The human body – it is a complex mechanism that is thought out to the smallest detail. The work of all systems in it is connected with each other, each body has its own "assistants" - special structures that help it perform its function, and the pathology of any of them necessarily affects the work of the whole organism. The kidneys are one of the most important organs in the human body. This paired organ is surrounded by a fibrous capsule and perirenal tissue. In response to inflammatory processes in the renal parenchyma, a pathology of the renal capsule, which is called perinephritis, may develop.
Clinical picture and methods of treatment of perinephritis
Perinephritis, in most cases, is a secondary disease that occurs against the background of pyelonephritis, pyonephrosis, carbuncle or kidney abscess. The pathological process can be unilateral or bilateral. There are two forms of perinephritis: exudative and productive. In the first case, exudate accumulates between the fibrous capsule and the renal parenchyma, which can suppurate. With productive perinephritis, a thickening of the fibrous capsule occurs, which shrinks and causes atrophy of the renal glomeruli and nephron tubules. In any case, the disease can be extremely dangerous for the patient.
Perinephritis:
- clinical picture of perinephritis: characteristic symptoms;
- laboratory and instrumental methods for diagnosing perinephritis;
- conservative and surgical methods for the treatment of perinephritis.
Clinical picture of perinephritis: characteristic symptoms
The clinical picture of perinephritis depends on which form of the disease is diagnosed in the patient. Exudative perinephritis is characterized by the following symptoms:
- general weakness of the body;
- febrile body temperature and chills;
- nausea and lack of appetite;
- tension of the muscles of the abdominal wall during palpation of the kidneys;
- positive Pasternatsky's symptom.
Productive perinephritis begins gradually and is characterized by the following symptoms:
- dull constant pain in the lumbar region;
- sometimes septic fever and chills;
- palpation of the kidney is painful, has a smooth surface;
- Pasternatsky's symptom is positive.
Laboratory and instrumental methods for diagnosing perinephritis
Diagnosis of perinephritis is based on a comparison of patient complaints, symptoms of the disease, as well as data from laboratory and instrumental research methods. The composition of urine in this pathology does not change, pathological elements are not determined. In the blood, leukocytosis, an increase in ESR and anemia are noted. On survey radiographs, the shadow of the lumbar muscle is not determined, the kidney is sometimes clearly contoured. On excretory urograms, there is a decrease in respiratory excursions at the height of inhalation and exhalation, as well as an orthostatic displacement of the kidney. Kidney function with perinephritis is also reduced. Differential diagnosis of the disease is carried out, first of all, with paranephritis.
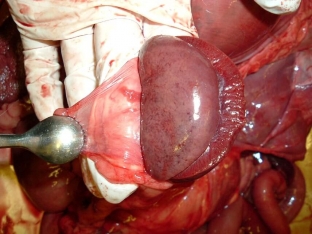
Conservative and surgical treatment of perinephritis
The choice of treatment for perinephritis depends on the form of the disease. With exudative perinephritis, surgery is performed – decapsulation, dissection and drainage of abscesses, as well as nephrostomy in violation of the outflow of urine. Conservative therapy is possible with productive perinephritis and involves the appointment of intensive anti-inflammatory therapy. If non-negotiable changes are found in the kidney – perform a nephrectomy. The prognosis of the disease depends on how timely treatment was started. In acute perinephritis, the prognosis is improved by the operation performed as early as possible, and the chronic process has a long and persistent course. Timely treatment of purulent-inflammatory processes in the kidneys helps prevent the development of perinephritis.







Add a comment