The second most common disease (after caries) – periodontitis – affects both the elderly and the young. The scourge of modernity – smoking or improper oral care leads to the accumulation of microbes and bacteria on the mucous membrane, plaque hardens and turns into tartar, which corrodes the gums and destroys the tissues surrounding the tooth. Sometimes even a healthy tooth falls out as a result of damage to the gums by this disease. It is necessary to prevent and protect your teeth and gums from the development of periodontitis since childhood. Although the occurrence of inflammatory processes in the gums is also provoked by genetic factors. But, do not be afraid of the symptoms of this disease, better stock up on knowledge on how to treat periodontitis and how to prevent it.
Periodontitis: features of the course
Bleeding gums are a concern for many people, but not everyone goes to the dentist for advice with this symptom. And it would be worth it! If the gums bleed every six months, this is a sign of vitamin deficiency, strong pressure on the gums, or the use of too stiff bristles. If bleeding occurs constantly, almost every day, this indicates the development of the disease. Most likely, the blood seeps from the gums due to the development of periodontitis.
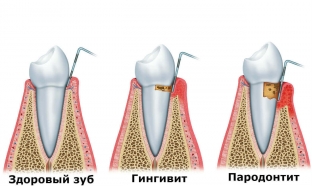
Periodontitis is the development of inflammatory processes in the tissues near the tooth. Periodontist – peridental tissues that hold the tooth in a physiological position in the alveolus. Therefore, if the periodontium becomes inflamed and begins to collapse, bone tissue decreases, the tooth loosens, and, as a result, falls out. In addition, periodontitis is accompanied by bad breath, soreness and discomfort against the background of a deterioration in the general appearance of the entire oral cavity.
Symptoms and causes of inflammation and bleeding of the gums
The first manifestation of periodontitis is the growth of tartar. A lot of particles stick to the teeth after eating: carbohydrates, proteins, pathogens. If plaque is not removed in time, it accumulates and hardens. Plaque settles at the base of the gums, near the pocket. Tartar irritates the mucous membrane, bacteria and microbes accumulate near the gums, provoking inflammation and the process of decay. As a result, the gum swells, the gingival papillae transform and weaken. Eventually, the ligaments that support the tooth also weaken and the tooth begins to wobble. More and more microbes penetrate inside and inflammation reaches its climax, the result of which is the loss of a healthy tooth.
Common causes of periodontitis:
- genetic predisposition;
- decreased immunity;
- improper oral care;
- cardiovascular disorders;
- stomach ulcer;
- digestion problems;
- gastritis;
- diabetes mellitus;
- neurological diseases.
How to treat periodontitis: methods of getting rid of the problem
Periodontitis is treatable only in the early stages. But when the patient goes to the dental clinic for help, periodontitis is usually in a chronic condition. In this case, the task of the doctor – improve the condition and slow down the further development of the disease.
First of all, the doctor removes plaque and tartar. Depending on the prevalence of periodontitis, complex therapy is prescribed: antibiotics, vitamin complexes, diet, hydromassage, electrophoresis, washing of gum pockets. The patient will then be required to rinse with medicinal herbs to heal wounds, take care of the oral cavity: brush teeth 2 times a day, rinse after meals, use dental floss. Many patients ask how to treat periodontitis in a severe case.
If the disease has grown over the entire dentition, the teeth are loose and the gums have sunk, exposing the tooth roots, it is supposed to use more radical methods of treatment: curettage, patchwork, splinting.
Curettage (curettage) is the removal of calculus deposits from deep within the gums. Flap surgery is performed when other methods of treating periodontitis are ineffective. During the operation, the gum is cut, deposits and dead tissue are removed, and all this happens with the use of anesthesia. And to keep the tooth in the socket, a splinting procedure is used to strengthen the tooth.
Read also: Anesthesia for dental treatment: how to get rid of pain
In addition to these methods, dentists recommend resorting to laser treatment of periodontitis. This is a minimally invasive way to deal with the problem. The laser cleans periodontal pockets and disinfects tissues for 4 minutes. Advantages of laser surgery: no blood or pain.
The final step on the way to treat periodontitis is prosthetics. This is even more likely not a method of dealing with the disease, but a way to eliminate the consequences of the disease. Affected teeth are removed and new ones are replaced.






Add a comment