More than 30% of the population suffers from alopecia. Different forms of this disease require appropriate treatment. Systemic therapy may include restoring the balance of hormones, vitamins, the use of antifungal and antiparasitic agents, prostaglandin analogues, vasodilators, and 5-alpha reductase inhibitors. There are other treatment options such as hair implants and corticosteroid injections. However, with any type of alopecia, the patient almost always requires topical treatment.
However, it is important to note that topicals should not be used when the skin is damaged, such as during a hair transplant operation.
At estet-portal.com we review the most effective topical treatments for various common causes of hair loss.
- Main causes of hair loss
- Subtleties of diagnosis and treatment of alopecia
- What to beware of when prescribing treatment for alopeciaand
Main causes of hair loss
Hair growth occurs in several stages, starting with the anagen phase. During this period, cell division occurs in the matrix of the hair bulb. After the hair reaches a certain length, which varies depending on the area of the body, it enters the catagen phase when cell division and pigmentation cease. During the telogen phase, a new follicle appears below the original follicle. It is dysfunctions at the telogen and anagen stages that lead to hair loss.
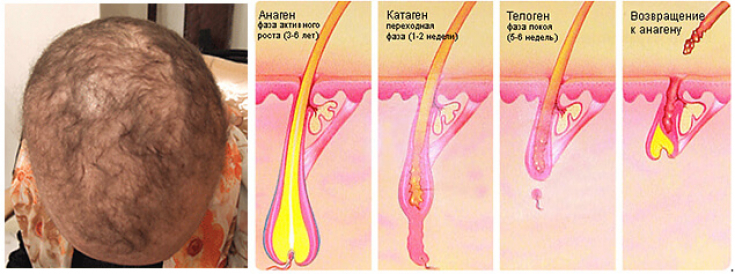
The causes of alopecia, in particular androgenetic alopecia, can be due to a number of factors, including seasonal variations, aging, nutritional factors, hormonal imbalances, autoimmune hair disorders, hairless gene mutation, inflammatory hair loss, and psychological factors.
Lower levels of melatonin and prolactin result in shorter hair.
There are three main types of alopecia:
Androgenetic alopecia: a common cosmetic hair disease resulting from the interaction of genetic, endocrine and aging factors leading to a patterned miniaturization of follicles. Microinflammation is one of the main causes of this process.
Alopecia areata: Most investigators agree that microscopic inflammatory changes appear to play an important role in alopecia areata.
fever, childbirth, iron deficiency, stress, chronic illness, and dietary changes are factors commonly associated with this disorder. Most often there is a time interval of two to three months between the triggering factor and the onset of the disorder, and in acute forms it lasts from four to six months.
Genetic predisposition to aplopecia foundSubtleties of diagnosis and treatment of alopeciaA biopsy is necessary to evaluate for inflammatory changes, bacterial, fungal, or parasitic infections. If none of the causes seem to be related to alopecia, then hormone imbalances and nutritional deficiencies should be ruled out, and a more extensive examination should be carried out, since hair loss can be the result of several causative factors at once.
Studies have shown the effectiveness of estradiol and progesterone when applied topically to the scalp in the treatment of alopecia.
Working with physiological doses and topical application reduces the risks associated with treatment. Also, when applied topically, the ingredients have a reduced systemic absorption, which reduces the number of side effects, while at the same time improving the local effect.
The main drugs used for the treatment of different types of alopecia are:
Estradiol
- Proogesterone
- Spironolactone
- Finasteride
- Latanoprost
- Minoxidil
- Each of these drugs affects different parts of the pathogenesis of alopecia.
Treatment of alopecia: basic drugs
Read the most interesting articles inTelegram!
What to watch out for when prescribing treatment for alopeciaHair loss should be treated like any other disease. Immediately after diagnosis, it is necessary to select therapy taking into account indications and contraindications, warnings, interactions, side effects, allergic reactions.
Estradiolor any other hormone should be avoided if there is a family history of cancer, if the patient has been treated for cancer, or if the patient has had cancer. Hormones should be used with caution in male patients as there is a risk of gynecomastia.
spironolactonehas been shown to be safe when applied topically, but its effect on oral estrogen-dependent malignancies remains controversial. There are insufficient data to state that topical
finasteride is safe.A number of side effects have been reported with oral finasteride, including depression, erectile dysfunction, and headaches.
Latanoprostapplied topically (or on the eyelashes) has no reported side effects, but it is advisable to avoid this treatment when glaucoma and keratitis are suspected. Finally, topical
minoxidilis reported to be contraindicated in pheochromocytoma and may cause scalp dryness and flaking.
Androgenetic Alopecia: An Injectable with Proven Effectiveness







Add a comment