Thyroid neoplasms are the second most common place among all endocrinological pathology. The main difficulty of this condition lies in the fact that the clinical picture of the disease may be absent for a long time, and only with a significant increase in the size of the thyroid nodule, patients can seek medical help.
The main task of the endocrinologist, at the stage of the patient's initial visit, is to make a timely competent diagnosis of the pathological condition, and to make a differential diagnosis between nodular goiter and oncopathology of the thyroid gland.
Statistical data on neoplasms of thyroid gland
Thyroid nodules are extremely common these days. Even with normal sizes of the thyroid gland, in more than 50% of cases, nodular formations are determined in it with ultrasound diagnostics.
Follow us on Instagram!
This problem is especially relevant today, so according to the latest data, it became known that the oncogenic effect of radioactive radiation affects the state of the thyroid gland no earlier than 20 years from the moment of exposure. After the accident at the Chernobyl nuclear power plant in 1986, a significant percentage of the population was exposed to high radiation doses.
But still, it is known that thyroid cancer accounts for less than 10% of all neoplasms of the thyroid gland, and more than 90% of such pathology as nodular non-toxic goiter. Most often, women over 30 years old are exposed to nodular goiter, which indicates the need for preventive examinations of the thyroid gland for this category.
Causes of thyroid nodules
The main reason for the formation of thyroid nodules is iodine deficiency, which a person must receive from food. According to WHO, the daily intake is considered to be at least 200 micrograms of iodine, mainly from iodized salt and seafood.
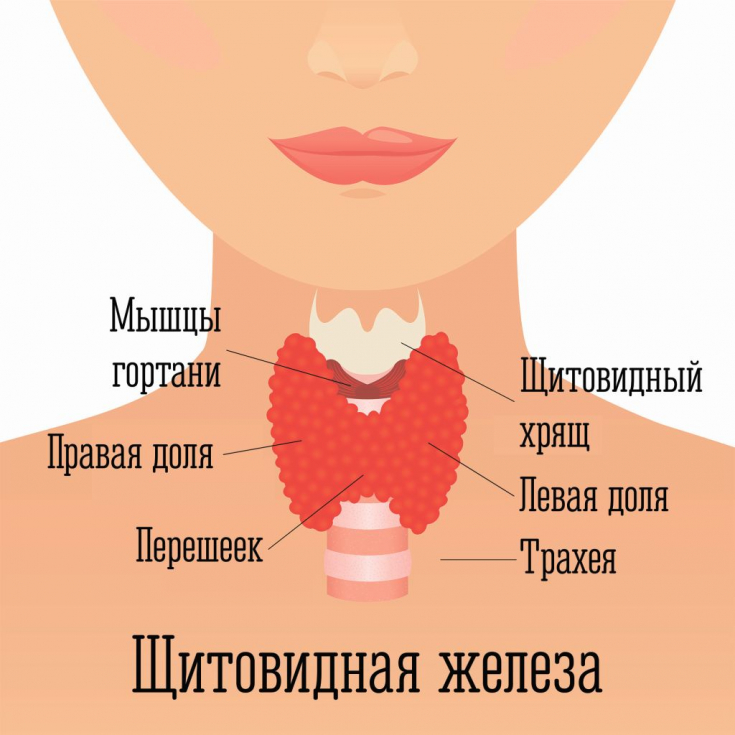
With insufficient intake of iodine in the body, the thyroid gland produces a smaller amount of thyroid hormones necessary for the body, which necessitates an increase in the production of thyroid-stimulating hormones, and, as a result, compensatory growth of thyroid tissue. This is the so-called goiter effect. Also in the etiology of nodular goiter, genetic factors, a previous bacterial or viral infection, have a certain significance.
Clinical picture of nodular non-toxic goiter
The symptomatology of nodular goiter directly depends on the size of the formation. Small nodes, up to 2 cm in size, often do not manifest themselves clinically, they are not determined either visually or by palpation, and are detected by chance during ultrasound or tomography of the cervical spine.
Early signs of nodular goiter may be general manifestations of energy metabolism disorders, such as weakness, drowsiness, fatigue, headache, since thyroid hormones play an important role in the regulation of energy metabolism in the body.
When the knot reaches a large size, it is visualized, deforms the anterior neck and can cause discomfort to the patient. Very rarely, symptoms such as dysphagia (difficulty swallowing) and difficulty in breathing may occur, & nbsp; which is associated with compression of the trachea and esophagus by very large nodes developing from dystopic thyroid tissue.
Diagnosis of thyroid nodules
As mentioned above, physical methods of examining the thyroid gland are not effective enough, since it is impossible to determine small thyroid nodules by palpation, and, moreover, palpation does not provide sufficient information about the functional state of the gland.
Gestational diabetes mellitus is a problem in pregnant women
If a neoplasm in the thyroid gland is detected by palpation, or if it is suspected, an ultrasound examination of the thyroid gland should be performed.
This diagnostic method will reliably indicate the location and exact dimensions of the thyroid nodule, as well as its structure, since a neoplasm of the thyroid gland can be oncological or cystic. Determination of thyroid hormones helps confirm the diagnosis. With nodular non-toxic goiter, a decrease in the concentration of thyroid and an increase in the concentration of thyroid-stimulating hormones of the thyroid gland will be characteristic. Fine-needle aspiration puncture biopsy (FNAB) remains the gold standard in the differential diagnosis of thyroid neoplasms.
The indications for a needle biopsy are the following:
- complicated family history (presence of thyroid cancer in one of the close relatives);
- availability of patient exposure data;
- ultrasound signs of thyroid cancer;
- Large neoplasms of the thyroid gland (more than 2 cm)
Therapeutic tactics for nodular non-toxic goiter
The choice of method for treating thyroid nodules directly depends on their size. In the presence of small nodes that do not cause discomfort to the patient, & nbsp; as well as diagnostic confirmation of benign & nbsp; their origin, can be limited to conservative methods of treatment.
After determining the levels of thyroid hormones, the patient is transferred to hormone replacement therapy.
The daily dose of drugs is calculated strictly individually, taking into account factors such as the patient's age, body weight, individual tolerance of the drug, and the presence of any concomitant diseases. An important point is the correction of the patient's diet. It is necessary to increase the intake of iodine in the body, which is achieved by increasing the consumption of products such as sea fish, seaweed, iodized salt, honey and rosehip decoctions, wheat bran.
If necessary, iodine therapy is used.
The decision on surgical treatment is also made strictly individually according to the following indications:
- large knots producing a compression effect on the trachea and esophagus;
- cosmetic defects in young patients associated with the presence of a node;
- impossibility to exclude the tumor nature of the thyroid nodule.
The volume of surgical intervention is determined in accordance with the size of the thyroid neoplasm. Often, it is sufficient to perform enucleation of the node or resection of a part of the affected lobe of the thyroid gland with a node. Patients with an established diagnosis of nodular non-toxic goiter are subject to long-term dispensary observation by an endocrinologist.







Add a comment