The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has released long-awaited quality criteria for sunscreens.
This development could spur major changes to some popular sunscreens, many of which include chemicals that have not been tested for safety.
In the article estet-portal.com you can get acquainted in detail with modern criteria, implementation and application, which will protect consumers from low-quality and unsafe sunscreens.
FDA proposes major changes to sunscreens
The new criteria cover the following aspects:
1. Safety of Active Ingredients
Out of 16 active ingredients on the market, two — zinc oxide and titanium dioxide — great for use in sunscreen. The other two ingredients, para-aminobenzoic acid (PABA) and trolamine salicylate, are not considered safe. These two ingredients are not currently available on the US market. There is not enough data on the remaining 12 components to draw firm conclusions in favor of their safety.
Zinc Oxide and Titanium Dioxide — the gold standard for sunscreen active ingredients.
2. Dosage Forms
Sprays, oils, lotions, creams, gels, pastes, ointments and sticks are generally recognized as safe and effective (GRASE). More information is needed on the safety of powders. Wipes, body washes, shampoos, and other forms will be categorized as new drugs because the FDA has not yet received data confirming their eligibility.
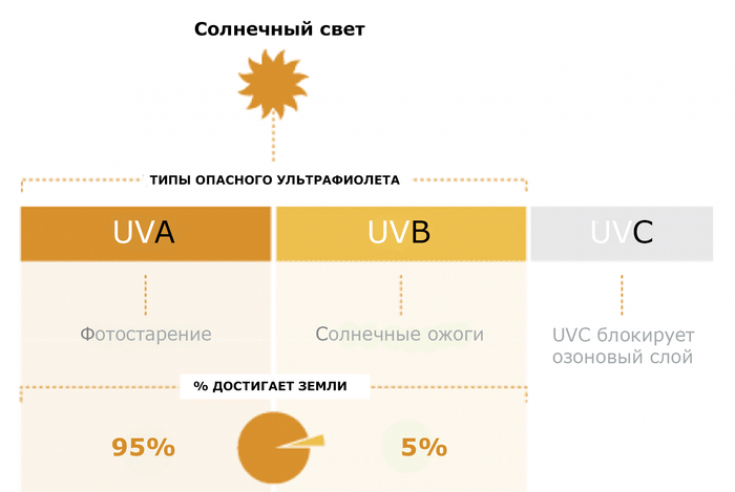
3. SPF
Increases maximum SPF (Sun Protection Factor) from 50+ to 60+.
There is no data to support the benefit of SPF above 60.
However, the FDA recommends that products be allowed up to SPF 80 to provide manufacturers with a wider range of options. Products with an SPF of 15 or higher should also provide broad spectrum protection. As SPF increases, UVA protection should also increase.
Photoaging: clinical progression and management
4. Label requirements
Active ingredients must be on the front of the product, which allows sunscreens to match other over-the-counter products. The front label should also include information about skin cancer and skin aging, the risk of which is increased if sunscreen recommendations are ignored.
5. Combined products
Products that combine sunscreen and insect repellent have not been proven to be effective and safe.
Watch the most interesting videos on our channel in Youtube
How dangerous is non-compliance with recommendations
According to the FDA, 12 sunscreen ingredients do not have enough data to confirm whether they are GRASE. This list includes: synoxate, dioxybenzone, ensulizol, homosalate, meradimat, octinoxate, octisalate, octocrylene, padimate O, sulisobenzone, oxybenzone and avobenzone.
Among the reasons cited is that oxybenzone is absorbed through the skin to a greater extent than previously thought. The question remains open about the ability of oxybenzone to influence the endocrine system, cause cancer, birth defects and other developmental disorders. Nearly all of the 12 components have limited or no absorption data.
A 2001 study provided evidence that oxybenzone increases uterine size in animals.
To put the results into perspective, the team looked at the dose used in the animal study and the average amount of use of the oxybenzone products. The authors concluded that the human regimens needed to achieve the same blood levels found in animal studies are largely unattainable.
Sunscreen saves lives, so it is important to use sunscreen that has been tested for quality and safety every day.
Thus, the FDA has provided guidelines and requirements for sunscreens, understanding and following which will allow you to make a choice in favor of products that are exceptionally effective and safe.
Thank you for staying with estet-portal.com. Read other interesting articles in the "Cosmetology" section. You may be interested in Sunscreens — the most important factor in rehabilitation after the procedure







Add a comment