Dermatoscopy is a visual method that has been successfully used for more than 10 years in the countries of America, Europe and Australia.
With the help of a special device – dermatoscope, the doctor receives a tenfold increase in skin structures. Digital dermatoscopy is the most modern and effective method for diagnosing skin neoplasms.
The International Dermatoscopy Cup, where estet-portal.com took part as an information partner, presented the latest developments in this field.
Read in the interview on estet-portal.com about the possibilities and features of dermatoscopy from a doctor -dermatologist, vice-president of the Latvian Association of Aesthetic Laser Surgery, member of the European Academy of Dermatology, Raimonds Karls.
- Reasons for using dermatoscopy in the practice of a dermatologist
- Dermatoscopy options and types of dermatoscopes
- Interpretation of results during dermatoscopyand
Reasons for using dermatoscopy in the practice of a dermatologist
R.K.: Dermatoscopy combines two main principles that facilitate a good diagnosis of skin lesions: close contact with the skin and illumination.
Follow us on Instagram!
When using dermatoscopy, the dermatologist examines individual lesions more closely.
This diagnostic accuracy allows diagnosing not only pigmented skin neoplasms and melanoma, but also a wide variety of dermatoses (inflammatory or parasitic).
Raymond Karls: dermatoscopy – it is a flag that heralds a whole new era in dermatology
Examination for malignancy of skin neoplasms is carried out using a medical device – dermatoscope.
There is no difference between epiluminescence microscopy and dermatoscopy. These names refer to one research technique.
In 2001, at the 1st World Congress of Dermatoscopy it was decided to combine terminology that originated in different times and places and use the term dermatoscopy.
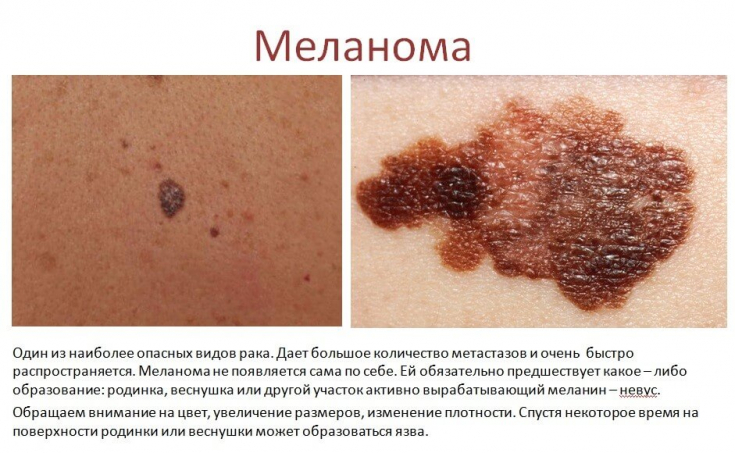
Basic value of the procedure – detection of melanomas at the initial stage of development.
Mole dermatoscopy also allows accurate diagnosis in the presence of skin diseases of melanocyticth and non-melanocytic etiology.
Dermatoscopy options and types of dermatoscopes
R.K.: Dermatoscopy allows you to visualize the horizontal plane up to the papillary layer of the skin. Structures in the mesh layer are not visible, just like with the naked eye.
Most pigmented skin lesions are sometimes very difficult to diagnose, and hypopigmented lesions or pigmentless melanoma present a particular diagnostic challenge.
Large tumors can be difficult to dermoscopy and thus clinical experience and clinical diagnosis remain important in such cases.
If dermatoscopy is difficult to diagnose, then biopsy.
Dermatoscopy is not a 100% method for diagnosing skin lesions!
There are 2 main types of dermatoscopes: oil immersion (non-polarized) and cross-polarization (polarized).
- Oil immersion dermoscopy (non-polarized) has a longer history of use in dermatology, however the inconvenience of using oil or contact fluid (alcohol gel or ultrasound gel) makes the manipulation time consuming, with multiple examinations. There is a two-way "contamination" as there is contact with the patient.
- Cross-polarized dermoscopy becomes the most attractive method, as it has excellent quality, and the image brightness is comparable to the oil immersion method.
This method is more expensive, but more versatile, and multiple structures can be examined quickly withoutthe need for couplant.
What can dermatoscopy do and when is it used
Interpretation of results during dermoscopy
R.K.: At the first stages, when a dermatologist is just starting to use the dermatoscopy method in his practice, we can use the following scales to interpret the results and quickly master the technique of the procedure.
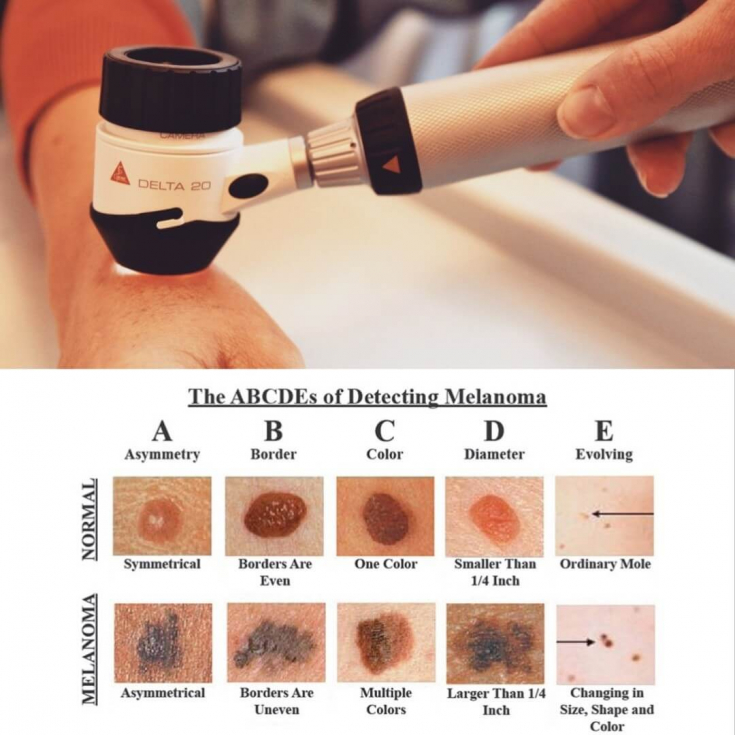
First, the mole or age spot is examined according to ABSD rules:
- Asymmetry (A) divided by two axes, then scored from 0 to 2 points.
- The boundaries of the mole (B) are divided into 8 segments, in each of which the intensity of pigmentation is compared and noted from 0 to 8 points.
- The color of the neoplasm (C) is evaluated on a scale from 1 to 6 points (white, black, blue, dark brown, light brown, red).
- The structure of a mole (D) consists of 5 elements: nodules, dots, unstructured areas, branched stripes, pigment network. It is evaluated from 1 to 5 points.
Revolution in oncology: the discovery of a vaccine against melanoma of the skin
As a result, individual index is calculated using the formula:
(A)*1.3 + (B)*0.1 + (C)*0.5 + (D)*0.5
When the index is less than 5.45, then melanoma is diagnosed with a probability of 93%.
Dermatoscopy results can be:
- Suspicion of malignancy. Requires surgery followed by histological examination.
- Asymmetry without signs of oncology. The results are stored in the database, a re-examination is recommended after 3-6 months.
- Symmetrical formations. Annual inspection recommended.
Research in this area is constantly expanding.
Currently, computer systems and artificial intelligence, which is being actively introduced into medicine, have some limitations, such as: expensive cost and large size compared to hand-held devices.
The software of computer systems at the moment can already comment on individual changes that are pre-selected for examination, while it is important to note that only a doctor can make the final diagnosis and conclusion!







Add a comment