Cytomegaly was described as early as the late 19th century under the name "kissing disease" because doctors suspected transmission of the infection through saliva and observed inflammation of the salivary glands. Only after almost a hundred years was the virus causing cytomegaly – a disease in which giant cells with large nuclear inclusions form in tissues and organs. Cytomegalovirus is very widespread. According to researchers, almost every second inhabitant of the planet is considered to be the carrier of this infectious agent. Asymptomatic carriage of cytomegalovirus can continue for life, but in the event of a significant weakening of the immune defense, the disease can develop with severe complications.
Features of the virus causing the development of cytomegaly
Cytomegalovirus is closely related in origin to the herpes simplex virus. Today it is known that it is transmitted not only by kissing, although the salivary glands really become the place of its primary fixation in the body – parotid, less often submandibular. From the salivary glands, cytomegalovirus spreads throughout the body by the hematogenous route, settling in the cells of various tissues and organs. With a reduced level of immunity, the virus causes cytomegaly of varying severity.
Infection with cytomegalovirus occurs very easily, since it is contained in all environments of the affected human body and can be transmitted through saliva, blood, urine, vaginal secretions, breast milk, semen, amniotic fluid. You can become infected through a blood transfusion, infection of a child occurs during childbirth. An infected person can remain an asymptomatic virus carrier all his life, and the presence of cytomegalovirus in the body will not manifest itself in any way.
Cytomegalovirus infection most often occurs during the following periods:
- intrauterine – from an infected pregnant woman;
- in preschool childhood – breastfeeding, contact from mother or relatives;
- in adulthood up to about 30 years old – usually sexually or by contact.
Cytomegaly, which has developed in a pregnant woman, is especially dangerous. In the early stages of pregnancy, it can cause spontaneous abortion, in later – provoke severe internal malformations of the child.
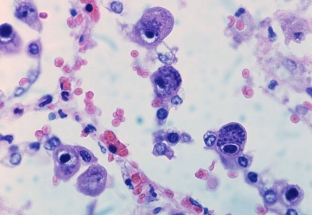
The course of cytomegaly and the features of the manifested symptoms
The course of cytomegaly and the symptoms it manifests depends on the state of the patient's body – more precisely, on the level of his immune defense. If the body is weakened for some reason (for example, during pregnancy), and a person encounters cytomegalovirus for the first time, then cytomegalovirus can occur in an acute form. Its manifestations strongly resemble a sore throat or SARS: the patient experiences general weakness, chills, headaches and muscle pains, while the spleen enlarges, a runny nose bothers, the salivary glands enlarge, a whitish coating appears on the tongue and gums.
Most often, after two weeks, cytomegaly ends with a complete recovery, and the patient turns into a lifelong asymptomatic carrier of the virus. If the immune response is not strong enough, then localized forms of cytomegaly may develop: in women – inflammation of the uterus, uterine appendages, in men – inflammation of the testicles, urethra.
With a significant decrease in the immune response or its absence (for example, with neoplasms), a generalized form of cytomegaly develops when multiple lesions of the internal organs by the virus occur – kidneys, liver, pancreas, joints, sepsis may develop. The addition of a secondary bacterial infection can further worsen the prognosis.
Therapeutic measures for cytomegalovirus and disease prognosis
Therapy of cytomegaly – non-specific, steroid drugs are prescribed (for example, prednisolone), the introduction of gamma globulin, in case of a bacterial infection, antibiotic therapy is added. With localized forms, if necessary, symptomatic therapy is prescribed. Treatment is recommended for special partners.
Regarding the prognosis of cytomegaly – the disease in a mild form usually has a completely favorable outcome. If the localized form – then the disease that has joined the cytomegaly usually proceeds severely. With a generalized form, especially with a secondary infection that has joined, toxicosis can develop, blood circulation is disturbed, and the disease receives an unfavorable prognosis.







Add a comment