Urticaria appears on the skin in the form of erythematous rashes that look like itchy spots and blisters. Each of the foci exists on the skin for no more than one day. Angioedema is considered a deeper form of urticaria. Physical urticaria appears in response to physical stimuli. These include mechanical trauma, changes in body temperature, water and light. Urticaria, the manifestation of which takes place over 6 weeks, is called acute. Urticaria lasting more than 6 weeks is considered chronic. What are the features of the treatment of urticaria in adults?
General Therapeutic Guidelines for the Treatment of Urticaria in Adults
Urtic urticaria is not associated with any underlying disease. It is neither malignant nor fatal. Urticaria is curable and not contagious, prone to spontaneous remission over a period of several & nbsp; weeks. It is important to explain to the patient that a tedious series of tests will not help the condition.
The patient should be warned to refrain from taking medications that worsen the urticaria. These are non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and histamine liberators.
Elimination diets do not always help in the treatment of urticaria in adults. Therefore, only those products that are proven to be problematic should be excluded.
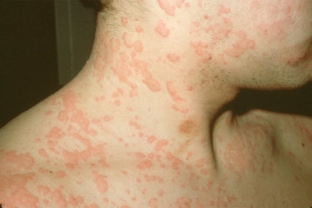
Basics of drug therapy for urticaria in adults
Urticaria is best controlled with adequate doses of H1 – antihistamines. These drugs help reduce itching, also lead to a decrease in the number, duration and size of rashes. Since the patient's body can react differently to drugs, it is sometimes necessary to change antihistamines due to side effects. Sometimes a combination of antihistamines is needed.
Characteristics of antihistamines in the treatment of urticaria in adults:
- Antihistamines are well adsorbed.
- The timing of taking the drug is of great importance and should correspond to the worst condition of the patient with urticaria.
- Drugs have longer half-lives in the elderly, so high doses are not immediately prescribed for the treatment of urticaria in adults.
- Virtually all antihistamines are teratogenic. However, older drugs such as chlorphenylamine are used during pregnancy and lactation.
Treatment of urticaria in adults with second-generation antihistamines
Second-generation antihistamines for the treatment of urticaria in adults are the drugs of choice. Read more about third-generation drugs on estet-portal.com. Second-generation drugs are highly likely to improve the course of urticaria. This group includes cetirizine, acrivastin, loratadine, ebastine, and mizolastine. These drugs block H1 receptors through competitive inhibition. The use of adequate doses does not cause drowsiness, psychomotor reactions and side effects. These drugs at a dose of 10 mg per day are effective in the treatment of urticaria in adults.
The third generation of H1 receptor antagonists is represented by the substance fexofenadine hydrochloride, which is an active metabolite of terfenadine – second generation drug. Fexofenadine is devoid of the cardiotoxic properties of the latter. The recommended dose per day is 180 mg. No side effects or drowsiness were reported.
If sedation is desired by the patient and may be beneficial, first-generation drugs for the treatment of urticaria in adults are appropriate.
Treatment of urticaria in adults with additional groups of drugs
The combination of H1 and H2 receptor antagonists is not used, although in some cases there is some improvement in the condition compared with the use of each drug separately. However, in practice, this combination does not give a clinically significant result.
The addition of mast cell stabilizers (nifedipine or theodillin) to treatment does not increase the effectiveness of treatment for urticaria in adults. When treating chronic urticaria, it is best to avoid systemic corticosteroids, as they become ineffective over a long period of time and their side effects are dangerous.
Thus, there are some aspects that are important to consider in the treatment of urticaria in adults. Therefore, self-treatment of urticaria and other allergic manifestations is unacceptable.







Add a comment