To date, modern literature has focused attention on the problem of mental disorders that occur more often in people with dermatological pathologies, such as vitiligo. Vitiligo is an autoimmune disease that is characterized by skin depigmentation. It is well known that autoimmune diseases, including vitiligo, can have an effect on the mental state of the patient. Thus, given the autoimmune nature of vitiligo, it becomes clear that patients with this pigmentation disorder are at greater risk of developing a depressive disorder.
- Reason for the relationship between major depressive disorder and vitiligo
- Study results of patients with major depressive disorder and vitiligo
- Conclusion Reason for the relationship between major depressive disorder and vitiligo
Read also:
Vitiligo treatment: efficacy and safety.The presence of serotonin at the neuronal synapse is associated with major depressive disorder, and based on the concept that both neurons and melanocytes are of ectodermal origin, it has been suggested that melanocytes may also produce serotonin in the skin, which plays a cellular modulating role.
Furthermore, experimental evidence suggests that skin serotonin levels may be reduced in vitiligo patients, and high skin serotonin levels may promote hair repigmentation in northern animals during the summer months.
Follow us onInstagram
!
Thus, there is a definite relationship between serotonin and melanocytes, which explains the nature of pigmentation disorders in patients with

Analyzing the results of the studies, factors such as age, gender, medication intake and the use of topical agents for the treatment of vitiligo were taken into account.
-
Read also:
The result showed a 64% increase in the risk of vitiligo among patients diagnosed with major depressive disorder. Given that patients with psychiatric disorders are more likely to be treated with antidepressants than the general population, it was also necessary to compare these rates. Patients taking antidepressants had a lower risk of developing vitiligo than people not taking antidepressants.
Follow us on
Facebook!
It is possible that treatment of depressive disorders reduces the circulation of pro-inflammatory cytokines and thus reduces the risk of an autoimmune response. Another explanation for the positive effect of antidepressants is the fact that this group of drugs has an immunomodulatory effect on the skin, namely: antidepressants affect the balance of T helpers, which in turn are associated with vitiligo.
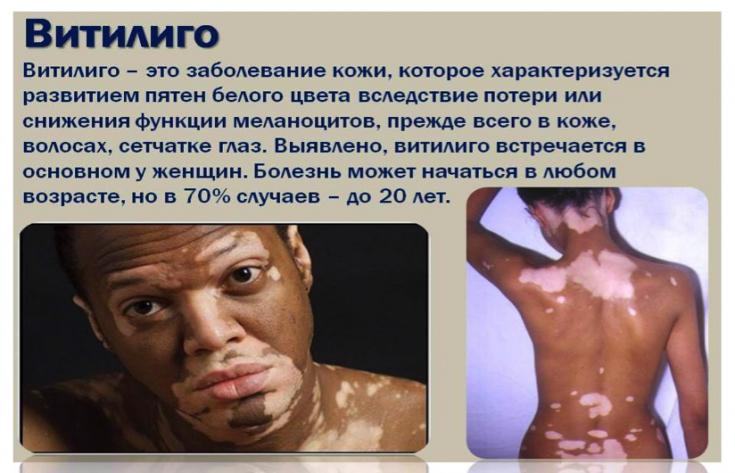 The analysis showed a 27% increase in the risk of major depressive disorder in patients with vitiligo. A recent meta-analysis of the prevalence of depression among patients with vitiligo found a nonsignificant decrease in depressive symptoms for every 10 years of age increase.
The analysis showed a 27% increase in the risk of major depressive disorder in patients with vitiligo. A recent meta-analysis of the prevalence of depression among patients with vitiligo found a nonsignificant decrease in depressive symptoms for every 10 years of age increase.
Read also:
Melanocyte transplantation is a successful treatment for vitiligo.Thus, younger patients (under 30 years of age) had a higher risk of developing mental disorders - 31%, while the risk rate in people after 30 years was 22%.
Conclusion:







Add a comment