Albinism – This is a congenital genetically determined condition, which is characterized by the absence of melanin pigment at the border of the dermis and epidermis, in the hair follicles, and the retina. About 13 types of albinism are known.
One of them is the Germansky-Pudlak syndrome, which is characterized by albinism and other equally important manifestations of the syndrome, which must be excluded when examining a patient with impaired melanin synthesis. estet-portal.com will help you understand the distinctive features of these dangerous syndromes.
Epidemiology of Hermansky-Pudlak Syndrome
This disease is more common in Puerto Rico – 1 case per 2000 inhabitants. However, reliable data indicate the ubiquity of the pathology, only the doctor's alertness and targeted diagnostics will help to make the correct diagnosis.
Germansky-Pudlak syndrome was described in 1959 independently by Germansky and Pudlak in Czechoslovakia. There are 4 types of this syndrome.
Affects women and men equally. The first manifestations can be seen in a newborn (albinism, strabismus, depigmentation of the iris). Inflammatory bowel disease occurs at the age of 12-30 years, pulmonary fibrosis – at age 40.
Follow us on Telegram
Albinism and other manifestations of Hermansky-Pudlak syndrome
Germansky-Pudlak Syndrome – it is an autosomal recessive disorder that includes oculocutaneous albinism, platelet dysfunction, and accumulation of lysosomal ceroid in tissues.
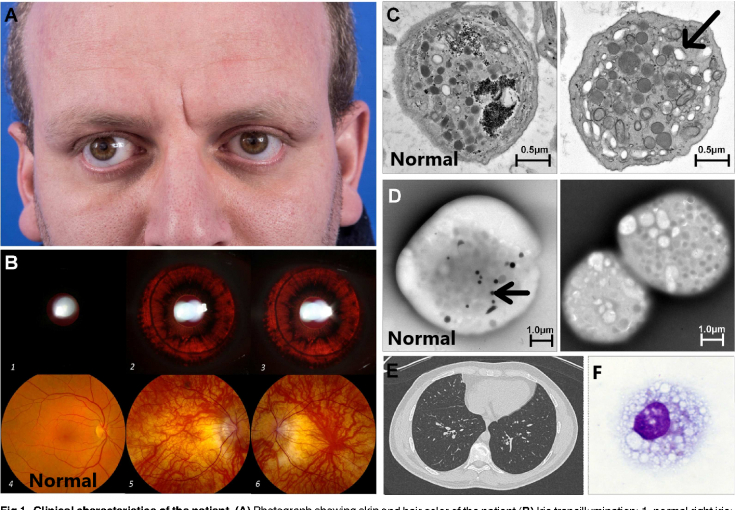
Main manifestations:
1. albinism, blond hair, but some patients may have chestnut hair color (A),
2. photophobia, strabismus (A), gross nystagmus,
3. hypopigmented fundus, peripapillary retinal atrophy, foveal hypoplasia (B),
4. nosebleeds, prolongation of the period of menstrual bleeding due to the depletion of the cytoplasm of platelets (C), lack of dense (delta) platelet granules containing ATP, ADP, Ca, serotonin (D),
5. pulmonary fibrosis (E), foamy cytoplasm of macrophages with lysosomal ceroid in bronchoalveolar lavage (F),
6. inflammatory bowel disease,
7. kidney disease,
8. cardiomyopathy.
Confirmation of the diagnosis of Hermansky-Pudlak syndrome
• To confirm the diagnosis, genetic testing of DNA for the presence of the pathological HPS1 gene, electron microscopy of platelets to detect delta granule deficiency and an increased content of lysosomes, as well as the presence of ceroid-lipofuscin inclusions in macrophages from bone marrow, intestines and other tissues should be performed.
• Complete blood count is not informative. Bleeding time averages 6-20 minutes. Some patients have decreased von Willebrand factor activity.
• All patients with Hermansky-Pudlak syndrome have tyrosine-positive oculocutaneous albinism. The hair follicle incubation test demonstrates the presence of normal tyrosinase activity.
• CT of the chest cavity reveals an increase in the interstitial pattern, fibrosis and thickening of the pleura. Spirometry will help confirm functional lung failure.
• Skin biopsy and histological examination is necessary to exclude malignancy of skin changes.
Management of the patient with Hermansky-Pudlak syndrome
Sunglasses with an ultraviolet filter can reduce photophobia and minimize the harmful effects of UV exposure. The ophthalmologist should select eyeglasses for the treatment of strabismus as early as possible.
Dangers of the active sun: why actinic keratosis occurs
To protect the skin from UV exposure, advise the patient to use high SPF creams and avoid direct sunlight.
To reduce the risk of fatal bleeding, sports with an increased risk of injury should be avoided. In the postoperative period, desmopressin is prescribed to reduce bleeding.
In 2008, vasopressin was successfully used during a caesarean section in a patient with Hermansky-Pudlak syndrome.
Infliximab is prescribed to reduce the progression of intestinal manifestations. Osteoporosis is common to all people with albinism. The administration of vitamin D in combination with Ca is necessary in this group of patients.
Pirfenidone reduces fibrosis in the lung tissue, which significantly prolongs the patient's life.
Prognosis of a patient with Hermansky-Pudlak syndrome
Pulmonary fibrosis in 50% of cases leads to death in the fourth decade of life. Bleeding is fatal in about 10% of patients. 13% of patients die from complications of syndrome-associated colitis. The remaining causes of death are associated with liver and kidney failure.
Skin lesions in connective tissue diseases
Skin complications include solar keratosis, melanoma, and basal cell carcinoma. 80% of patients lose their sight and develop cataracts. You may be interested in an article on our website estet-portal.com in the "Dermatology" section; Children of the moon: why albinism manifests itself in humans
Adapted from Medscape







Add a comment