What is the actinomycosis disease, and what are the reasons for its development, we considered in a previous article on estet-portal.com. In addition to the causative agent and the mechanism of development of actinomycosis, it is important to know the typical symptoms of actinomycosis.
The clinical picture of actinomycosis is diverse, it occurs in all countries in the practice of doctors of various specialties (dentists, surgeons, dermatologists, gynecologists, etc.). Main localizations — maxillofacial (up to 80%), thoracic, abdominal, pararectal, mycetoma (Madura foot). What are the symptoms of actinomycosis?
Main signs and symptoms of actinomycosis
Actinomycosis can develop in some parenchymal organs. What diseases can be caused by actinomycetes, read further on estet-portal.com. In addition, the symptoms of actinomycosis manifest themselves not only in the classical form with characteristic tissue infiltration, abscesses and fistulas, but also in the form of the dominant pathogenic flora of a nonspecific inflammatory process that complicates the course of the underlying disease.
Actinomycetes may play an active role in the etiology of chronic tonsillitis. The palatine tonsils are colonized by actinomycetes in chronic tonsillitis and, in association with other bacteria, often provoke inflammatory reactions, which are symptoms of actinomycosis.
Actinomycotic bacteremia of the oral cavity may occur as a result of dental procedures. In 30% of cases out of 80% of detected bacteremia, the actinomycotic nature of stomatitis is determined, the etiological agents of which are saprophytes of the oral cavity — A. viscosus, A. odontolyticus and A. naeslundi.
Joining the local pathogenic flora, actinomycetes contribute to the development of a long-term non-healing inflammatory process with acne, trophic ulcers, hyperemia, maceration on the skin. Having a high degree of intestinal colonization, they are one of the main agents of dysbacteriosis. Summarizing all of the above, it should be noted that bacteria from a large group of actinomycetes can appear as participants in any infectious and inflammatory manifestations in the human body - from dermatitis to endocarditis.
Thus, there are the following variants of actinomycotic lesions that cause the manifestation of symptoms of actinomycosis:
- chronic tonsillitis;
- bacteremia of the oral cavity;
- trophic ulcers;
- intestinal dysbacteriosis;
- dermatitis;
- endocarditis.
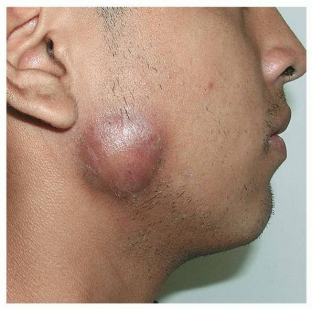
How is diagnostics carried out when symptoms of actinomycosis are detected?
A reliable sign and symptom of actinomycosis is the detection of characteristic actinomycotic drusen in the form of small yellowish grains, resembling grains of sand, in pus from fistulas, in biopsy specimens of affected tissues. In the native (not stained) form, in histological preparations, drusen are clearly visible against the background of purulent detritus in the form of radiant formations with a denser homogeneous-granular center from a thin, densely intertwined mycelium.
For the ability to form radially arranged threads of mycelium, often with "cones" at the ends, actinomycetes were once called "radiant mushrooms". Leading importance in the formation of Druse — tissue colonies of actinomycetes — has a response of the macroorganism to antigens secreted by actinomycetes into the environment. Druse formation helps to slow down the dissemination of the pathogen in the affected organism, as well as the localization of the pathological process.
Symptoms of actinomycosis are accompanied by characteristic specific tissue reactions: granulomatous productive inflammation, leukocyte infiltration, microabscesses, "cellular" tissue structure, specific granuloma surrounded by polynuclears, giant and plasma cells, lymphocytes and histiocytes.
In the body of patients, drusen do not develop at all stages of the disease and are not characteristic of every variety of "radiant fungus", therefore they are not always found, and the absence of drusen at the initial stages of diagnosis does not negate actinomycosis.
In addition, these formations are able to spontaneously lyse, decalcify, deform, calcify and undergo other degenerative changes.
Thus, the symptoms of actinomycosis can be very diverse, depending on the organ that is affected by actinomycetes.







Add a comment