Dry mouth and swelling in the place where the salivary glands are located – these are the first symptoms that begin with the inflammatory process. The causes of inflammation of the salivary glands are associated with infection of the saliva in the mouth, which then carries the infection further through the ducts. Inflammation of the salivary glands can be a primary disease, although it develops to a greater extent as a secondary one, as a complication after an illness, or is a symptom of another ailment. Most often, the disease proceeds unilaterally, although there are cases of bilateral inflammation.
Description of inflammation of the salivary glands
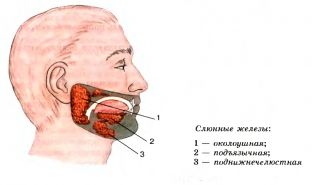
Inflammation of the salivary glands, or sialoadenitis, develops most often in children, but can also affect a healthy adult. Three pairs of large salivary glands are located in the body of each person and there are also many salivary ducts that transport secretions to the mouth and help soften and wet food to turn into a viscous lump. If the salivary glands cannot fully perform their direct functions, then chewing or swallowing food becomes painfully difficult.
3 pairs of salivary glands:
- The parotid pair of salivary glands is located in the region of the auricle. If these glands become inflamed, then the disease is called parotitis or mumps.
- Salivary submandibular glands – are located in the region of the posterior teeth under the jaw.
- Salivary sublingual glands – are located at the bottom of the entire oral cavity, under the mucous membrane.
What are the main causes of inflammation of the salivary glands
When pathogenic bacteria or fungi enter the body, an inflammatory process begins. Sialoadenitis can be primary or secondary and has the following causes:
- the presence of an infectious disease: scarlet fever, measles, influenza;
- pathological narrowing of the stenon's duct;
- surgery resulting in dehydration;
- formation of stones in the duct of the salivary gland;
- formation of a blockage in the duct.
Symptoms and diagnosis of sialadenitis
Inflammation can occur in each of the three glands, but they are united by a common symptomatology:
- dry mouth due to a sharp decrease in saliva secretion;
- sharp or aching pain in the area of the salivary gland, pain can also be felt that radiates to the ear, neck, head;
- pain during chewing, swallowing or force is required to open the mouth;
- redness, swelling is observed at the location of the salivary gland;
- not quite a pleasant taste in the mouth;
- a dense neoplasm is felt at the site of inflammation;
- possible appearance of pus in the ducts;
- feeling of pulsation and pressure in the area of the gland – a clear sign of pus;
- weakness, chills;
- Temperature rises to 39 degrees or more.
If we talk about mumps (mumps), then this disease is contagious, transmitted by airborne droplets. Therefore, immediately after the appearance of the first signs, it is worth isolating from healthy people so as not to provoke the spread of infection. The causative agent of parotitis can affect not only the salivary glands, but also others: genital, mammary or pancreas. If treatment is not started in time, suppuration develops in the inflamed salivary glands, which can lead to a rupture at the site of the abscess.
A therapist or dentist can diagnose the development of inflammation of the salivary glands on examination. At the initial stage, there may not be enough obvious and painful sensations near the salivary glands. It may feel like a little tugging on the neck or a sore throat. Most often, such inflammation of the salivary glands proceeds quickly and manifests itself with rich symptoms, so the doctor will be able to suspect sialadenitis and prescribe a specific diagnosis: CT (computed tomography), MRI (magnetic resonance imaging), ultrasound.
How to properly treat inflammation of the salivary glands
Treatment of inflammation of the salivary glands is performed on an outpatient basis. It is recommended to adhere to strict bed rest, to provide the necessary balanced nutrition so that the food is small and viscous (does not cause discomfort when swallowing). Since during the course of the disease the body experiences severe intoxication, therefore, it is necessary to drink plenty of water, always warm. To ensure a quick outflow of saliva, it is recommended to hold a slice of lemon in your mouth before eating. It is also shown to lean on acidic foods so that more saliva is released. To reduce pain, you can take anti-inflammatory drugs, which also lower the body temperature. Patients can be prescribed physiotherapy procedures: UHF, Sollux. If there was a severe abscess in the area of the affected salivary gland,






Add a comment