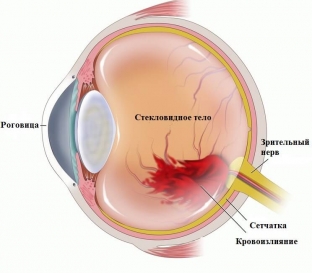
Among hemorrhages in the eye area, hemophthalmus is considered especially dangerous. Most often, it develops as a result of severe injuries or penetrating wounds of the eye, when, due to damage to the blood vessels, blood enters the vitreous body. Partial hemophthalmos also occurs when the hemorrhage is caused by some internal disease, due to which the integrity of the capillaries is violated, as well as after surgery on the eyeball or as a result of retinal detachment. In any case, the patient needs immediate medical attention to prevent vision loss.
What happens with hemophthalmia and why it threatens with loss of vision
Distinguish hemophthalmia total – when vitreous hemorrhage takes more than ¾ its volume, subtotal – when the vitreous body is affected by about half, and partial – when the hemorrhage occupies less than 1/3 of its volume.
When bleeding from damaged vessels, erythrocytes enter the vitreous body. After a few days, these blood cells begin to break down, and as a result of this process, hemoglobin grains settle in the vitreous body, which transforms into hemosiderin and begins to destroy the retina. In addition, under the action of hemosiderin, dense strands begin to form, attaching to the retina, due to these strands, its detachment may later begin.
With hemophthalmia, the patient usually presents the following complaints at the doctor's appointment:
- fog before the eyes, sensation of moving shadows in the field of view (due to the movement of blood clots);
- decrease in visual acuity, sometimes sudden, and distortion of the level of perception of light;
- appearance of moving opacities of red or black color;
- the impression of flashing lights.
Usually, with hemophthalmia, the patient sees better in the morning, because during the period of night sleep, the blood has time to settle to the bottom of the eyeball.
At the appointment, the patient should be asked in detail when the alarming symptoms appeared and in connection with what. It should be remembered that the cause of hemophthalmia can be diabetic retinopathy, arterial hypertension, high myopia with retinal tears, macular degeneration, systemic lupus erythematosus, a number of diseases associated with vascular occlusion (vasculitis), microaneurysms of the retinal arteries, some neoplasms.
How to treat hemophthalmos and is it possible to prevent it
If the hemophthalmia has developed recently, the patient needs bed rest with a cold bandage over the eyes for two to three hours. To prevent the development of new bleeding, calcium preparations are prescribed orally and in the form of eye drops, vitamin B2, rutin. Then after a day or two it is recommended to start taking & nbsp; absorbable drugs, corticosteroids – to prevent the formation of strands, injections of collazilin – to prevent the formation of collagen ligaments, as well as anticoagulants – to prevent blood clotting. Showing ultrasonic, laser procedures.
If within ten days the drug treatment does not show the desired effect, a surgical operation is prescribed to remove blood from the eye cavity. With partial hemorrhage, the prognosis of the disease is usually favorable, with total and subtotal - the threat of loss of vision is significant.
As a preventive measure against hemophthalmia, it is recommended to observe safety measures for the eyes, treat diseases that can provoke hemorrhages in the eye area in a timely manner and categorically not allow self-treatment, since only early qualified medical assistance can prevent vision loss.







Add a comment