Urinary incontinence – this is a widespread urological pathology that can affect people of completely different sex and age. In itself, urinary incontinence is not a disease, but one of the dysuric manifestations of the pathology of the urinary system of the body. This condition can disturb a person at any time of the day and manifest itself in completely different clinical forms. If a patient visits a urologist with a complaint of urinary incontinence – it is necessary to find out in detail the nature of his complaints, since in each individual case the specific features of the manifestation of urinary incontinence can be the best clue for the correct diagnosis of the disease of the urinary system. What you need to know about urinary incontinence – tells estet-portal.com.
Features of clinical manifestations of different forms of urinary incontinence
First of all, you need to understand the fine line between incontinence and incontinence. Urinary incontinence – this is a complete loss of the ability to retain urine, while it can be released uncontrollably when an urge to urinate occurs. If the patient complains of involuntary urination that occurs without a preliminary urge, regardless of the position of the body in space – we are talking about complete urinary incontinence. Urinary incontinence often occurs with congenital anomalies, trauma, as well as congenital and acquired neurogenic disorders. The clinical features of urinary incontinence can be very different: some patients report involuntary urination during physical exertion, some – in a dream or due to the inability to hold an imperative urge.
Incontinence:
- classification of urinary incontinence: what are the forms of pathology;
- why does urinary incontinence occur during exercise;
- bedwetting in children: pathology or norm.
Classification of urinary incontinence: what are the forms of pathology
For the correct diagnosis of a disease of the urinary system, it is necessary to find out during the survey, in what form urinary incontinence manifests itself in each individual patient. There are the following types of urinary incontinence:
- true urinary incontinence occurs when the anatomical integrity of the urinary tract is intact, with urine not being retained due to dysfunction of the bladder sphincter;
- false urinary incontinence is due to congenital or acquired defects of the urinary tract, such as exstrophy of the bladder, complete epispadias, ectopia of the urethral opening;
- daytime urinary incontinence often occurs during physical exertion, due to an increase in intra-abdominal pressure;
- Bedwetting is characterized by the involuntary release of urine during sleep.
Quite often, urinary incontinence occurs as a result of bladder injury, after which fistulas form, for example, vesicovaginal or urethral-vaginal.
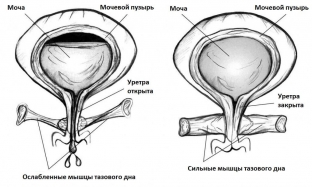
Why does urinary incontinence occur during exercise
Stress incontinence occurs during daytime, during exercise, coughing, sneezing or laughing, as a result of increased intra-abdominal pressure. Often this pathology occurs in women who have received a birth injury. Against the background of the injury, relaxation of the pelvic diaphragm, prolapse of the vaginal walls, prolapse of the uterus or the bottom of the bladder occurs, while incontinence is due to the weakening of the sphincter of the bladder as a result of its displacement. It is possible to diagnose such a pathology with the help of a correctly collected anamnesis, on the basis of which the doctor receives information about a previous birth injury, as well as with the help of urodynamic studies that help determine the state of the bladder sphincter. The treatment of stress urinary incontinence is to perform special exercises, helping to improve the tone of the sphincter. In severe cases, it is necessary to eliminate the pathological condition surgically.
Bedwetting in children: pathology or norm
Bedwetting is also called enuresis or nocturnal diuresis. A similar condition is observed most often in childhood in the absence of an organic pathology of the urinary or nervous systems of the body. During the day, the child moves, while his intra-abdominal pressure increases, which, in turn, increases the pressure in the bladder itself, as a result of which urine is reflexively retained. During sleep, when the child is at rest, urine can be released uncontrollably outside. In most cases, this urinary incontinence disappears even before puberty, but in some cases the problem persists, and it is necessary to study the condition of the child's body in more detail. Bedwetting can also occur with some serious urological conditions.







Add a comment