Injuries to the nose and paranasal sinuses are among the most common injuries of the whole body. Since the nose in the literal sense of the word is an outstanding part of the face, its traumatization occurs quite often, and in people of completely different age categories. Otorhinolaryngologists and plastic surgeons are engaged in the treatment of nasal injuries, who must have the necessary information about all possible causes of trauma to the nose, the classification of such injuries, as well as symptoms of damage to the structures of the nose and paranasal sinuses, since the choice of medical tactics in the treatment of nasal injuries depends on this. It is this information that estet-portal.com wants to share.
Classification of nasal injuries depending on the nature of the damage
According to their origin, all injuries of the nose are divided into three main categories: domestic, military and injuries resulting from a seizure, for example, trauma to the nose during an epileptic seizure. Depending on the nature of the damage, two large categories of nasal injuries are distinguished:
- closed nasal injuries - in most cases, they occur in the form of abrasions, bruises or bruises in the soft tissues of the nose. Less common are closed nasal fractures, which may be combined with displacement of the bones of the nose;
- open nasal injuries - may or may not penetrate the nasal cavity, with a sharp object wound being the most common cause of such nasal injuries.
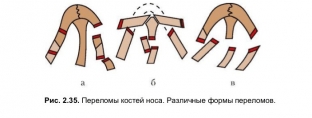
Types of nose deformities resulting from nasal trauma
For the choice of tactics for the treatment of nasal injuries, especially for determining surgical tactics, the classification of external injuries of the nose, compiled back in 1993, is of particular importance. According to this classification, the following types of nose deformities as a result of an injury are distinguished:
- rhinoscoliosis – nasal displacement to the side;
- Rhinokyphosis – the formation of a hump as a result of damage to the nose;
- rhinolordosis – formation of depression of the back of the nose;
- platyrinia – flattened nose;
- brachyrinia – a significant increase in the width of the nose after injury;
- leptorhynia – significant narrowing of the nose;
- mollerinia – as a result of injuries, the nose loses its support and becomes too soft.
What can happen as a result of a sinus injury
Injuries to the nasal sinuses are quite common, and depending on the nature of the damage, they can lead to the following conditions:
- injuries in the area of the frontal sinuses – lead to a fracture of the anterior wall of the sinuses, form not only a cosmetic defect, but also disrupt the patency, making it difficult for the outflow through the channels of the frontal sinuses;
- damage to the ethmoid bone – can provoke a rupture of the mucous membrane and the formation of subcutaneous emphysema on the face, in addition, the ethmoidal artery is often damaged, resulting in hemorrhage in the tissue of the orbit;
- maxillary sinus injuries – are manifested by deformities in this area, often combined with damage to nearby structures of the face with the development of characteristic symptoms;
- Injuries to the sphenoid bone are quite rare, due to its location deep in the base of the skull, most often manifested by damage to the optic nerves and serious bleeding.
Diagnosis of nasal injuries: instrumental methods and characteristic symptoms
Diagnosis of nasal injuries is not a difficult process, since already with an objective examination and collected, if possible, anamnesis, it is possible to determine the cause and nature of the damage. To clarify the prevalence of the process, instrumental research methods, such as computed tomography, MRI and X-ray examination, as well as the characteristic symptoms of damage to the nose and paranasal sinuses, help:
- step symptom – palpable bony protrusions on the back and slopes of the nose, indicating a fracture of the bones of the external nose;
- crepitation of bone fragments indicates a fracture of the ethmoid bone with a rupture of the mucous membrane;
- glasses symptom - hemorrhage around the orbit and eyelids, which indicates trauma to the facial skeleton, and is also a sign of a fracture of the base of the skull and sphenoid bone;
- double spot symptom – the formation of a light rim around a spot of blood escaping from the nose. This symptom indicates the leakage of cerebrospinal fluid along with blood through the nasal passages, which is typical for a fracture of the cribriform plate with a rupture of the dura mater.







Add a comment