Modern medicine does not stand still, and every year provides more and more opportunities for the most effective detection and elimination of pathological conditions of the body. A correct and timely diagnostic process, to a large extent, determines the effectiveness of the selected treatment regimen and the prognosis for the life and working capacity of the patient. Even with such a dangerous disease as kidney cancer, modern diagnostic methods open up a lot of opportunities. The diagnosis of kidney cancer largely depends on the patient himself, who seeks qualified medical help in a timely manner.
Laboratory and instrumental methods for diagnosing kidney cancer
Diagnosing kidney cancer involves several basic types of laboratory and instrumental research methods. Since any violations of kidney function immediately attract attention with the appearance of fairly characteristic symptoms, the pathology of this organ can be suspected already at the stage of collecting an anamnesis. Laboratory studies of urine and instrumental methods that help to study the function of the kidneys, violations of their structure and blood supply help to clarify the prevalence of the pathological process and decide how dangerous the situation is and what treatment regimen should be recommended to the patient.
Renal Cancer Diagnosis:
- what lab results to expect for kidney cancer;
- Ultrasound and computed tomography – basic methods for diagnosing kidney cancer;
- Renal angiography provides the necessary information about the blood supply to the tumor.
What Lab Results to Expect for Kidney Cancer
Diagnosis of kidney cancer begins already at the stage of collecting an anamnesis, when the patient complains of blood in the urine and pain in the kidney area. An important role is also played by information about what harmful factors were present in the patient's life and could provoke pathology, whether his family history is aggravated, and so on. At the stage of examination of the patient, palpation of a rounded tuberous neoplasm in the kidney area draws attention. Based on the results of laboratory tests, the following changes characteristic of kidney cancer are determined:
- in the general blood test: increased ESR and signs of anemia;
- in a biochemical blood test: an increase in the activity of alkaline phosphatase and the level of alpha-2 globulins, as well as a decrease in the concentration of protein in the blood serum;
- in the general analysis of urine: leukocyturia, the presence of erythrocytes and protein in the urine in large quantities.
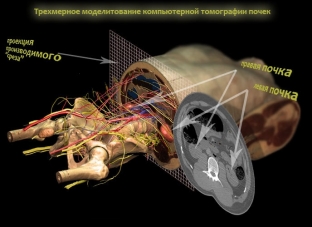
Ultrasound and computed tomography – main methods for diagnosing kidney cancer
Ultrasound and computed tomography are by far the most informative research methods in the diagnosis of kidney cancer. In addition, computed tomography also helps to establish the presence and localization of distant metastases. In an ultrasound examination, a kidney tumor is visualized as a volumetric formation of a round or oval shape, medium echogenicity, & nbsp; having uneven contours and deformation of the pyelocaliceal system of the kidney. If the tumor is in the stage of necrosis – in the kidney, fluid inclusions of various shapes can be detected, and when the tumor calcifies, its structure becomes hyperechoic. On tomograms, the tumor is defined as a rounded formation with a homogeneous or heterogeneous structure, having a density higher than that of normal renal parenchyma.
Renal angiography in the diagnosis of kidney cancer is used to detect early forms of a tumor, in addition, this method helps to establish the location of the neoplasm relative to the main vessels, which is very important for performing surgery. The first stage of the study is abdominal aortography, which can be used to determine the features of the blood supply to the tumor. Tumor vessels are often located chaotically, they are deformed, often curved or too straight. The area of pathological vascularization can be clearly limited from the surrounding parenchyma or have signs of infiltration with the process spreading beyond the kidney capsule. In the second phase of the study, which is called nephrogenic or parenchymal, the size, shape and position of the kidney tumor are determined.







Add a comment