With the development of inflammatory processes on the scalp and in the region of the eye orbit (purulent wound, furuncle, conjunctivitis, barley, papillitis), as well as infectious processes in the body (tonsillitis, influenza, SARS), the pharyngeal ring may become inflamed with the development of inflammation of the parotid gland . In addition, the cause of inflammation of the parotid glands may be exacerbation of periodontitis of the molars. What is the mechanism for the development of inflammation of the salivary glands and how the disease manifests itself, read in our article.
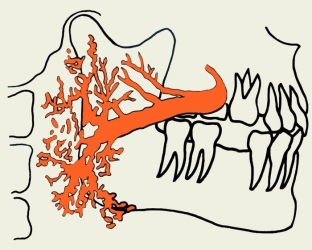
The structure of the salivary glands. The mechanism of development of inflammation of the parotid gland
Lymph nodes are located around the salivary gland, the number of which ranges from 6 to 13. It is in these nodes that lymph outflows from various parts of the head and from the maxillofacial region. This is the mechanism of development of lymphadenitis of parotid nodes.
It has been established that acinar tissue penetrates into some nodes, which communicates with the entire ductal system of the salivary gland. Such features of the structure of the lymph nodes create conditions for the defeat of the glandular tissue when they become infected. Therefore, in one case, lymphadenitis of the parotid gland may occur, which is called Herzenberg's false parotitis, and in the other case, lymphogenous parotitis develops, in which the lymph node with penetrated glandular tissue is inflamed.
Clinical manifestations and severity of inflammation of the parotid gland
The disease develops in the presence of infectious agents or inflammatory processes in the body with reduced immunity. This is often observed with a long course of influenza, tonsillitis and severe purulent diseases in the head area. Inflammation of the parotid gland is manifested by the presence of a small seal in any part of the gland. The seal is felt when chewing, which in most cases makes you turn to a doctor. Most patients feel a lump in front of the tragus.
The course of inflammation of the parotid gland has 3 degrees:
- Mild - the swelling becomes painful, swelling is present. Patients report dry mouth, which is due to reduced salivation. At the same time, saliva has an increased viscosity.
- Intermediate – characterized by an increase in temperature to subfebrile figures and a violation of the general condition. With an average degree in the gland, there is pain of a pulsating nature. The salivary gland externally acquires a red tint and is soldered with an infiltrate. Spontaneous opening of the abscess may occur, after which externally unaltered saliva is released from the gland.
- Severe degree - characterized by the rapid development of the process and abscess formation of the gland. This is how the phlegmon of the salivary gland develops.
Diagnosis and treatment of inflammation of the parotid gland
Diagnosis is established on the basis of anamnesis and typical complaints. In laboratory studies, it is revealed that the inflammatory component is weakly expressed in the secretion of the parotid gland. The sialographic picture may be normal. In some cases, a defect in the filling of the contrast agent can be detected on the sialogram. Cytological examination of the gland secretion reveals inflammatory cells (histiocytes, lymphocytes, neutrophils, plasma cells and macrophages).
It is mandatory to carry out therapy for the underlying disease, which provoked the development of inflammation of the parotid gland. In the period of serous inflammation, it is advisable to carry out novocaine blockades in the area of the inflamed salivary gland. Alternating blockades with compresses of 30% dimethyl sulfoxide solution brings a good effect. In the presence of lymphogenous parotitis, antibiotics are additionally instilled into the parotid duct and novocaine blockades are continued. With the development of an abscess of the lymph node, its opening is indicated by surgery.
Acute lymphogenous parotitis requires long-term treatment. The lymph node may be enlarged for a long time. Inflammation of the parotid gland cannot become chronic, therefore it has a favorable prognosis.







Add a comment