Viruses cause about 8% of all pneumonia cases. The results of recent studies show that viruses play an important role, causing about 13-50% of cases of respiratory diseases, and 8-27% falls on mixed bacterial-viral infections. The most prone to the development of viral pneumonia are older people and patients with existing concomitant chronic diseases.
Find out in the article onestet-portal.comwhat are the differences in clinical symptoms for different types of viral pneumonia.
- Clinical presentation in viral pneumonia
- Distinction of symptoms in viral pneumonia
- The most common pathogens in viral pneumonia
Clinical picture of viral pneumonia
Viral pneumonia most commonly affects infants, young children, and the elderly. Thus, the results of a study of a patient population for viral pneumonia show that the virus is the second etiological cause (after Streptococcus pneumoniae) of the development of pneumonia, the frequency of which is 13-50%.
Follow us on Instagram!
The clinical picture of viral pneumonia depends on the causative agent of the disease. Thus, etiologically different viral pneumonias usually occur at specific periods of the year among certain population groups or among individuals with concomitant cardiopulmonary or immunodeficiency diseases.
Read also: Coronavirus in the world. Panic or danger? A French Perspective on the Epidemic
The most common symptoms of all viral pneumonias are fever, chills, non-productive cough, rhinitis, myalgia, headache and fatigue. The symptoms of viral pneumonia are very similar to those of bacterial pneumonia, although some studies show that the incidence of chest pain and the severity of the disease are less pronounced with viral pneumonia. Important in the diagnosis of AP is the determination of immunization status, travel history and possible contact with a sick person.
Different symptoms in viral pneumonia
In patients with immunodeficiency diseases, timely recognition of the clinical symptoms of viral pneumonia, existing risk factors and new clinical changes is important. A typical viral pneumonia caused by the influenza virus is manifested by a sudden onset of fever, chills, myalgia, arthralgia, cough (mostly unproductive), tonsillitis and rhinorrhea. The incubation period is 1-2 days and the symptoms last about 3-5 days.

General constitutional symptoms: fever, non-productive cough, rhinitis, myalgia, severe headache mainly in the frontal region, weakness. When examining the patient, you can detect: tachypnea / shortness of breath, tachycardia / bradycardia, wheezing in the lungs (dry / wet), participation in the act of breathing of auxiliary muscles (retraction of the intercostal spaces), areas of dullness during percussion of the lungs, weakened breathing, concomitant pleurisy, pleural friction noise.
Read also: All you need to know about vaccination
Influenza pneumonia
Influenza viruses are the most common cause of viral pneumonia. Primary influenza pneumonia is manifested by persistent symptoms of cough, headache in the forehead, myalgia and general malaise for more than 3-5 days. Symptoms of influenza pneumonia may worsen as the disease progresses (symptoms of respiratory failure such as cyanosis and shortness of breath).
Follow us on Facebook!
Respiratory syncytial viral pneumonia (RSVP)
Respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) is the most common cause of lower respiratory tract infection in newborns/children, and the second most common cause of viral pneumonia that affects adults. Patients with RSVP usually present with fever, nonproductive cough, otalgia and dyspnoea on physical examination, and present dry/moist rales.
Parainfluenza virus (HSV)
HSV is second only to RSVP as a cause of lower respiratory tract infections in children and pneumonia/bronchiolitis in neonates
One of the specific symptoms that doctors pay attention to in case of coronavirus infection is the loss of smell.
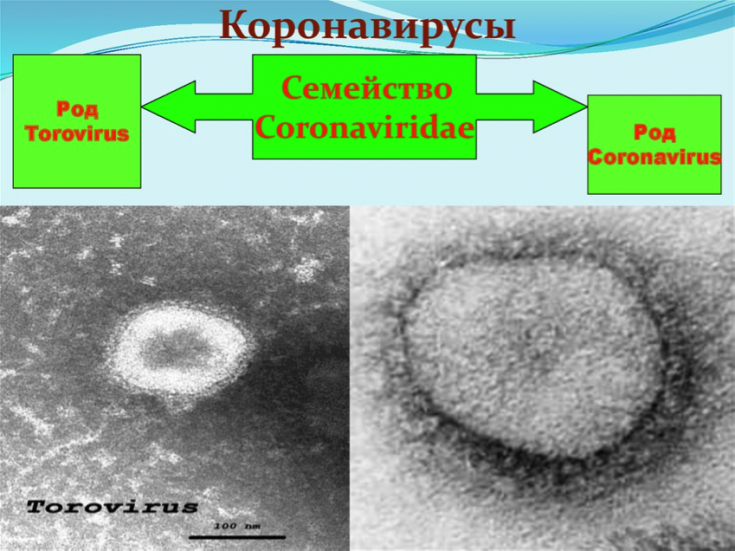
Coronavirus
When the respiratory system is affected by coronavirus, shortness of breath, painful dry cough, shortness of breath occur ˗ this requires the organization of intensive monitoring, intensive care.
The most common pathogens in viral pneumonia
Both DNA and RNA viruses are involved in the etiology of viral pneumonia.
Viral pneumonia pathogen families:
- Adenoviruses.
- Coronaviruses: SARS, MERS, 2019-nCoV (Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, 2020).
-Arboviruses: hantavirus.
- Orthomyxoviruses: influenza virus.
- Papovaviruses: JC virus, BK virus.
- Paramyxoviruses: parainfluenza virus, RSV, human metapneumovirus, measles virus.
- Picornaviruses: enterovirus, coxavirus, echovirus, rhinoviruses.
Read also: At the peak of the season: when is antibiotic therapy needed for pharyngotonsillitis?
Differential diagnosis of viral pneumonia should be carried out with: aspiration pneumonitis / pneumonia, bacterial pneumonia, fungal pneumonia, hantavirus pulmonary syndrome (hantavirus cardiopulmonary syndrome), hydrothorax, etc. Detection of viral antigen is one of the new diagnostic tests, however, the results are usually less sensitive and less specific than results from conventional cell cultures.
More up-to-date information on our YouTube-channel:







Add a comment