Methods of treatment of staghorn stones today remain one of the most pressing issues of modern urology. Coral-like stones are formed in the renal pelvis and cups, have a rather peculiar clinical picture and make it difficult to diagnose urolithiasis. At the same time, it is staghorn stones that can lead to serious impairment of kidney function and require the earliest possible start of therapeutic measures. What techniques are used to treat coral stones today - tells estet-portal.com.
Basic treatment methods for staghorn stones
So much attention is paid to the problem of treating staghorn stones in urolithiasis due to the fact that this type of stones often causes serious complications of urolithiasis. The clinical picture of staghorn stones is not pronounced, it is often difficult to suspect pathology, because the first symptoms of the disease can appear already in the last stages of stone development, when kidney function is significantly impaired. The complicated course of urolithiasis in staghorn kidney stones often requires the use of surgical methods for treating the pathology.
Topical treatments for staghorn stones:
- anatrophic nephrolithotomy – surgery to treat staghorn stones;
- external lithotripsy as a treatment for staghorn stones;
- percutaneous nephrolithotripsy will help to completely remove the staghorn stone;
- combination treatment is most effective for staghorn stones.
Anatrophic nephrolithotomy – surgery to treat staghorn stones
In recent years, for the treatment of staghorn kidney stones, anatrophic nephrolithotomy has been widely used – organ-preserving operation, in which the so-called "separation" is performed; kidneys. Highlights perform anatrophic nephrolithotomy as follows:
- the kidney is dissected in the avascular zone, that is, in the area in which the smallest number of vessels passes;
- a clamp is applied to the renal artery to prevent bleeding from the vessel;
- intraoperatively, the kidney is cooled to prevent its ischemia;
- in the postoperative period, the kidney is washed with antiseptic and litholytic solutions through the nephrostomy.
External lithotripsy as a treatment for staghorn stones
External shock wave lithotripsy is also one of the effective methods of treating staghorn stones. Lithotripsy is often performed in 2-5 sessions, since an attempt to completely crush the stone in one session often leads to the development of complications. Crushing of coral-like stones from cup fragments is started, then they move on to the calculus in the cavity of the pelvis. Before crushing large stones, it is necessary to install a puncture nephrostomy in order to provide additional outflow of urine with fragments of crushed stone.
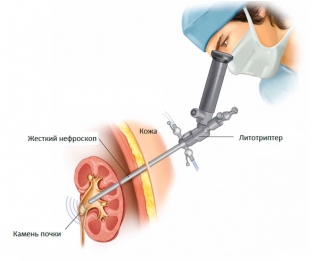
Percutaneous nephrolithotripsy will help to completely remove the staghorn stone
It is often not possible to completely remove a staghorn stone by lithotripsy, and the fragments left in the kidney cavity become the nucleus for the formation of a new calculus. Therefore, to date, the most effective treatment for staghorn stones, especially large ones, is a combination of extracorporeal lithotripsy and percutaneous nephrolithotripsy. The latter involves the creation of a puncture fistula of the pyelocaliceal system of the kidney to remove fragments of previously crushed stones through it. The entire procedure must be performed under ultrasound or endoscopic control. The interval between stone crushing and percutaneous nephrolithotripsy should be at least three days.
Combination treatment is most effective for staghorn stones
Thus, taking into account the structural features, the complexity of the diagnostic process and the likelihood of possible complications, the treatment of staghorn stones should be comprehensive and individually selected in each individual case. It is this approach that helps to achieve the maximum therapeutic effect. To date, the following schemes for the combined treatment of coral stones are most often used:
- open surgery + remote lithotripsy + metaphylaxis;
- percutaneous nephrolithotripsy + extracorporeal lithotripsy + metaphylaxis;
- external lithotripsy + percutaneous nephrolithotripsy + metaphylaxis.







Add a comment