Oophoritis – this is an inflammatory process in the ovaries, which most often develops due to infection. Quite often, oophoritis is accompanied by inflammation of the fallopian tubes, provoking the appearance of tubo-ovarian formations. This disease is often the cause of the development of various pathologies of the female reproductive system, and in some cases leads to infertility or ectopic pregnancy. You can read about other pathologies of the reproductive system on the website estet-portal.com, and now let's try to figure out what this disease is, for what reasons it occurs and how it proceeds & nbsp; treatment.
Pathogeny of oophoritis and causes of the development of the disease
Most often oophoritis occurs due to infection with pathogens. In response to an infection, the body begins to produce a large number of white blood cells, which, in turn, provoke the production of prostaglandins. Prostaglandins are cellular mediators of inflammation – active biological substances that perform the following tasks:
- irritate pain receptors;
- expand blood vessels;
- increase exudative processes;
- increase hyperthermia in the affected area;
- increase the speed of movement of leukocytes;
- increase puffiness.
In 90% of cases, oophoritis accompanies inflammation of the fallopian tubes – salpingitis. In some cases, inflammation leads to pyovar – extensive purulent fusion of ovarian tissues.
Continuous inflammation makes it impossible for damaged cells to recover. Instead, the areas that were affected by oophoritis are replaced by connective tissue.
This process forms scars and changes the structure of organs, provoking many pathologies, including often infertility and ectopic pregnancy.
Reason there is a lot of development of oophoritis. Most often, the disease occurs in connection with:
- genital or non-specific bacterial infection;
- diseases of the endocrine gland;
- various pathologies of the genitourinary system.
It is worth noting that smoking, hypothermia, frequent stress and overwork can contribute to the development of the disease, as they reduce the protective functions of the body.
Symptoms of oophoritis at different stages of development
There are three stages in the development of oophoritis:
- Sharp – less than 3 months have passed since the onset of the disease.
- Subacute – the disease lasts from 3 months to six months.
- Chronic – the disease has been going on for more than six months.
The stage of the disease determines the symptoms of the disease. spicy oophoritis accompanied by:
- high body temperature;
- loss of appetite;
- bouts of nausea and vomiting;
- drawing pains in the lower abdomen and in the lumbar region;
- mucous or mucopurulent discharge from the genital tract.
The subacute and chronic forms are characterized by mild symptoms. Among them are:
- periodic pulling pain in the abdomen;
- Vaginal discharge with impurities of pus.
- Menstruation cycle failures.
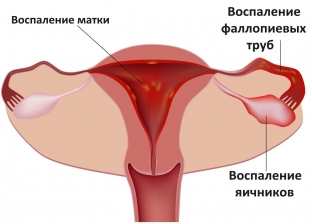
Pus, which is released in large volumes, may be a sign of pyovar – purulent fusion of the tissues of the ovaries or fallopian tubes. In the vast majority of cases, pyovar requires surgical intervention.
Despite the mild clinical picture, the chronic form leads to infertility in 20% of cases, and can also cause:
- peritonitis – inflammation of the tissues of the peritoneum;
- abscess of organs of the reproductive system;
- bleeding;
- diseases of the gastrointestinal tract;
- diseases of the excretory system, which often include cystitis and pyelonephritis;
- diseases of the endocrine gland.
Methods for diagnosing ovarian inflammation
To diagnose oophoritis, it is necessary to resort to laboratory and instrumental studies. Typically, diagnosis includes the following tests:
- Identification and examination of the urogenital tract for the detection of pathogenic bacteria. The type of microorganisms is determined by microscopy, culture (inoculation) and polymerase chain reaction.
- Enzymatic immunoassay, which detects specific antibodies in the blood. These antibodies are produced when exposed to pathogens.
- Ultrasound diagnosis of the ovaries. This study allows you to visually determine the change in the structure of the tissues of the organs of the reproductive system.
If the disease progresses with complications, the attending physician may prescribe additional tests.
- Endoscopic examination (laparoscopy). This analysis is carried out to determine the complete clinical picture. It allows you to assess the condition of the organs and prescribe the necessary treatment.
- MRI or computed tomography. This type of diagnostics allows early detection of neoplasms and accurately determines the condition of the affected tissues.
Read also: Ovarian Wasting Syndrome: How to Identify It
Methods of treatment of oophoritis depending on the stage of development
After conducting all the necessary studies, the attending physician must prescribe a comprehensive treatment. Treatment methods vary depending on the degree of tissue damage, the presence of pathologies and complications.
- The acute form of the disease requires hospital treatment. Treatment is carried out in three directions.
- Etiotropic therapy. This treatment involves the use of antibiotics to fight pathogens. The duration of treatment determines the severity of the inflammation.
- Pathogenic therapy. The task of this type of treatment – reduce inflammation. In the acute form, nonsteroidal drugs are used.
- Symptomatic therapy. This type of treatment involves pain relief and is aimed at reducing the manifestations of the disease.
- The subacute form of the disease implies the same principles of treatment as the acute form. Some drugs can be replaced, but the treatment is still carried out in three directions. Sometimes patients are prescribed physiotherapy. It should be noted that with this form of the disease, very few women turn to specialists for help. The problem is that the external manifestations of the disease are on the decline and the patient may consider this the end of the disease.
- Treatment of chronic oophoritis is characterized by a longer duration and a change in treatment methods. The problem is that in the chronic form, pathogens acquire a kind of immunity and resist antibiotic treatment for a long time. In addition, oophoritis, which lasts more than six months, in most cases is accompanied by inflammation of the fallopian tubes, appendages and other organs of the small pelvis, and therefore requires a different approach. In some cases, specialists resort to surgical intervention.
Since oophoritis is considered one of the most common "female" diseases, today it is successfully treated at any stage. The main thing is not to resort to self-prescribing medications.
Diagnosis and treatment should only be carried out by a qualified specialist: only then the disease will quickly recede, causing a minimum of harm. As you can see, despite the fact that oophoritis is a rather serious disease, modern methods of treatment can quickly suppress it at any stage. Main – at the very first manifestations of the disease, consult a doctor and follow all recommendations. You can learn about other, and not only women's diseases and their treatment on our website estet-portal.com.
Read also: Why ovaries hurt: 5 main reasons






Add a comment