Bladder stones are one of the most widespread problems of modern urology. Patients of absolutely different ages turn to the urologist with characteristic complaints, and according to the results of examinations, they are diagnosed with urolithiasis. Nevertheless, the localization of calculi in the bladder determines some features of the course, diagnosis and treatment of this type & nbsp; urolithiasis. Bladder stones can cause serious complications and therefore require timely detection and effective treatment.
Peculiarities of diagnosis and treatment of bladder stones
Most often, bladder stones occur in men, which can be explained by their frequent pathological changes in the prostate gland, which disrupt the normal structure of the bladder and create conditions favorable for the formation of stones in it. For the same reason, older men are more prone to the formation of bladder stones. Stones in the bladder can be primary, that is, formed directly in the cavity of the bladder, as well as secondary, which descend into the bladder from the kidney. Kidney and bladder stones do not differ in their structure: they can be oxalate, urate, fastate and mixed stones.
Bladder stones:
- characteristic symptoms of bladder stones;
- features of the diagnosis of stones in the bladder;
- effective methods of treating bladder stones.
Characteristic symptoms of bladder stones
In the presence of stones in the bladder, a fairly typical clinical picture develops. The stone often damages the wall of the bladder, resulting in pain, which can be aggravated by active movements of the patient, as well as during exercise. The patient constantly feels the desire to empty the bladder, but very often urination is difficult, during straining only a few drops of urine are excreted. A change in body position often helps to empty the bladder. A common symptom of bladder stones is hematuria – excretion of blood in the urine. In case of accession of an infectious process, a clinical picture of cystitis occurs – frequent urination, accompanied by painful sensations, nocturia, gross hematuria.
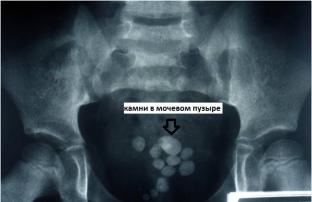
Features of the diagnosis of bladder stonesThe diagnostic process of bladder stones is not difficult, since the characteristic clinical picture often helps to suspect this particular pathology. Of the additional research methods, X-ray and ultrasound examinations, as well as cystoscopy are most often used.
- Plain radiography visualizes the shadow of a calculus in the bladder cavity, with the exception of urate stones – they do not give a characteristic shadow on the plain radiograph;
- Ultrasound examination of the bladder stone is defined as a well-designed, echopositive mass. Ultrasound helps determine the shape, size and number of calculi;
- Cystoscopy is the most effective method for diagnosing bladder stones, as it can directly determine both the characteristics of the formed stones and the condition of the bladder itself.
To treat urolithiasis in the presence of stones in the bladder, the following methods are most often used:
- transurethral extraction of small stones;
- crushing of stones using mechanical, electro-hydraulic or ultrasonic methods, followed by washing out and extraction of fragments;
- performing cystolithotomy – open surgery for large stones.







Add a comment