Rubromycosis is caused by a special fungal pathogen that does not limit its interests to the nail plates, and in the absence of timely proper treatment, it can spread throughout the body. Foot lesions with rubromycosis can transmit the pathogen to the hands, then it covers the forearms, shins, buttocks, disguises itself as other dermatological diseases and causes difficulties in diagnosis. The process of fighting this fungal infection is very long and requires the patient to carefully follow the doctor's prescriptions.
Methods of infection with rubromycosis and characteristic manifestations of infection
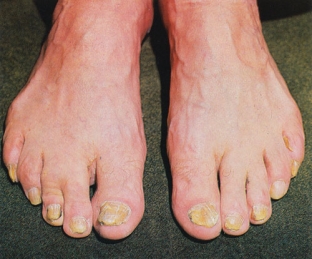
The peculiarity of the skin disease caused by the fungus Trichophyton rubrum is the high enzymatic activity of the pathogen. It causes lesions of the feet, as well as large folds of the skin, sometimes even covers the scalp. Rubromycosis is diagnosed, as a rule, on the feet, and it is extremely rare that only the nails – basically the whole foot is affected by the fungus.
Rubromycosis is very virulent and can be transmitted through personal contact between people and through the sharing of clothing or household items. From the defeat of the foot, rubromycosis can pass to the hands, and then take a generalized form – spread throughout the body.
The reasons for the active spread of rubromycosis:
- taking antibiotics, cytostatics, hormones;
- diseases of the vessels of the lower extremities, circulatory disorders in them;
- decreased immunity.
A person may well be a carrier of infection without external signs of the disease, immunity does not develop after rubromycosis.
First, after infection, the disease manifests itself in the folds of skin between the toes, then the entire sole is involved in the process – the skin looks inflamed and with a distinct mucoid peeling. If treatment is not started at that stage, then the lesion spreads to the lateral surfaces of the foot, to the toes, and then covers the nails and inflames other areas of the skin.
If rubromycosis has spread to the palms, then it often cannot be diagnosed in time due to constant washing of hands. The lesion becomes clearly visible when the inflammation passes to the back of the hand.
Nails are usually affected all at the same time – they thicken, become covered with yellowish stripes, crumble. In a neglected state, without treatment, the nail plate can generally collapse and separate from the nail bed.
Generalized form of rubromycosis – manifestation features
If limited lesions of the feet or hands are not treated in a timely manner, rubromycosis can turn into a generalized form, manifesting itself in two forms:
- erymatous-squamous – causes severe itching, outwardly resembles manifestations of atopic dermatitis, rubromycosis spots have a scalloped edge with an intermittent edematous roller, peel off and are grouped in rings or garlands, covers skin folds;
- follicular-nodular – more often it affects the limbs, but it can also occur on the face, outwardly the skin lesions resemble erythema nodosum, and on the face – lupus erythematosus, can merge & nbsp; and grow peripherally.
Lack of polymorphism and maceration – important diagnostic features of rubromycosis, in addition to a scalloped ridge along the edges of the affected areas.
Peculiarities of treatment of rubromycosis and disease prevention
The treatment of rubromycosis is a very meticulous, step-by-step and lengthy process. The patient must be prepared for this and be aware that any failure in the regimen of taking the drugs prescribed by the doctor leads to the development of resistance of the causative agent of rubromycosis to treatment.
The first step is to solve the problem of weeping of the inflamed skin of its edema. Soothing lotions, desensitizing drugs are prescribed, if necessary – therapy against allergies and various systemic diseases, against which rubromycosis has developed.
After stopping the inflammatory process, the task is to exfoliate the thickened epidermis with the help of keratolytics, the use of soap and soda baths and cleaning of horny masses. Further, the cleansed skin and nails are treated with antimycotics with simultaneous ingestion of antifungal drugs. Antimycotic patches are recommended for nails.
Patients are prescribed a diet high in protein and vitamins A, E, and increased attention to personal hygiene is recommended – with daily change of bed linen and underwear and its disinfecting treatment.







Add a comment