Nail lesions today cause many problems related to the diagnosis of the causes that caused them and the choice of therapy. Unfortunately, systemic antifungal drugs are often unreasonably prescribed for onychodystrophy, which is associated with difficulties in diagnosing. It is very important for a doctor to identify at an early stage those nail lesions that are combined with pathologies of the internal organs, and to refer the patient to the appropriate specialist in a timely manner, since onychodystrophy can be the first manifestations of serious diseases.
Which ones clinical forms of onychodystrophies?
Onychodystrophy – these are trophic disorders that occur with nails under the influence of external and internal factors. Deformation of the nail plates often becomes part of the symptom complex of diseases of the internal organs, which is important when making a general diagnosis, notes estet-portal.com. According to some changes in the nail, many serious diseases can be suspected, and by prescribing an additional examination, these diseases can be detected at an early stage of their development.
Clinical manifestations of onychodystrophies:
- Hippocratic nails;
- onycholysis;
- koilonisia;
- onychogryphosis;
- scleronychia;
- transverse groove of the nail;
- onychomadesis;
- longitudinal grooves of the nail;
- Onychoshisis.
Causes and manifestations of the main forms of onychodystrophies
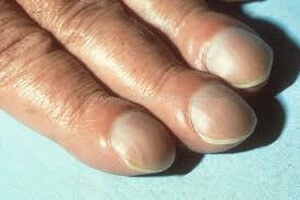 Hippocratic Nails – the form of the lesion, in which the nails thicken slightly and at the same time soften, acquire a slightly convex hour glass shape and a slightly curved free edge. Often found in diseases of the lungs and heart, neuropsychiatric disorders, ulcerative colitis, leukemia, venous congestion. Sometimes this form of nails can be hereditary.
Hippocratic Nails – the form of the lesion, in which the nails thicken slightly and at the same time soften, acquire a slightly convex hour glass shape and a slightly curved free edge. Often found in diseases of the lungs and heart, neuropsychiatric disorders, ulcerative colitis, leukemia, venous congestion. Sometimes this form of nails can be hereditary.
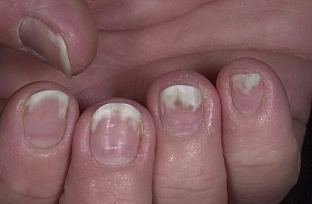 Onycholysis – it is the inability of the nail to adhere to the nail bed. With such onychodystrophy, the nail is separated from the bed from the free edge towards the hole, most often the separated part is about half of the entire plate and acquires a grayish color. It can be both partial and total, develops with endocrine disorders, skin diseases.
Onycholysis – it is the inability of the nail to adhere to the nail bed. With such onychodystrophy, the nail is separated from the bed from the free edge towards the hole, most often the separated part is about half of the entire plate and acquires a grayish color. It can be both partial and total, develops with endocrine disorders, skin diseases.
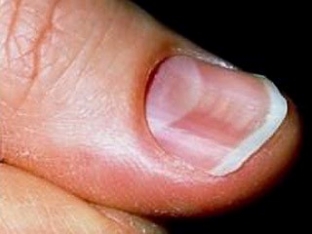 Koilonychia – deformation in the form of a bowl-shaped depression on the surface of the nail plate. More often, such onychodystrophy is observed on the second and third fingers, it can be congenital or develop against the background of anemia, severe infections, rheumatoid arthritis, ulcerative colitis.
Koilonychia – deformation in the form of a bowl-shaped depression on the surface of the nail plate. More often, such onychodystrophy is observed on the second and third fingers, it can be congenital or develop against the background of anemia, severe infections, rheumatoid arthritis, ulcerative colitis.
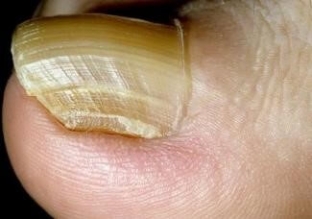 Onychogryphosis – a sharp curvature, increase and thickening of the nail, when it begins to resemble a bird's beak in shape. Usually affects the big toes. The nail plate changes its texture and color, becomes convex, bumpy, very dense, yellowish-brown or even almost black. The tip goes beyond the finger and bends down, sometimes even twisting in a spiral. The cause of this pathology may be chronic irritation of the nail or its injury, flat feet, as well as onychomycosis or diseases associated with circulatory disorders in the lower extremities.
Onychogryphosis – a sharp curvature, increase and thickening of the nail, when it begins to resemble a bird's beak in shape. Usually affects the big toes. The nail plate changes its texture and color, becomes convex, bumpy, very dense, yellowish-brown or even almost black. The tip goes beyond the finger and bends down, sometimes even twisting in a spiral. The cause of this pathology may be chronic irritation of the nail or its injury, flat feet, as well as onychomycosis or diseases associated with circulatory disorders in the lower extremities.
 Scleronychia – a peculiar type of nail hypertrophy, in which they abruptly stop growing, completely lose their elasticity, thicken, turn yellow (sometimes to a brown tint) and gradually separate from the nail bed. The process with this onychodystrophy simultaneously covers all fingers, lasts for months, sometimes it can heal spontaneously. The cause of development is most often long-term treatment with keratolytic drugs for onychomycosis.
Scleronychia – a peculiar type of nail hypertrophy, in which they abruptly stop growing, completely lose their elasticity, thicken, turn yellow (sometimes to a brown tint) and gradually separate from the nail bed. The process with this onychodystrophy simultaneously covers all fingers, lasts for months, sometimes it can heal spontaneously. The cause of development is most often long-term treatment with keratolytic drugs for onychomycosis.
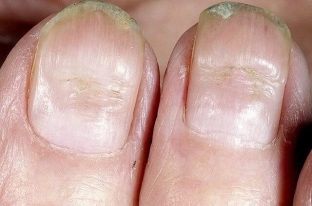 Transverse groove of the nail – one of the most common dystrophies of the nail, which is also called Bo's furrow. This is an arcuate depression in the form of a groove that crosses the surface of the nail across – from one roller to another Its appearance can provoke rashes on the back of the hands with eczema and psoriasis. It may appear 1-2 weeks after severe stress or an infectious disease.
Transverse groove of the nail – one of the most common dystrophies of the nail, which is also called Bo's furrow. This is an arcuate depression in the form of a groove that crosses the surface of the nail across – from one roller to another Its appearance can provoke rashes on the back of the hands with eczema and psoriasis. It may appear 1-2 weeks after severe stress or an infectious disease.
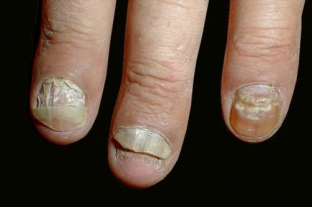 Onychomadesis – separation from the bed of the entire nail plate, starting from the proximal section, and most often only on the thumbs and toes.
Onychomadesis – separation from the bed of the entire nail plate, starting from the proximal section, and most often only on the thumbs and toes.
The main cause of this onychodystrophy is, as a rule, circulatory disorders and pathology of the nail matrix, but can be provoked by staphylococci, streptococci, some types of fungi and diseases associated with these microorganisms.
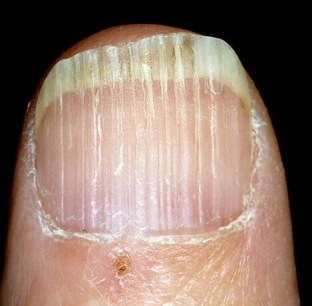 Longitudinal grooves of the nail – appear when the nail is traumatized and when blood circulation is disturbed, but can serve as a symptom of coronary insufficiency, diseases of the spinal cord, and even HIV infection. Sometimes they occur with psoriasis, lichen planus, and also with rheumatoid arthritis. Longitudinal grooves can be located along the lateral edges of the nail or occupy its entire surface, be continuous or consist of several parts like beads from beads.
Longitudinal grooves of the nail – appear when the nail is traumatized and when blood circulation is disturbed, but can serve as a symptom of coronary insufficiency, diseases of the spinal cord, and even HIV infection. Sometimes they occur with psoriasis, lichen planus, and also with rheumatoid arthritis. Longitudinal grooves can be located along the lateral edges of the nail or occupy its entire surface, be continuous or consist of several parts like beads from beads.
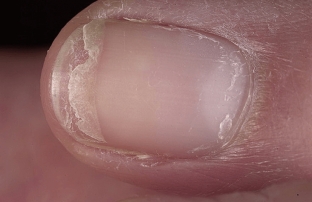 Onychoschisis – splitting of nails, which women most often complain about, often doing manicures using various varnishes and removing it with acetone-containing products. The nail with onychodystrophy grows normally to the free edge, and then splits parallel to it into several layers. Further, the nail breaks off or grows in several thin layers; if you cut it – looks normal, but after growing back it exfoliates again.
Onychoschisis – splitting of nails, which women most often complain about, often doing manicures using various varnishes and removing it with acetone-containing products. The nail with onychodystrophy grows normally to the free edge, and then splits parallel to it into several layers. Further, the nail breaks off or grows in several thin layers; if you cut it – looks normal, but after growing back it exfoliates again.
Difficulties in the treatment of onychodystrophies, general and specific treatment
The complexity of the treatment of onychodystrophies is explained by many factors. Firstly, it is difficult to determine the cause of the disease that caused the damage to the nails. Secondly, nail treatment is usually very long, the effect does not come soon, which reduces the adherence of patients to treatment.
Therapy should include, in addition to drugs and procedures, a diet high in protein foods, as well as dishes containing gelatin.
For the general treatment of damaged nails, drugs of different pharmacological groups are used – antihistamines, vascular, quinoline drugs, and in severe cases – corticosteroids, cytostatics, aromatic retinoids.
Basic therapy for nail lesions is carried out with the help of combined vitamin-mineral complexes that can accelerate the growth of nail plates. Widespread use in the treatment of nail injuries found hardware methods – UV, PUVA therapy, electrophoresis.
Thus, nail lesions require an in-depth study using dermatoscopy and other methods in order to diagnose the cause of onychodystrophy at an early stage, as well as differentiated treatment depending on the type of lesion and the causes that caused it.







Add a comment