Deficiency of thyroid hormones can cause a significant decline in the quality of life: from depression and neuroses to hypothyroid coma. In this article on estet-portal.com, we will consider one of the most common and relevant endocrinological pathologies of our time - hypothyroidism.
Due to the polymorphism of the clinical picture of hypothyroidism, patients with thyroid hormone deficiency can be observed by doctors of various specialties for a long time.
For more information about what are the causes of thyroid hormone deficiency, as well as how to properly treat this disease, based on its causes, read this article.
Causes for the development of pathology: permanent and transient types of hypothyroidism
The state of thyroid hormone deficiency can be divided into two groups: permanent and transient hypothyroidism.
Depending on the etiological cause, permanent hypothyroidism can be primary or central.
Primary hypothyroidism is the cause of permanent hypothyroidism in 95% of cases.
The most common cause of primary hypothyroidism is autoimmune thyroiditis, which develops as a result of the synthesis of antibodies to thyroperoxidase. Other causes of primary hypothyroidism include thyroid surgery and radioiodine therapy.
Central hypothyroidism is the cause of permanent hypothyroidism in 5% and develops due to deficiency or lack of influence of thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH).
Transient hypothyroidism can occur in several cases, among which should be highlighted:
1. Subacute thyroiditis;
2. Hypothyroidism in the postpartum period (usually within 4-8 months after birth). In this case, the pathology most often manifests with transient thyrotoxicosis.
3. At the background of taking certain medications, in particular lithium and amiodarone.
The above reasons for the development of transient hypothyroidism must be remembered in order to avoid errors in the diagnosis.
You may be interested in: How to deal with injection procedures for hypothyroidism in women
Features of the course of hypothyroidism: symptoms and clinical picture of the disease
As already mentioned, hypothyroidism is characterized by a wide variety of clinical symptoms. Deficiency of thyroid hormones leads to a slowdown in almost all metabolic processes in the body. For severe hypothyroidism, mental disorders are characteristic: abulia, depressive disorders, memory impairment, a constant feeling of fatigue.
Follow us on Telegram
Hypothyroidism leads to slow speech and motor functions, bradycardia, weight gain, and constipation. Patients often complain of a feeling of severe muscle weakness. Objectively, their skin becomes dry, pale and cold to the touch. The hair can become coarse and cause hair loss.
In women, thyroid hormone deficiency leads to menstrual irregularities. In some cases, hypothyroidism can cause amenorrhea, infertility, hyperprolactinemia.
In older patients, in some cases, hypothyroidism can even mimic dementia.

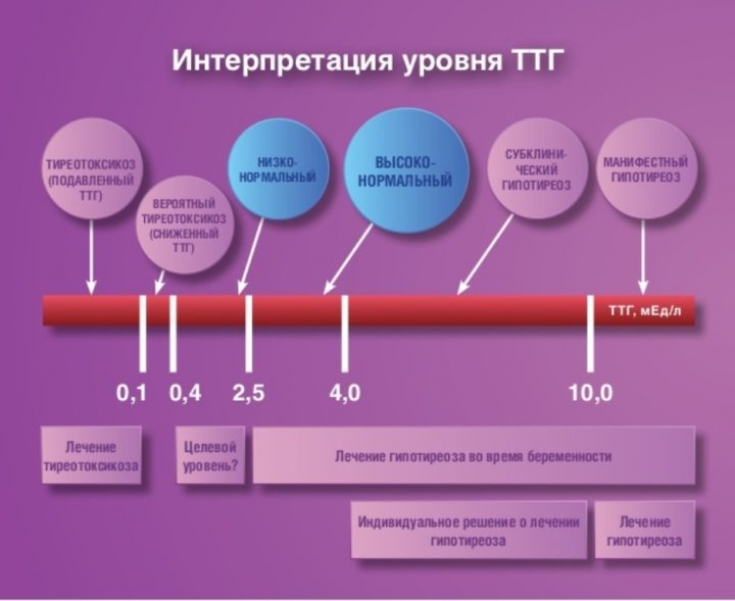
Hormonal therapy for subclinical and clinical hypothyroidism
Treatment of subclinical hypothyroidism. Indications for the treatment of subclinical hypothyroidism are an increase in TSH levels by 10 times or more, as well as hypothyroidism during pregnancy.
If there is a slight increase in TSH levels, therapy should be started if there are clinical symptoms of hypothyroidism (even mild ones), pregnancy, identification of TSH antibodies, goiter and hypercholesterolemia.
For young patients, the initial dose of thyroxin is 50-100mcg/day.
If the patient has been deficient in thyroid hormones for a long time, then hormone therapy should be prescribed gradually: thyroxine is started from the minimum dose and increased by 25 mcg every two weeks until reaching 100 mcg / day.
The starting dose of thyroxine depends on how long the patient has been deficient in thyroid hormones.
The maintenance dose depends on the weight of the patient. The usual maintenance dose is 100-200 mcg/day. The doses of drugs that are used in subclinical hypothyroidism are lower than clinical ones.
Read also: Main Causes and Consequences of Elevated FSH
TSH is checked no earlier than 4 weeks after the last increase in the dose of hormones. After that, the maintenance dose of thyroxine is changed to the required level.
After reaching a constant maintenance dose, TSH is checked every 1-2 years.
Peculiarities of using thyroxine replacement therapy in special cases
In elderly patients, as well as in persons with coronary heart disease, the initial dose of thyroxine is 25 mcg / day. The dose is gradually increased at intervals of 3 to 4 weeks. In this case, the maintenance dose is often below the standard, and the concentration of TSH is close to the upper limit of the control level.
In conflicting cases, for example, if hypothyroidism may be transient, repeat TSH levels at the sixth week after stopping treatment. If the TSH level is above the reference level, then the patient needs to receive continuous thyroxine replacement therapy.
Some medications, especially iron and calcium supplements, interfere with the absorption of thyroxine, so these medications should not be taken within 4 hours of taking thyroxine.
Thank you for staying with estet-portal.com. Read other interesting articles in the "Endocrinology" section. You may also be interested in : How to recognize diabetic neuropathy
Adapted from EBM Guidelines "Hypothyroidism"







Add a comment