for non-obese patients (body mass index less than 30) who seek moderate localized fat reduction.
BMI over 30 patients often have visceral fat, which increases the risk of cardiovascular and other diseases. These patients initially benefit much more from overall weight loss followed by tightening of sagging skin.
When selecting patients, it is important to carefully discuss their motivation to reduce body fat, as well as social and psychological well-being during the consultationand.
Read the most interesting articles in Telegram!
Basic non-surgical methods of removing fat deposits
- Cryolipolysis
Cryolipolysis is becoming more and more popular.
The essence of the procedure is controlled cooling, causing adipocyte apoptosis.
Cryolipolysis devices typically contain a cup-shaped applicator that is applied to the area of concern causing tissue to be drawn into the handpiece under vacuum.
Each area is treated for approximately 45 minutes and then massaged.
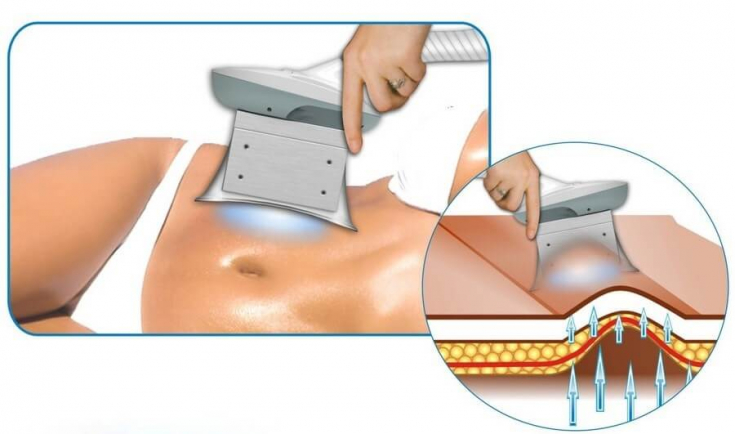
The first results of cryolipolysis are usually visible within three days after treatment, and the full effect – in three to four weeks.
Cryolipolysis treatments should be done at eight week intervals to allow sufficient recovery time between treatments.
- High Intensity Focused Ultrasound
This technique uses high frequency focused ultrasound energy to raise the temperature around the fatty tissue and cause coagulative necrosis.
The procedure typically involves placing the HIFU device two or three times in the treatment area, each time for 15 to 20 minutes.
A clinical response is usually seen within two weeks, with final results visible after 3 months.
A study by Jewell et al. confirms an average reduction in waist circumference of 4.2 to 4.7 cm 12 weeks after the HIFU procedure.
Ultrasonic liposuction (lipolysis) – non-surgical method of getting rid of fat
- Radiofrequency Lipolysis
Radio frequency causes thermal damage of targeted tissue layers using electrical energy.
Radio frequency devices have traditionally been used for skin tightening, but today they are also used for fat reduction.
Fat volume reduction is usually seen three to eight weeks after treatment, with a reduction in waist circumference of up to 3 cm after 10 treatments.
The main problem of this technique – selection method of pain relief as local anesthetics are not recommended during radiofrequency lipolysis as they can increase pain and interfere with radiofrequency waves.
- Low Level Laser Therapy (LLLT)
LLLT uses non-thermal adipocyte ablation to correct focal adiposity and tighten the skin.
It takes up to three weeks to see final results.
A trial by Jackson et al. showed a 2.6 cm reduction in waist circumference after LLLT over a two-week treatment period.
- Injectable lipolysis
Injection lipolysis is used to eliminate local fat deposits in the face, abdomen, arms, thighs and sides.
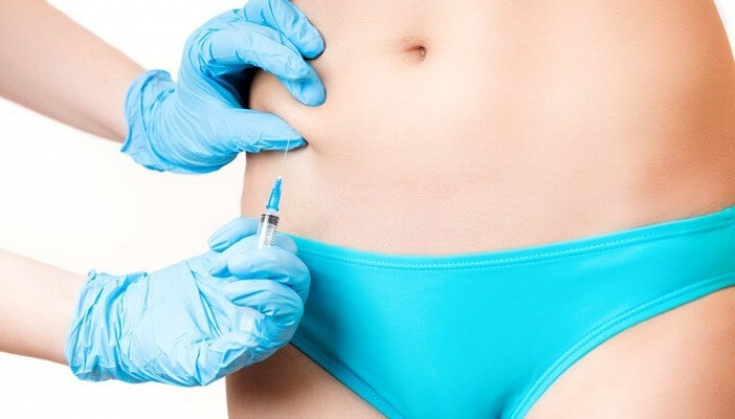
A local anesthetic is applied prior to the procedure, followed by lipolytic phosphatidylcholine with deoxycholic acid.
Three to 15 treatments are usually required, with optimal effects seen after four to six weeks.
The addition of deoxycholic acid causes destruction of fat cells. This aims to prevent the re-filling of fat cells and reduce the number of treatments requiredp.
Complications and side effects
Non-invasive fat reduction methods are generally very safe and most patients report only mild and transitory side effects.
The most common side effects are:
- slight discomfort;
- erythema;
- edema.
Paradoxical fatty hyperplasia is a rare complication of cryolipolysis, usually occurring two months after treatment with an incidence of 1 in 20,000 treated patients.
Rare adverse events after radiofrequencyfat removal include:
- scars;
- burns;
- purpura;
- edema;
- hyperpigmentation;
- blisters.
It is generally considered that low-level laser therapy causes the fewest complications.







Add a comment