Among dermatological diseases manifested by the appearance of vesicles on the skin, the most famous is pemphigus vulgaris (pemphigus). It belongs to chronic dermatostomatitis, has about 97 varieties and accounts for about 1% of all dermatoses. Pemphigus is very difficult, often has disabling consequences, and, unfortunately, has recently become diagnosed more often than usual, which requires attention from the doctor when examining patients with characteristic skin lesions. Find out the main forms of pemphigus vulgaris and the features of their manifestation.
What are the causes of pemphigus vulgaris?
There are many different theories regarding the causes of pemphigus development: neurogenic; violations of water-salt metabolism – water retention and sodium chloride in the skin; bacterial (hematogenous infection); endocrine – predominantly lesion of the adrenal cortex; viral; hereditary; theory of enzyme origin and others.
At present, doctors adhere to the autoimmune theory of the origin of true pemphigus, based on the detection of autoantibodies of the immunoglobulin G class, localized in the intercellular fluid of the stratified epithelium.
The most common form of pemphigus – Pemphigus vulgaris. Pemphigus vulgaris occurs in a severe form with rashes of different sizes of vesicles on the skin and mucous membranes.
Phases of the clinical course of pemphigus vulgaris:
- acute phase;
- severe phase;
- remission phase.
Clinical manifestations of the acute phase of pemphigus vulgaris
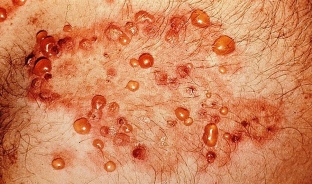
Usual pemphigus vulgaris may begin acutely with the appearance of a large number of tense or flaccid vesicles located on normal skin and mucous membranes. What are the features of blisters in pemphigus vulgaris, read further on estet-portal.com. Quite often, the disease begins with the appearance of individual vesicles on the skin in the area of natural openings, on the scalp or on the trunk. Bubbles ranging in size from a pea to a chicken egg occur in the spiny layer of the epidermis on an unchanged or inflamed mucous membrane and skin.
The blister is filled with a clear yellow-lemon liquid with an admixture of degenerative epithelial cells and a large number of eosinophilic cells. Swollen and infiltrated mucosa has a huge amount of hemorrhages. After 2-3 days, the fluid in the blisters becomes cloudy, the blisters lose their tension, sag, and a "pear symptom" appears.
After 3-5 days, the bladder shell is destroyed, and an eroded, very painful surface opens, which heals slowly, without scar formation, but a brown spot remains.
Nikolsky's symptom is always positive. With pemphigus vulgaris, erosions do not epithelialize for a long time, sometimes for several weeks, becoming covered with bloody and purulent crusts.
Characteristically undulating course of pemphigus vulgaris, when periods of rashes are replaced by periods of remission. When the shells of the bubbles break, erosions occur, which are painful when exposed to temperature and chemical irritants. The phase lasts from several days to several months and even years. In the field of view of the microscope, up to 5-10 Tzank cells are detected. Nikolsky's symptom is not always positive, often mild.
Clinical manifestations of the severe stage of pemphigus vulgaris
With exacerbation of pemphigus vulgaris, rashes of small blisters appear, which often merge. Erosions covered with fibrinous layers bleed and are sharply painful, the mucous membrane is edematous. Symptom Nikolsky expressed. In the field of view of the microscope, up to 30-50 Tzank cells are detected. The general condition of the patient is severe: decreased appetite, insomnia, intoxication, hypersalivation develop, on the red border of the lips erosions appear, covered with bloody crusts. The general condition worsens, cachexia increases, and the patient dies. The disease can pass into the third phase - remission, or preferential epithelialization.
Clinical features of the remission phase of pemphigus vulgaris
The phase of remission, or predominant epithelialization, is characterized by the subsidence of acute phenomena under the influence of corticosteroids. At this time, erosions heal, new blisters occur less frequently, Nikolsky's symptom almost does not appear, Tzank cells are detected in moderate amounts. It should be noted that Nikolsky's symptom is not strictly pathognomonic for pemphigus vulgaris, however, its role in diagnosis and prognosis is great and generally recognized.
The Nikolsky phenomenon in pemphigus vulgaris can manifest itself in three ways:
- if you pull the membrane of the bladder, then the epithelium is exfoliated without visible changes at the same time;
- rubbing of intact skin or scraping it with a blunt instrument between the affected areas leads to rejection of the upper layers of the epithelium;
- rubbing the skin at a distance from the rash causes injury to the upper layers of the epidermis.
New blisters appear even before the old ones heal, the process spreads to the mucous membrane of the pharynx, larynx, nose, causing a specific bad breath. In the oral cavity, it is almost impossible to find typical blisters filled with serous and less often hemorrhagic contents, that is, there is constant trauma to the blisters when the lower jaw and tongue move.
Erosions are often observed, and along the periphery – bubble remnants. In some cases, the main symptom of the disease is the defeat of the mucous membrane of the oral cavity and the red border of the lips; the transition of the process to the skin is prevented by timely adequate treatment of pemphigus vulgaris.







Add a comment