As children, we often heard from parents and teachers the proverb «repetition – mother of learning", "the work of the master is afraid" etc. However, why, from a scientific point of view, constant training and practice favorably affects the state of the brain? A significant role in this is played by a special substance – myelin, which forms the sheath of the axons of nerve cells. You will learn more about the process of myelination and training in the article prepared for you by estet-portal.com.
The adult human brain never stops developing
When we learn a new skill, whether it's programming, playing chess, rollerblading or dancing, we change our brains without realizing it.
Scientific research has shown that the brain is incredibly plastic, meaning it doesn't fully form at age 25 and doesn't stay the same for the rest of your life. While certain things (such as language) are much easier for children than for adults, there is plenty of evidence that the neural network of the adult brain can also be transformed.
But how does it happen? To perform a certain task, we need to activate certain areas of the brain. The human brain coordinates a complex set of responses, including motor function, visual and auditory information processing, speech, and more. At first, we may stumble, forget some things and words, but practice helps us to cope with the task better, while feeling more natural and comfortable.
Continuous learning helps the brain to optimize the execution of a set of coordinated actions through the process of myelination – the formation of a layer of myelin around the axons of nerve fibers.
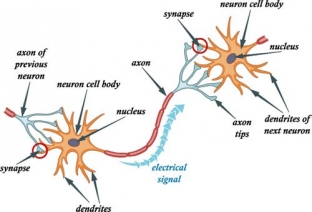
The role of myelin in the speed of transmission of nerve impulses
Neurons – the basic building blocks of the brain. A neuron consists of dendrites that receive signals from other neurons, a cell body that processes these signals, and an axon – a long "cable" that connects and interacts with the dendrites of other neurons. When different parts of the brain interact and coordinate their activity with each other, they send nerve impulses – electric charges that pass along the axon of a neuron and are transmitted to the next neuron in the chain.
When a neuron "fires up", the so-called domino effect is triggered: this process affects the number of neurons needed to transmit a signal to the end point. All this happens incredibly quickly, which allows us to react with lightning speed to this or that event.
Sometimes we refer to our brain as gray matter because the cell bodies of neurons give it that color, but it is also known to have white matter, which makes up about 50% of the brain.
So, the white matter – these are axons covered with a myelin sheath, giving them a white color. Myelin – consisting mainly of fats (by 75%) and proteins, a substance that covers the axons of nerve cells. Scientists have found that myelination increases the speed and strength of nerve impulses, "forcing" an electrical charge to jump through the myelin sheath to the next open section of the axon.
Myelination increases the speed and strength of nerve impulses, "forcing" an electrical charge to jump through the myelin sheath to the next open section of the axon.
In other words, myelin allows electrical signals to "teleport" instead of directly following the axon, allowing for ultra-fast transmission of nerve impulses.
Practice, nerve activity and myelin synthesis
We found that the myelin sheath – an important component of the brain structure, which provides faster transmission of nerve impulses. But is it possible to somehow "increase" myelin around axons?
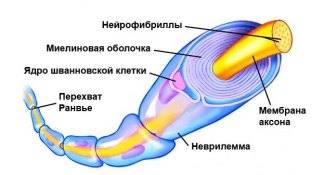
It is important to understand that the process of myelination occurs naturally, predominantly during childhood. Children – "myelin generators" that absorb information about the world around them like sponges. With age, this ability decreases, but does not disappear completely, that is, in adults, the myelination process also proceeds, only more slowly, and efforts to "build up" more myelin is needed.
Children – "myelin generators" that absorb information about the world around them like sponges.
Scientists believe that two types of glial cells in the brain play a role in the creation of new myelin. The first type – astrocytes that monitor the activity of the axons of nerve cells. A large number of repeated signals from a particular axon induces the astrocyte to release chemicals that stimulate the second type of cells – oligodendrocytes – to the production of myelin, enveloping the axon.
Because constant practice, whether it's writing articles for a blog, learning a foreign language, origami, knitting, or any other skill you learn, helps create new patterns of electrical signaling between neurons. Over time, this starts the process of myelination of the corresponding axons and increases the strength and speed of signaling.
Why myelin helps nerve cells work better
How does myelin improve brain function? We can certainly say that myelin increases the strength and speed of transmission of nerve impulses, which helps us in learning.
One of the proofs of this is the images of the brains of professional musicians. A lot of research has been done on the differences between the brains of musicians and ordinary people. One of them used diffusion MRI technology, which provides information about the tissues and fibers of the scanned area of the brain in a non-invasive way.
The researchers concluded that a certain amount of practice during childhood and adolescence among pianists was associated with increased white matter density in areas of the brain responsible for motor skills, visual and auditory information processing, compared with ordinary people. There was also a direct correlation between hours of practice and white matter/myelin density.
Constant learning new – the best way to stimulate myelin synthesis.
Another argument in favor of the proverb "it's never too late to learn" is what happens in the absence of activity that promotes myelin formation. Demyelination – known factor playing a role in the development of multiple sclerosis and other neurodegenerative diseases. Because myelin – an important substance for maintaining the functions of the brain and, accordingly, the body.
Read also: Neurobiology tricks: how to make your brain happier
It is important to understand that not only the quantity but also the quality of practice is important for myelin formation. To improve your skills, of course, it is important not only to mindlessly repeat the same action, but also to focus on how well you are doing a task, develop ways to optimize the learning process, try and put efforts to become better in any business. . Learn new things, develop yourself, master new skills – all this will help your brain to work as long and better as possible!






Add a comment