Be a doctor or healthcare professional – it sounds proud. However, this profession is associated with a high risk of developing occupational dermatoses.
For example, one study of 706 nurses found that 47.3% of them had some form of occupational skin disease, allergic and contact dermatitis.
For information on what factors contribute to the occurrence of occupational diseases in physicians, as well as how to protect yourself from them, read on estet-portal.com in this article.
Occupational dermatological diseases in healthcare workers
There are many factors that increase the risk of developing occupational skin lesions in healthcare workers, including:
- Exposure to various cleaning products, medications, latex and a range of other potential allergens and/or irritants;
- Long working hours which increase the duration of exposure;
- High levels of wet work and frequent handwashing, which can lead to contact dermatitis;
- Exposure to needles, lancets and other sharp instruments that increase the risk of mechanical injury.
Urticaria after stress: mechanism of development and methods of treatment
The skin is a protective barrier against pathogen penetration and contact with irritants or sensitizers. However, the nature of some professions compromises this barrier.
Healthcare workers are considered to be at high risk of developing skin conditions.
Medical personnel are particularly at risk of latex allergy, contact dermatitis and mechanical injury.
Latex allergy is a type 1 hypersensitivity reaction to latex proteins (contact urticaria) and in extreme cases can be fatal.
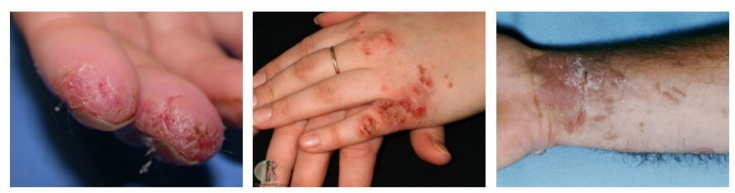
Contact dermatitis can be caused by allergens or irritants (water, harsh soaps, rubbing), with irritant dermatitis considered to be more common. Studies have shown that rubber, aldehydes and hydrogen peroxide are associated with an increased risk of dermatitis.
The most common signs and symptoms of dermatitis include:
- redness and itching;
- edema;
- pain;
- burning;
- flaking.
Does allergies occur after the use of hyaluronic acid: causes of trouble
Handling needles and other sharp objects exposes medical staff to an extremely high risk of injury, cuts or needle sticks. This puts doctors and nurses at extremely high risk of transmitting diseases such as HIV, hepatitis C or secondary bacterial infectionsii.
How can a doctor protect his skin
Due to the risk of disease transmission between patients and medical personnel, gloves should be used both when performing manipulations, caring for patients, and when handling body fluids.
Read the most interesting articles in Telegram!
Gloves should also be worn when in contact with disinfectants, cleaners, and other chemicals. However, if the gloves are made of rubber, they may cause latex sensitivity or dermatitis; The increased use of non-latex gloves in the medical profession has helped reduce this risk.
Safety in the workplace should be a priority for both management and employees.
Proper hand care reduces the chance of occupational dermatoses and includes:
- Use gloves (preferably non-latex) to reduce exposure to irritants, allergens and potentially contaminated materials;
- The use of alcohol-based hand gels reduces the need for constant handwashing;
- Applying barrier creams, emollients, or lotions to moisturize and protect the skin.
Types of skin allergic reactions: causes, methods of detection
may include:
Reducing or eliminating exposure to potential allergens and irritants;- Use of gloves;
- Use of moisturizing and protective creams;
- Use of oral or topical steroids;
- Antibiotics to treat secondary infections.
- For persistent or severe inflammatory lesions, second-line drugs such as methotrexate, cyclosporine, and azathioprine must be considered.
YouTube:






