Any change in size, consistency, or subjective swelling of the patient on palpation of the lymph nodes is termed lymphadenopathy.
Swollen cervical lymph nodes in children can signal the presence of various diseases: both infectious and non-infectious.
To quickly make a correct diagnosis, the physician must know the clinical features of the most common cervical lymphadenopathy.
For more information about what a doctor needs to consider when conducting a differentialdiagnosis of enlarged cervical lymph nodes in children, read on estet-portal.com in this article.
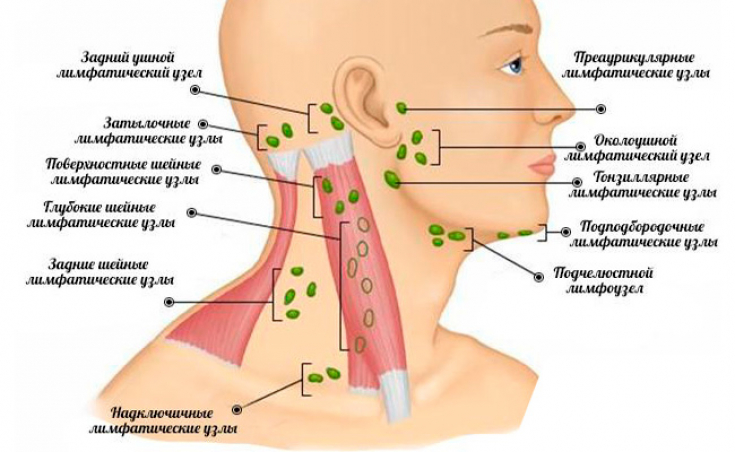
Bilateral or unilateral lymphadenopathy: pay attention to localization
In the case of infection, an enlargement of the lymph node can be both a consequence of its direct damage by a pathogenic agent, and reactive inflammation.
Bilateral enlargement of the cervical lymph nodes in children in most cases is associated with a viral infection (Adenovirus, Cytomegalovirus, Ebstein-Barr virus).
In turn, unilateral enlargement of the lymph nodes is more often caused by group A beta-hemolytic streptococci (up to 80% of cases) associated with streptococcal tonsillitis.
In such cases, the lymph node can reach 2.5 & ndash; 6 cm in diameter, it is sensitive, the skin above it – hyperemic. In this case, fever and other systemic symptoms may be completely absent. Less commonly, inflammation of the lymph nodes can be caused by anaerobic or mixed flora.
A solitary enlarged lymph node is also a typical symptom of Kawasaki disease, atypical mycobacterial infection, and, less commonly, – cat scratch disease.
Follow our news on Facebook
Enlarged cervical lymph nodes require dynamic monitoring
Enlargement of lymph nodes in the angles of the jaw (in the absence of other symptoms) and near the sternocleidomastoid muscle is almost always "innocent"; symptom.
According to the EMB Guidelines, more than half of apparently healthy school-age children can be identified with at least one cervical lymph node larger than 1 cm in diameter.
However, if an enlarged lymph node is found, it is important to observe the change in size within four weeks.
Most of the lymph nodes found by the parents are "remnants" of infections and they are decreasing over a given period of time.
When the risk of parotid inflammation increases
Swollen lymph nodes in atypical places should alert
You need to be on the lookout for swollen lymph nodes in unusual locations, especially in the subclavian fossae.
In some cases, there is a long-term enlargement of the cervical lymph nodes. The most common infectious causes of chronic lymphadenitis of the neck are toxoplasmosis and atypical mycobacteria. In such cases, to confirm the diagnosis, additional research methods are necessary: PCR, determination of antibody avidity and, if necessary, biopsy.
When conducting a differential diagnosis of chronic cervical lymphadenopathy, the possibility of tuberculosis must also be taken into account.
Primary syphilis: attention to lymph nodes
Therapeutic measures for enlarged cervical lymph nodes
Bilateral acute lymphadenitis in most cases does not require any treatment, as it is associated with a viral infection.
According to international recommendations and postulates of evidence-based medicine, the prescription of homeopathic medicines is inappropriate due to the lack of their effectiveness.
In case of unilateral enlargement of the lymph node associated with streptococcal or staphylococcal flora, it is advisable to prescribe antibacterial drugs: penicillin, cephalexin or clindamycin.
A clinical response can be observed within 36-48 hours if the treatment is successful.
Thank you for staying with estet-portal.com. Read other interesting articles in the "Infectology" section. You may also be interested in The human lymphatic system: guarding the whole organism







Add a comment